- About This Manual
- I Introduction
- II Managing Virtual Machines with
libvirt - III Hypervisor-Independent Features
- IV Managing Virtual Machines with Xen
- 18 Setting Up a Virtual Machine Host
- 19 Virtual Networking
- 20 Managing a Virtualization Environment
- 21 Block Devices in Xen
- 22 Virtualization: Configuration Options and Settings
- 23 Administrative Tasks
- 24 XenStore: Configuration Database Shared between Domains
- 25 Xen as a High-Availability Virtualization Host
- V Managing Virtual Machines with QEMU
- VI Managing Virtual Machines with LXC
- Glossary
- A Virtual Machine Drivers
- B Appendix
- C XM, XL Toolstacks and Libvirt framework
- D GNU Licenses
openSUSE Leap 42.2
Virtualization Guide
Describes virtualization technology in general, and introduces libvirt—the unified interface to virtualization—and detailed information on specific hypervisors.
- About This Manual
- I Introduction
- II Managing Virtual Machines with
libvirt - 8 Starting and Stopping
libvirtd - 9 Guest Installation
- 10 Basic VM Guest Management
- 11 Connecting and Authorizing
- 12 Managing Storage
- 13 Managing Networks
- 14 Configuring Virtual Machines
- 14.1 Machine Setup
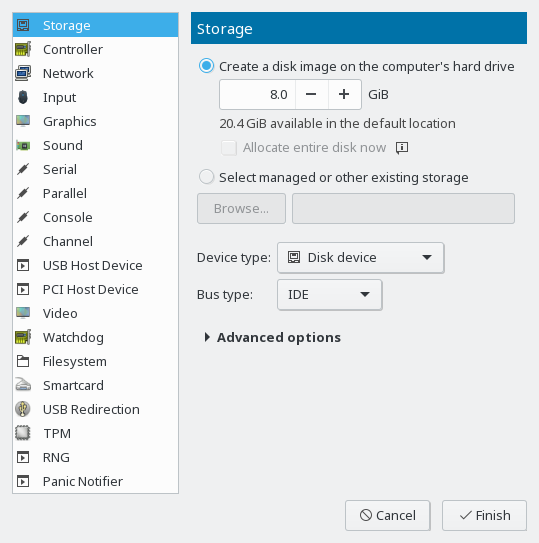
- 14.2 Storage
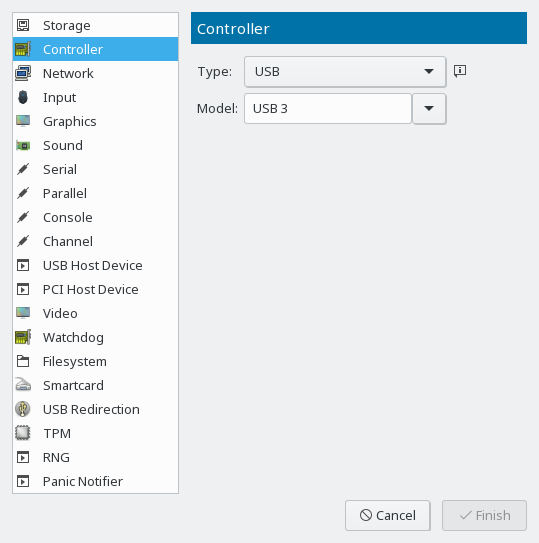
- 14.3 Controllers
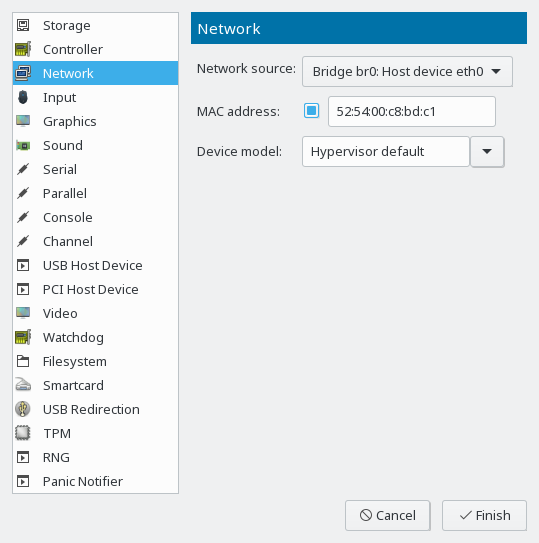
- 14.4 Networking
- 14.5 Enabling Seamless and Synchronized Mouse Pointer Movement
- 14.6 Adding a CD/DVD-ROM Device with Virtual Machine Manager
- 14.7 Adding a Floppy Device with Virtual Machine Manager
- 14.8 Ejecting and Changing Floppy or CD/DVD-ROM Media with Virtual Machine Manager
- 14.9 Changing the Machine Type with
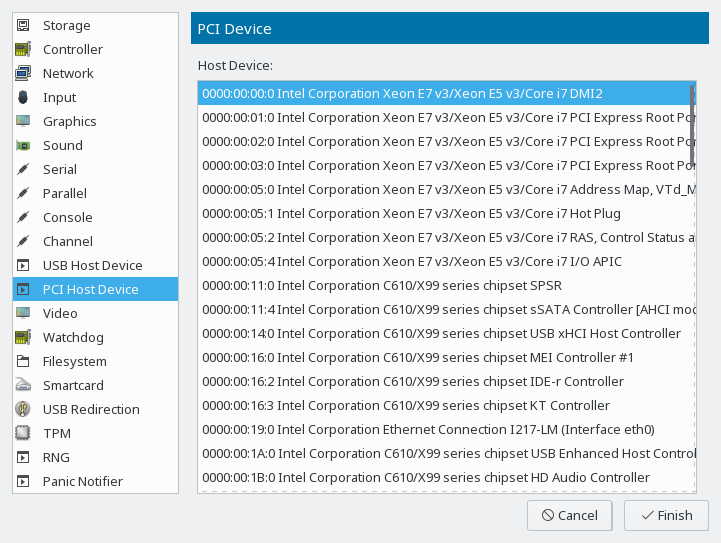
virsh - 14.10 Adding a PCI Device to a VM Guest
- 14.11 Adding SR-IOV Devices
- 8 Starting and Stopping
- III Hypervisor-Independent Features
- IV Managing Virtual Machines with Xen
- 18 Setting Up a Virtual Machine Host
- 19 Virtual Networking
- 20 Managing a Virtualization Environment
- 21 Block Devices in Xen
- 22 Virtualization: Configuration Options and Settings
- 23 Administrative Tasks
- 24 XenStore: Configuration Database Shared between Domains
- 25 Xen as a High-Availability Virtualization Host
- V Managing Virtual Machines with QEMU
- 26 QEMU Overview
- 27 Setting Up a KVM VM Host Server
- 28 Guest Installation
- 29 Running Virtual Machines with qemu-system-ARCH
- 30 Virtual Machine Administration Using QEMU Monitor
- 30.1 Accessing Monitor Console
- 30.2 Getting Information about the Guest System
- 30.3 Changing VNC Password
- 30.4 Managing Devices
- 30.5 Controlling Keyboard and Mouse
- 30.6 Changing Available Memory
- 30.7 Dumping Virtual Machine Memory
- 30.8 Managing Virtual Machine Snapshots
- 30.9 Suspending and Resuming Virtual Machine Execution
- 30.10 Live Migration
- 30.11 QMP - QEMU Machine Protocol
- VI Managing Virtual Machines with LXC
- Glossary
- A Virtual Machine Drivers
- B Appendix
- C XM, XL Toolstacks and Libvirt framework
- D GNU Licenses
- 2.1 Xen Virtualization Architecture
- 3.1 KVM Virtualization Architecture
- 13.1 Connection Details
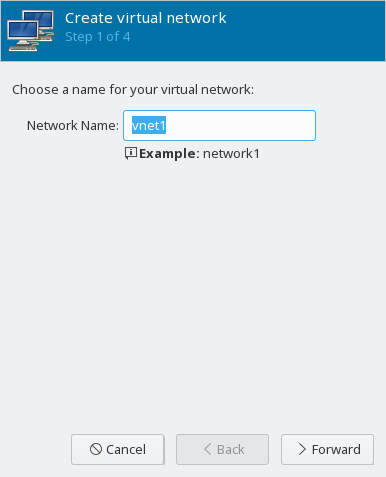
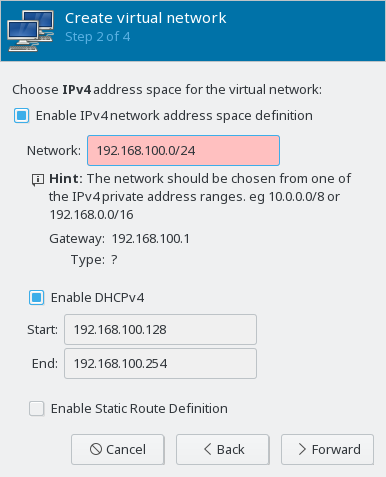
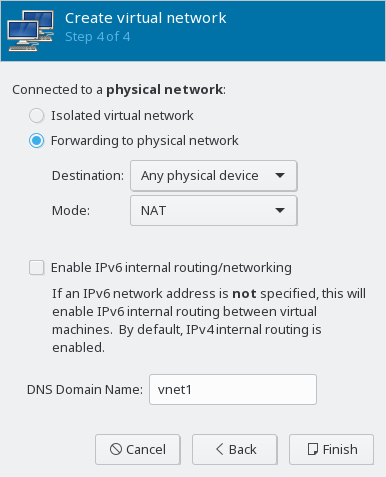
- 13.2 Create virtual network
- 13.3 Create virtual network
- 13.4 Create virtual network
- 14.1 View of a VM Guest
- 14.2 Overview details
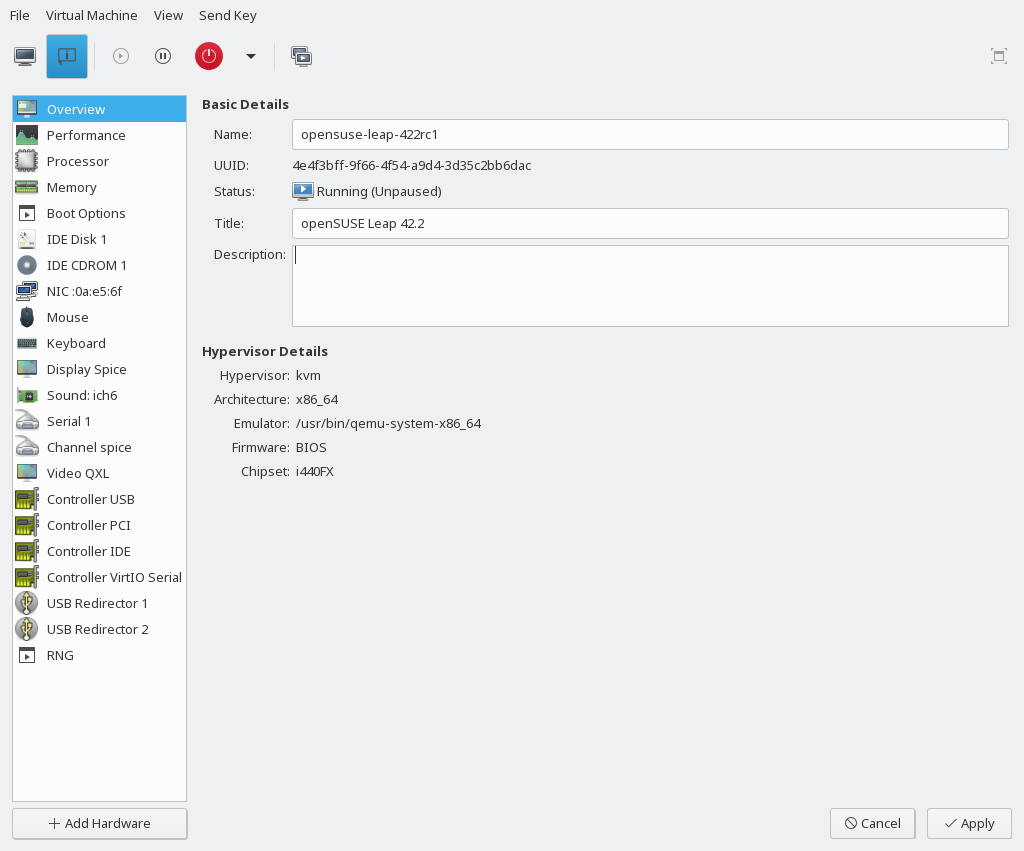
- 14.3 VM Guest Title and Description
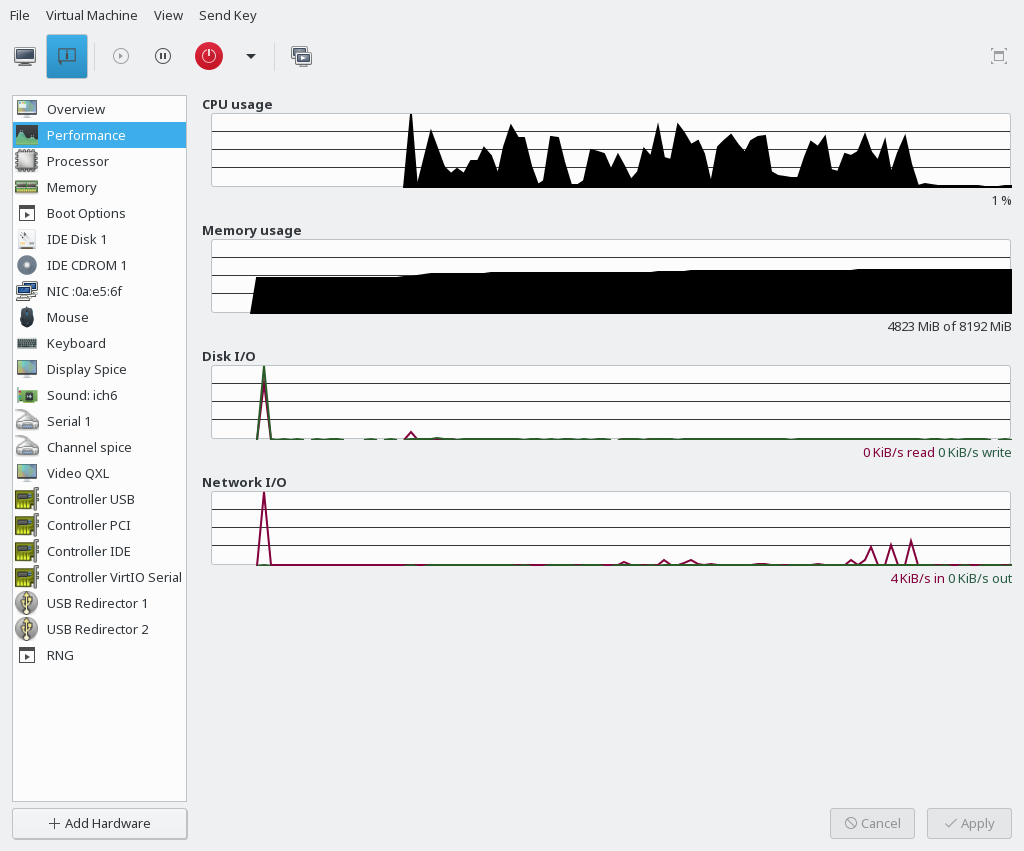
- 14.4 Performance
- 14.5 Statistics Charts
- 14.6 Processor View
- 14.7 Memory View
- 14.8 Boot Options
- 14.9 Add a New Storage
- 14.10 Add a New Controller
- 14.11 Add a New Controller
- 14.12 Adding a PCI Device
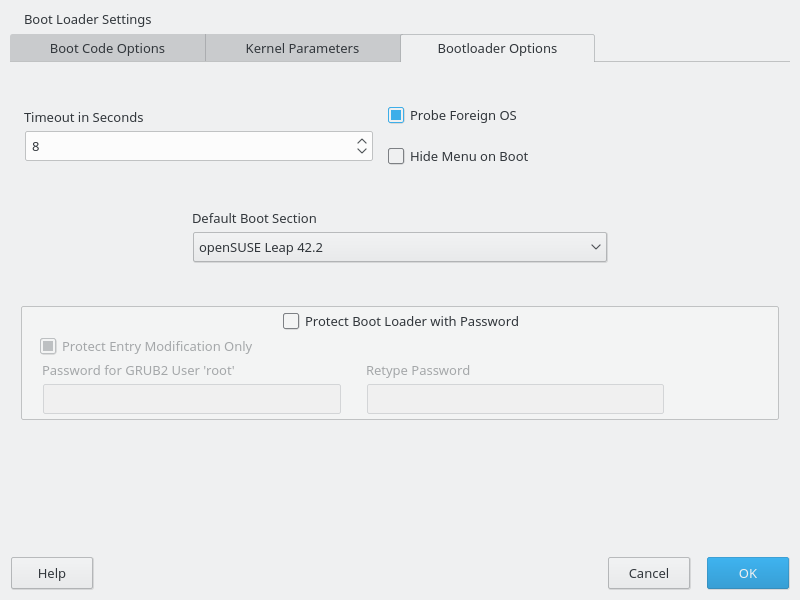
- 23.1 Boot Loader Settings
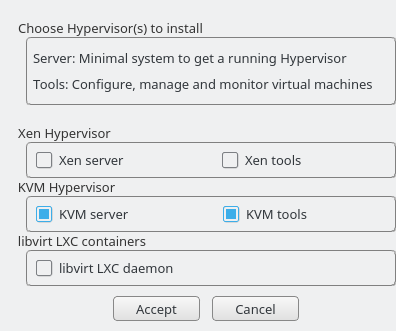
- 27.1 Installing the KVM Hypervisor and Tools
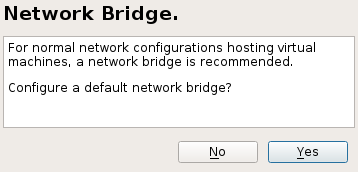
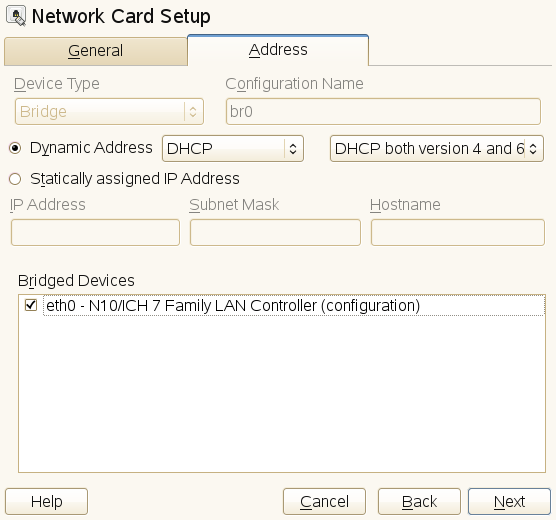
- 27.2 Network Bridge
- 28.1 New 2 GB Partition in Guest YaST Partitioner
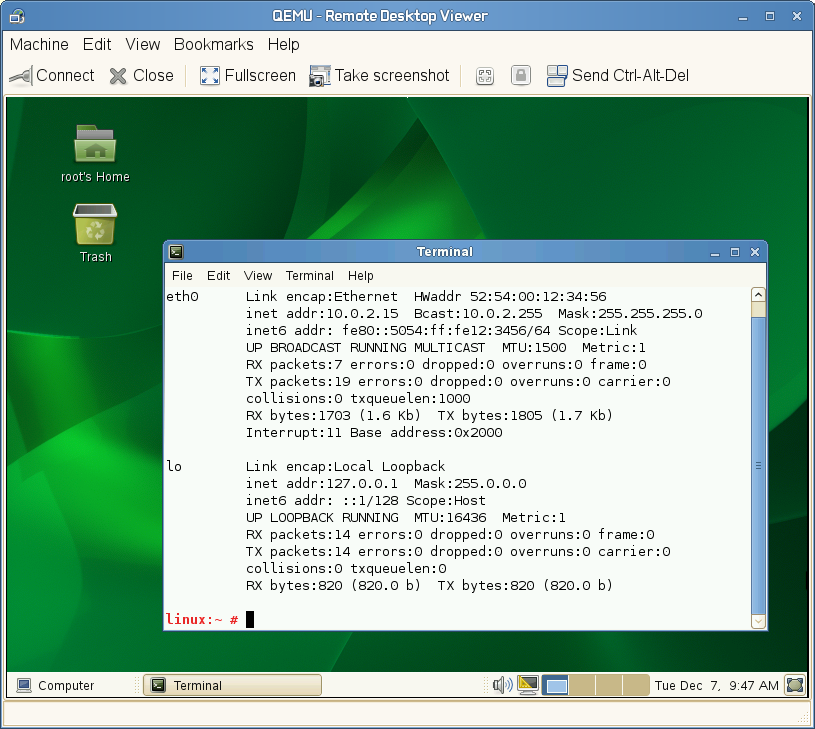
- 29.1 QEMU Window with SLES 11 SP3 as VM Guest
- 29.2 Configuring Network Bridge with YaST
- 29.3 QEMU VNC Session
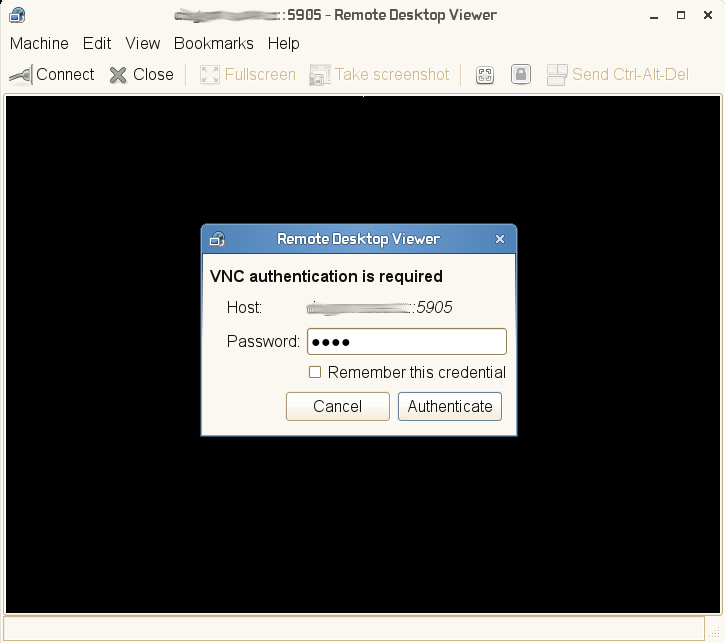
- 29.4 Authentication Dialog in Vinagre
- 7.1 Paravirtualized OS Support
- 7.2 Feature Support—Host (
Dom0) - 7.3 Feature Support—Paravirtualized Guest
- 7.4 Feature Support—Fully Virtualized Guest
- 25.1 Xen Remote Storage
- C.1 Notation Conventions
- C.2 New Global Options
- C.3 Common Options
- C.4 Domain Management Removed Options
- C.5 USB Devices Management Removed Options
- C.6 CPU Management Removed options
- C.7 Other Options
- C.8
xlcreateChanged Options - C.9
xmcreateRemoved Options - C.10
xlcreateAdded Options - C.11
xlconsoleAdded Options - C.12
xminfoRemoved Options - C.13
xmdump-coreRemoved Options - C.14
xmlistRemoved Options - C.15
xllistAdded Options - C.16
xlmem-*Changed Options - C.17
xmmigrateRemoved Options - C.18
xlmigrateAdded Options - C.19
xmrebootRemoved Options - C.20
xlrebootAdded Options - C.21
xlsaveAdded Options - C.22
xlrestoreAdded Options - C.23
xmshutdownRemoved Options - C.24
xlshutdownAdded Options - C.25
xltriggerChanged Options - C.26
xmsched-creditRemoved Options - C.27
xlsched-creditAdded Options - C.28
xmsched-credit2Removed Options - C.29
xlsched-credit2Added Options - C.30
xmsched-sedfRemoved Options - C.31
xlsched-sedfAdded Options - C.32
xmcpupool-listRemoved Options - C.33
xmcpupool-createRemoved Options - C.34
xlpci-detachAdded Options - C.35
xmblock-listRemoved Options - C.36 Other Options
- C.37 Network Options
- C.38
xlnetwork-attachRemoved Options - C.39 New Options
- 9.1 Example of a
virt-installcommand line - 10.1 Typical Output of
kvm_stat - 13.1 NAT Based Network
- 13.2 Routed Network
- 13.3 Isolated Network
- 13.4 Using an Existing Bridge on VM Host Server
- 20.1 Guest Domain Configuration File:
/etc/xen/sled12.cfg - 27.1 Exporting Host's File System with VirtFS
- 29.1 Restricted User-mode Networking
- 29.2 User-mode Networking with Custom IP Range
- 29.3 User-mode Networking with Network-boot and TFTP
- 29.4 User-mode Networking with Host Port Forwarding
- 29.5 Password Authentication
- 29.6 x509 Certificate Authentication
- 29.7 x509 Certificate and Password Authentication
- 29.8 SASL Authentication
- C.1 Converting Xen Domain Configuration to
libvirt
Copyright © 2006– 2018 SUSE LLC and contributors. All rights reserved.
Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or (at your option) version 1.3; with the Invariant Section being this copyright notice and license. A copy of the license version 1.2 is included in the section entitled “GNU Free Documentation License”.
For SUSE trademarks, see http://www.suse.com/company/legal/. All other third-party trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Trademark symbols (®, ™ etc.) denote trademarks of SUSE and its affiliates. Asterisks (*) denote third-party trademarks.
All information found in this book has been compiled with utmost attention to detail. However, this does not guarantee complete accuracy. Neither SUSE LLC, its affiliates, the authors nor the translators shall be held liable for possible errors or the consequences thereof.
About This Manual #
This manual offers an introduction to setting up and managing
virtualization with KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine), Xen, and
Linux Containers (LXC) on openSUSE Leap. The first part introduces the
different virtualization solutions by describing their requirements, their
installations and SUSE's support status. The second part deals with
managing VM Guests and VM Host Servers with libvirt. The following
parts describe various administration tasks and practices and the last
three parts deal with hypervisor-specific topics.
Many chapters in this manual contain links to additional documentation resources. This includes additional documentation that is available on the system and documentation available on the Internet.
For an overview of the documentation available for your product and the latest documentation updates, refer to https://doc.opensuse.org/.
1 Available Documentation #
We provide HTML and PDF versions of our books in different languages. The following manuals for users and administrators are available for this product:
- Book “Start-Up”
This manual will see you through your initial contact with openSUSE® Leap. Check out the various parts of this manual to learn how to install, use and enjoy your system.
- Book “Reference”
Covers system administration tasks like maintaining, monitoring and customizing an initially installed system.
- Virtualization Guide
Describes virtualization technology in general, and introduces libvirt—the unified interface to virtualization—and detailed information on specific hypervisors.
- Book “AutoYaST”
AutoYaST is a system for installing one or more openSUSE Leap systems automatically and without user intervention, using an AutoYaST profile that contains installation and configuration data. The manual guides you through the basic steps of auto-installation: preparation, installation, and configuration.
- Book “Security Guide”
Introduces basic concepts of system security, covering both local and network security aspects. Shows how to use the product inherent security software like AppArmor or the auditing system that reliably collects information about any security-relevant events.
- Book “System Analysis and Tuning Guide”
An administrator's guide for problem detection, resolution and optimization. Find how to inspect and optimize your system by means of monitoring tools and how to efficiently manage resources. Also contains an overview of common problems and solutions and of additional help and documentation resources.
- Book “GNOME User Guide”
Introduces the GNOME desktop of openSUSE Leap. It guides you through using and configuring the desktop and helps you perform key tasks. It is intended mainly for end users who want to make efficient use of GNOME as their default desktop.
Find HTML versions of most product manuals in your installed system under
/usr/share/doc/manual. The latest documentation updates
are available at
http://doc.opensuse.org/
where you can download the documentation for your product in various formats.
2 Feedback #
Several feedback channels are available:
- Bugs and Enhancement Requests
For services and support options available for your product, refer to http://www.suse.com/support/.
To report bugs for a product component, go to https://scc.suse.com/support/requests, log in, and click .
- User Comments
We want to hear your comments about and suggestions for this manual and the other documentation included with this product. Use the User Comments feature at the bottom of each page in the online documentation or go to http://www.suse.com/documentation/feedback.html and enter your comments there.
For feedback on the documentation of this product, you can also send a mail to
doc-team@suse.com. Make sure to include the document title, the product version and the publication date of the documentation. To report errors or suggest enhancements, provide a concise description of the problem and refer to the respective section number and page (or URL).
3 Documentation Conventions #
The following notices and typographical conventions are used in this documentation:
/etc/passwd: directory names and file namesPLACEHOLDER: replace PLACEHOLDER with the actual value
PATH: the environment variable PATHls,--help: commands, options, and parametersuser: users or groupspackage name : name of a package
Alt, Alt–F1: a key to press or a key combination; keys are shown in uppercase as on a keyboard
, › : menu items, buttons
Dancing Penguins (Chapter Penguins, ↑Another Manual): This is a reference to a chapter in another manual.
Commands that must be run with
rootprivileges. Often you can also prefix these commands with thesudocommand to run them.root #commandCommands that can be run by non-privileged users.
tux >commandNotices

Warning: Warning Notice
Vital information you must be aware of before proceeding. Warns you about security issues, potential loss of data, damage to hardware, or physical hazards.

Important: Important Notice
Important information you should be aware of before proceeding.

Note: Note Notice
Additional information, for example about differences in software versions.
Tip: Tip Notice
Helpful information, like a guideline or a piece of practical advice.
Part I Introduction #
- 1 Virtualization Technology
Virtualization is a technology that provides a way for a machine (Host) to run another operating system (guest virtual machines) on top of the host operating system.
- 2 Introduction to Xen Virtualization
This chapter introduces and explains the components and technologies you need to understand to set up and manage a Xen-based virtualization environment.
- 3 Introduction to KVM Virtualization
- 4 Introduction to Linux Containers
Linux containers are a lightweight virtualization method to run multiple virtual units (“containers”) simultaneously on a single host. This is similar to the chroot environment. Containers are isolated with kernel Control Groups (cgroups) and kernel Namespaces.
- 5 Virtualization Tools
libvirtis a library that provides a common API for managing popular virtualization solutions, among them KVM, LXC, and Xen. The library provides a normalized management API for these virtualization solutions, allowing a stable, cross-hypervisor interface for higher-level management tools. The library also provides APIs for management of virtual networks and storage on the VM Host Server. The configuration of each VM Guest is stored in an XML file.With
libvirtyou can also manage your VM Guests remotely. It supports TLS encryption, x509 certificates and authentication with SASL. This enables managing VM Host Servers centrally from a single workstation, alleviating the need to access each VM Host Server individually.Using the
libvirt-based tools is the recommended way of managing VM Guests. Interoperability betweenlibvirtandlibvirt-based applications has been tested and is an essential part of SUSE's support stance.- 6 Installation of Virtualization Components
None of the virtualization tools is installed by default.
- 7 Supported Guests, Hosts and Features
Supported virtualization limits for Xen and KVM are outlined in the Release Notes.
1.1 Overview #
SUSE Linux Enterprise includes the latest open source virtualization technologies, Xen and KVM. With these Hypervisors, SUSE Linux Enterprise can be used to provision, de-provision, install, monitor and manage multiple virtual machines (VM Guests) on a single physical system (for more information see Hypervisor).
Out of the box, SUSE Linux Enterprise can create virtual machines running both modified, highly tuned, paravirtualized operating systems and fully virtualized unmodified operating systems. Full virtualization allows the guest OS to run unmodified and requires the presence of AMD64/Intel 64 processors which supports either Intel* Virtualization Technology (Intel VT) or AMD* Virtualization (AMD-V)).
The primary component of the operating system that enables virtualization is a Hypervisor (or virtual machine manager), which is a layer of software that runs directly on server hardware. It controls platform resources, sharing them among multiple VM Guests and their operating systems by presenting virtualized hardware interfaces to each VM Guest.
SUSE Linux Enterprise is an enterprise-class Linux server operating system that offers two types of Hypervisors: Xen and KVM. Both Hypervisors support virtualization on 64-bit x86-based hardware architectures. Both Xen and KVM support full virtualization mode. In addition, Xen supports paravirtualized mode. SUSE Linux Enterprise with Xen or KVM acts as a virtualization host server (VHS) that supports VM Guests with its own guest operating systems. The SUSE VM Guest architecture consists of a Hypervisor and management components that constitute the VHS, which runs many application-hosting VM Guests.
In Xen, the management components run in a privileged VM Guest often called Dom0. In KVM, where the Linux kernel acts as the hypervisor, the management components run directly on the VHS.
1.2 Virtualization Capabilities #
Virtualization design provides many capabilities to your organization. Virtualization of operating systems is used in many computing areas:
Server consolidation: Many servers can be replaced by one big physical server, so hardware is consolidated, and Guest Operating Systems are converted to virtual machine. It provides the ability to run legacy software on new hardware.
Isolation: guest operating system can be fully isolated from the Host running it. So if the virtual machine is corrupted, the Host system is not harmed.
Migration: A process to move a running virtual machine to another physical machine. Live migration is an extended feature that allows this move without disconnection of the client or the application.
Disaster recovery: Virtualized guests are less dependent on the hardware, and the Host server provides snapshot features to be able to restore a known running system without any corruption.
Dynamic load balancing: A migration feature that brings a simple way to load-balance your service across your infrastructure.
1.3 Virtualization Benefits #
Virtualization brings a lot of advantages while providing the same service as a hardware server.
First, it reduces the cost of your infrastructure. Servers are mainly used to provide a service to a customer, and a virtualized operating system can provide the same service, with:
Less hardware: You can run several operating system on one host, so all hardware maintenance will be reduced.
Less power/cooling: Less hardware means you do not need to invest more in electric power, backup power, and cooling if you need more service.
Save space: Your data center space will be saved because you do not need more hardware servers (less servers than service running).
Less management: Using a VM Guest simplifies the administration of your infrastructure.
Agility and productivity: Virtualization provides migration capabilities, live migration and snapshots. These features reduce downtime, and bring an easy way to move your service from one place to another without any service interruption.
1.4 Understanding Virtualization Modes #
Guest operating systems are hosted on virtual machines in either full virtualization (FV) mode or paravirtual (PV) mode. Each virtualization mode has advantages and disadvantages.
Full virtualization mode lets virtual machines run unmodified operating systems, such as Windows* Server 2003. However, it also requires the VM Host Server to support hardware-assisted virtualization technology, such as AMD* Virtualization or Intel* Virtualization Technology.
Some guest operating systems hosted in full virtualization mode can be configured to run the Novell* Virtual Machine Drivers instead of drivers originating from the operating system. Running virtual machine drivers improves performance dramatically on guest operating systems, such as Windows Server 2003. For more information, see Appendix A, Virtual Machine Drivers.
Paravirtual mode does not require the host computer to support hardware-assisted virtualization technology, but does require the guest operating system to be modified for the virtualization environment. Typically, operating systems running in paravirtual mode enjoy better performance than those requiring full virtualization mode.
Operating systems currently modified to run in paravirtual mode are called paravirtualized operating systems and include openSUSE Leap and NetWare® 6.5 SP8.
1.5 I/O Virtualization #
VM Guests not only share CPU and memory resources of the host system, but also the I/O subsystem. Because software I/O virtualization techniques deliver less performance than bare metal, hardware solutions that deliver almost “native” performance have been developed recently. openSUSE Leap supports the following I/O virtualization techniques:
- Full Virtualization
Fully Virtualized (FV) drivers emulate widely supported real devices, which can be used with an existing driver in the VM Guest. The guest is also called Hardware Virtual Machine (HVM). Since the physical device on the VM Host Server may differ from the emulated one, the hypervisor needs to process all I/O operations before handing them over to the physical device. Therefore all I/O operations need to traverse two software layers, a process that not only significantly impacts I/O performance, but also consumes CPU time.
- Paravirtualization
Paravirtualization (PV) allows direct communication between the hypervisor and the VM Guest. With less overhead involved, performance is much better than with full virtualization. However, paravirtualization requires either the guest operating system to be modified to support the paravirtualization API or paravirtualized drivers. See Section 7.1.1, “Availability of Paravirtualized Drivers” for a list of guest operating systems supporting paravirtualization.
- PVHVM
This type of virtualization enhances HVM (see Full Virtualization) with paravirtualized (PV) drivers, and PV interrupt and timer handling.
- VFIO
VFIO stands for Virtual Function I/O and is a new user-level driver framework for Linux. It replaces the traditional KVM PCI Pass-Through device assignment. The VFIO driver exposes direct device access to user space in a secure memory (IOMMU) protected environment. With VFIO, a VM Guest can directly access hardware devices on the VM Host Server (pass-through), avoiding performance issues caused by emulation in performance critical paths. This method does not allow to share devices—each device can only be assigned to a single VM Guest. VFIO needs to be supported by the VM Host Server CPU, chipset and the BIOS/EFI.
Compared to the legacy KVM PCI device assignment, VFIO has the following advantages:
Resource access is compatible with secure boot.
Device is isolated and its memory access protected.
Offers a user space device driver with more flexible device ownership model.
Is independent of KVM technology, and not bound to x86 architecture only.
As of openSUSE Leap 42.2, the USB and PCI Pass-through methods of device assignment are considered deprecated and were superseded by the VFIO model.
- SR-IOV
The latest I/O virtualization technique, Single Root I/O Virtualization SR-IOV combines the benefits of the aforementioned techniques—performance and the ability to share a device with several VM Guests. SR-IOV requires special I/O devices, that are capable of replicating resources so they appear as multiple separate devices. Each such “pseudo” device can be directly used by a single guest. However, for network cards for example the number of concurrent queues that can be used is limited, potentially reducing performance for the VM Guest compared to paravirtualized drivers. On the VM Host Server, SR-IOV must be supported by the I/O device, the CPU and chipset, the BIOS/EFI and the hypervisor—for setup instructions see Section 14.10, “Adding a PCI Device to a VM Guest”.
Important: Requirements for VFIO and SR-IOV
To be able to use the VFIO and SR-IOV features, the VM Host Server needs to fulfill the following requirements:
IOMMU needs to be enabled in the BIOS/EFI.
For Intel CPUs, the Kernel parameter
intel_iommu=onneeds to be provided on the Kernel command line. For more information, see Book “Reference”, Chapter 12 “The Boot Loader GRUB 2”, Section 12.3.3.2 “ Tab”.The VFIO infrastructure needs to be available. This can be achieved by loading the Kernel module
vfio_pci. For more information, see Book “Reference”, Chapter 10 “ThesystemdDaemon”, Section 10.6.4 “Loading Kernel Modules”.
2 Introduction to Xen Virtualization #
This chapter introduces and explains the components and technologies you need to understand to set up and manage a Xen-based virtualization environment.
2.1 Basic Components #
The basic components of a Xen-based virtualization environment are the Xen hypervisor, the Dom0, any number of other VM Guests, and the tools, commands, and configuration files that let you manage virtualization. Collectively, the physical computer running all these components is called a VM Host Server because together these components form a platform for hosting virtual machines.
- The Xen Hypervisor
The Xen hypervisor, sometimes simply called a virtual machine monitor, is an open source software program that coordinates the low-level interaction between virtual machines and physical hardware.
- The Dom0
The virtual machine host environment, also called Dom0 or controlling domain, is composed of several components, such as:
The SUSE Linux Enterprise operating system gives the administrator a graphical and command line environment to manage the virtual machine host components and its virtual machines.

Note
The term “Dom0” refers to a special domain that provides the management environment. This may be run either in graphical or in command line mode.
The xl tool stack based on the xenlight library (libxl). Use it to manage Xen guest domains.
QEMU—an open source software that emulates a full computer system, including a processor and various peripherals. It provides the ability to host operating systems in both full virtualization or paravirtualization mode.
- Xen-Based Virtual Machines
A Xen-based virtual machine, also called a VM Guest or DomU, consists of the following components:
At least one virtual disk that contains a bootable operating system. The virtual disk can be based on a file, partition, volume, or other type of block device.
A configuration file for each guest domain. It is a text file following the syntax described in the manual page
man 5 xl.conf.Several network devices, connected to the virtual network provided by the controlling domain.
- Management Tools, Commands, and Configuration Files
There is a combination of GUI tools, commands, and configuration files to help you manage and customize your virtualization environment.
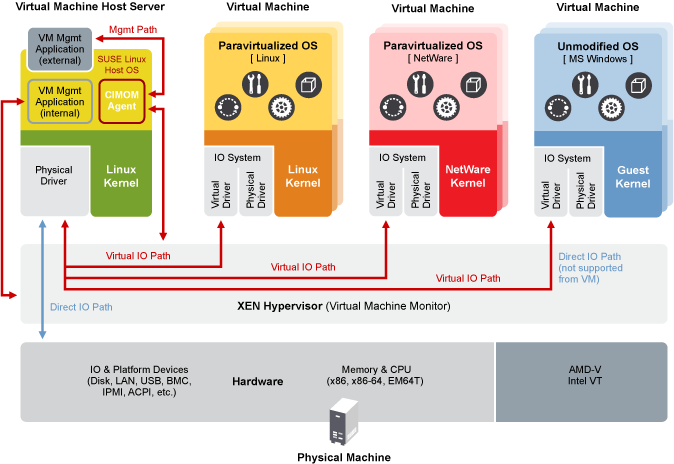
2.2 Xen Virtualization Architecture #
The following graphic depicts a virtual machine host with four virtual machines. The Xen hypervisor is shown as running directly on the physical hardware platform. Note that the controlling domain is also a virtual machine, although it has several additional management tasks compared to all the other virtual machines.
Figure 2.1: Xen Virtualization Architecture #
On the left, the virtual machine host’s Dom0 is shown running the SUSE Linux Enterprise operating system. The two virtual machines shown in the middle are running paravirtualized operating systems. The virtual machine on the right shows a fully virtual machine running an unmodified operating system, such as the latest version of Microsoft Windows/Server.
3 Introduction to KVM Virtualization #
3.1 Basic Components #
KVM is a full virtualization solution for the AMD64/Intel 64 and the z Systems architectures supporting hardware virtualization.
VM Guests (virtual machines), virtual storage, and virtual networks
can be managed with QEMU tools directly, or with the
libvirt-based stack. The QEMU tools include
qemu-system-ARCH, the QEMU monitor,
qemu-img, and qemu-ndb. A
libvirt-based stack includes libvirt itself, along with
libvirt-based applications such as virsh,
virt-manager, virt-install, and
virt-viewer.
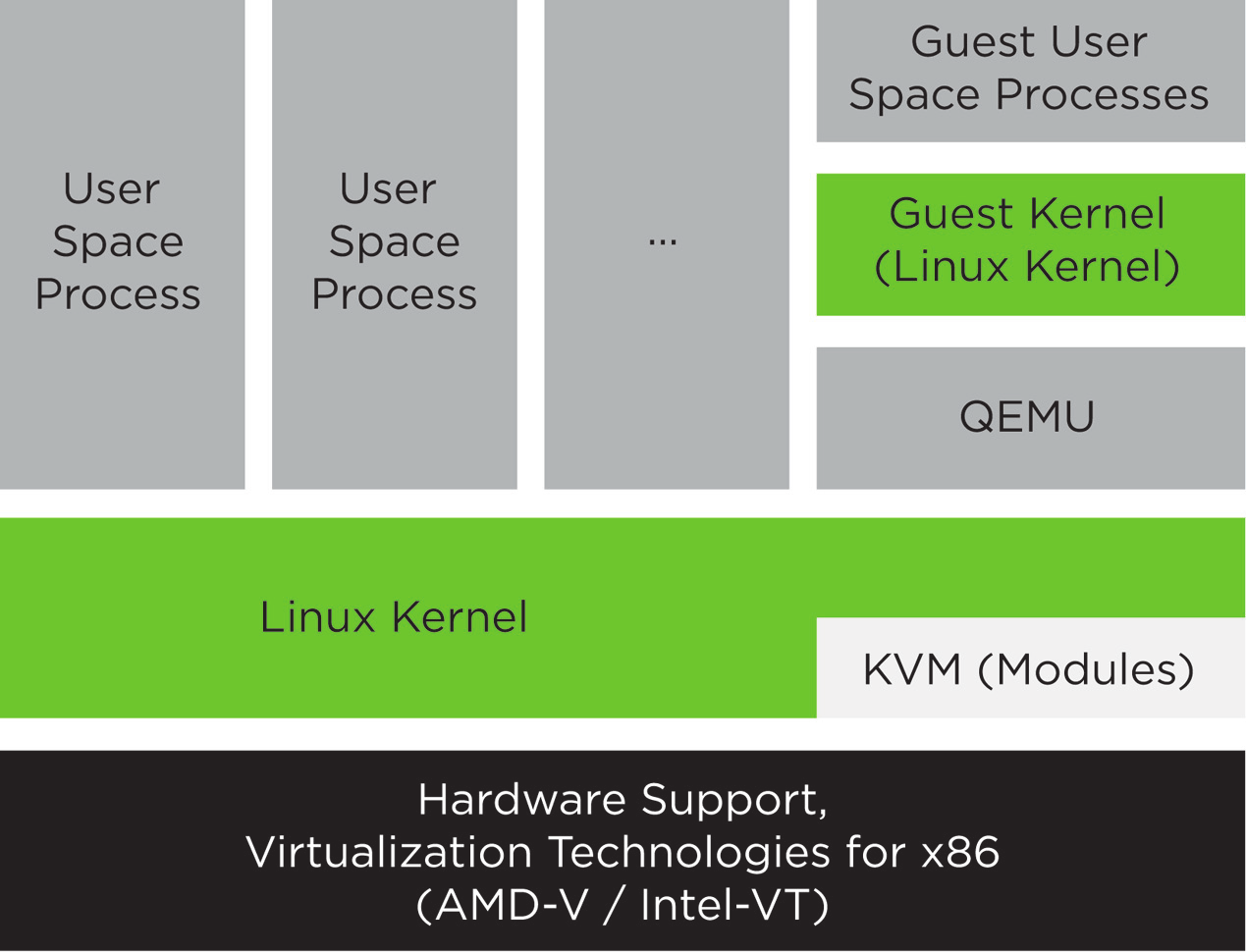
3.2 KVM Virtualization Architecture #
This full virtualization solution consists of two main components:
A set of Kernel modules (
kvm.ko,kvm-intel.ko, andkvm-amd.ko) that provides the core virtualization infrastructure and processor-specific drivers.A user space program (
qemu-system-ARCH) that provides emulation for virtual devices and control mechanisms to manage VM Guests (virtual machines).
The term KVM more properly refers to the Kernel level virtualization functionality, but is in practice more commonly used to refer to the user space component.
Figure 3.1: KVM Virtualization Architecture #
Note: Hyper-V Emulation Support
QEMU can provide certain Hyper-V hypercalls for Windows* guests to partly emulate a Hyper-V environment. This can be used to achieve better behavior for Windows* guests that are Hyper-V enabled.
4 Introduction to Linux Containers #
Linux containers are a lightweight virtualization method to run multiple virtual units (“containers”) simultaneously on a single host. This is similar to the chroot environment. Containers are isolated with kernel Control Groups (cgroups) and kernel Namespaces.
Containers provide virtualization at the operating system level where the kernel controls the isolated containers. This is unlike full virtualization solutions like Xen or KVM where the processor simulates a complete hardware environment and controls virtual machines.
Conceptually, containers can be seen as an improved chroot technique. The difference is that a chroot environment separates only the file system, whereas containers go further and provide resource management and control via cgroups.
Benefits of Containers #
Isolating applications and operating systems through containers.
Providing nearly native performance as container manages allocation of resources in real-time.
Controlling network interfaces and applying resources inside containers through cgroups.
Limitations of Containers #
All containers run inside the host system's kernel and not with a different kernel.
Only allows Linux “guest” operating systems.
Security depends on the host system. Container is not secure. If you need a secure system, you can confine it using an AppArmor or SELinux profile.
5 Virtualization Tools #
Abstract#
libvirt is a library that provides a common API for managing popular
virtualization solutions, among them KVM, LXC, and Xen. The library
provides a normalized management API for these virtualization solutions,
allowing a stable, cross-hypervisor interface for higher-level management
tools. The library also provides APIs for management of virtual networks
and storage on the VM Host Server. The configuration of each VM Guest is stored
in an XML file.
With libvirt you can also manage your VM Guests remotely. It supports
TLS encryption, x509 certificates and authentication with SASL. This
enables managing VM Host Servers centrally from a single workstation,
alleviating the need to access each VM Host Server individually.
Using the libvirt-based tools is the recommended way of managing
VM Guests. Interoperability between libvirt and libvirt-based
applications has been tested and is an essential part of SUSE's support
stance.
5.1 Virtualization Console Tools #
The following libvirt-based tools for the command line are available on openSUSE Leap. All tools are provided by packages carrying the tool's name.
virshA command line tool to manage VM Guests with similar functionality as the Virtual Machine Manager. Allows you to change a VM Guest's status (start, stop, pause, etc.), to set up new guests and devices, or to edit existing configurations.
virshis also useful to script VM Guest management operations.virshtakes the first argument as a command and further arguments as options to this command:virsh [-c URI] command domain-id [OPTIONS]
Like
zypper,virshcan also be called without a command. In this case it starts a shell waiting for your commands. This mode is useful when having to run subsequent commands:~> virsh -c qemu+ssh://wilber@mercury.example.com/system Enter passphrase for key '/home/wilber/.ssh/id_rsa': Welcome to virsh, the virtualization interactive terminal. Type: 'help' for help with commands 'quit' to quit virsh # hostname mercury.example.comvirt-installA command line tool for creating new VM Guests using the
libvirtlibrary. It supports graphical installations via VNC or SPICE protocols. Given suitable command line arguments,virt-installcan run completely unattended. This allows for easy automation of guest installs.virt-installis the default installation tool used by the Virtual Machine Manager.
5.2 Virtualization GUI Tools #
The following libvirt-based graphical tools are available on openSUSE Leap. All tools are provided by packages carrying the tool's name.
- Virtual Machine Manager (
virt-manager) The Virtual Machine Manager is a desktop tool for managing VM Guests. It provides the ability to control the life cycle of existing machines (start/shutdown, pause/resume, save/restore) and create new VM Guests. It allows managing various types of storage and virtual networks. It provides access to the graphical console of VM Guests with a built-in VNC viewer and can be used to view performance statistics.
virt-managersupports connecting to a locallibvirtd, managing a local VM Host Server, or a remotelibvirtdmanaging a remote VM Host Server.To start the Virtual Machine Manager, enter
virt-managerat the command prompt.
Note
To disable automatic USB device redirection for VM Guest using spice, either launch
virt-managerwith the--spice-disable-auto-usbredirparameter or run the following command to persistently change the default behavior:tux >dconf write /org/virt-manager/virt-manager/console/auto-redirect falsevirt-viewerA viewer for the graphical console of a VM Guest. It uses SPICE (configured by default on the VM Guest) or VNC protocols and supports TLS and x509 certificates. VM Guests can be accessed by name, ID, or UUID. If the guest is not already running, the viewer can be told to wait until the guest starts, before attempting to connect to the console.
virt-vieweris not installed by default and is available after installing the packagevirt-viewer.
Note
To disable automatic USB device redirection for VM Guest using spice, add an empty filter using the
--spice-usbredir-auto-redirect-filter=''parameter.yast2 vmA YaST module that simplifies the installation of virtualization tools and can set up a network bridge:
6 Installation of Virtualization Components #
None of the virtualization tools is installed by default.
6.1 Installing KVM #
To install KVM and KVM tools, proceed as follows:
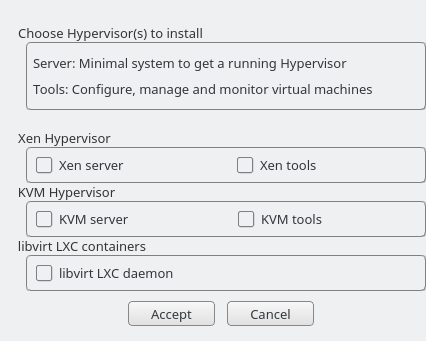
Start YaST and choose › .
Select for a minimal installation of QEMU tools. Select if a
libvirt-based management stack is also desired. Confirm with .To enable normal networking for the VM Guest, using a network bridge is recommended. YaST offers to automatically configure a bridge on the VM Host Server. Agree to do so by choosing , otherwise choose .
After the setup has been finished, you can start setting up VM Guests. Rebooting the VM Host Server is not required.
6.2 Installing Xen #
To install Xen and Xen tools, proceed as follows:
Start YaST and choose › .
Select for a minimal installation of Xen tools. Select if a
libvirt-based management stack is also desired. Confirm with .To enable normal networking for the VM Guest, using a network bridge is recommended. YaST offers to automatically configure a bridge on the VM Host Server. Agree to do so by choosing , otherwise choose .
After the setup has been finished, you need to reboot the machine with the Xen kernel.

Tip: Default Boot Kernel
If everything works as expected, change the default boot kernel with YaST and make the Xen-enabled kernel the default. For more information about changing the default kernel, see Book “Reference”, Chapter 12 “The Boot Loader GRUB 2”, Section 12.3 “Configuring the Boot Loader with YaST”.
6.3 Installing Containers #
To install containers, proceed as follows:
Start YaST and choose › .
Select and confirm with .
6.4 Patterns #
It is possible using Zypper and patterns to install virtualization
packages. Run the command zypper in -t pattern
PATTERN. Available patterns are:
- KVM
kvm_server: sets up the KVM VM Host Server with QEMU tools for managementkvm_tools: installs thelibvirttools for managing and monitoring VM Guests
- Xen
xen_server: sets up the Xen VM Host Server with Xen tools for managementxen_tools: installs the libvirt tools for managing and monitoring VM Guests
- Containers
There is no pattern for containers; install the libvirt-daemon-lxc package.
7 Supported Guests, Hosts and Features #
Supported virtualization limits for Xen and KVM are outlined in the Release Notes.
7.1 Supported VM Guests #
This section lists the support status for various guest operating systems virtualized on top of openSUSE Leap 42.2. All guest operating systems are supported both fully-virtualized (“FV” in the following table) and paravirtualized (“PV” in the following table) with two exceptions: Windows, which is only supported fully-virtualized, and OES and NetWare operating systems, which are only supported on Xen paravirtualized. All guest operating systems are supported both in 32-bit and 64-bit flavors, unless stated otherwise (see NetWare).
Table 7.1: Paravirtualized OS Support #
|
Operating System |
FV Support (Xen/KVM) |
PV Support (Xen) |
|---|---|---|
|
openSUSE Leap 42.2 |
Full |
Full |
|
SLES 12 SP1 |
Full |
Full |
|
SLES 12 |
Full |
Full |
|
SLES 11 SP4 |
Full |
Full |
|
SLES 11 SP3 |
Full |
Full |
|
SLES 10 SP4 |
Full |
Full |
|
SLED 12 SP1 |
Technology preview1 |
Technology preview1 |
|
openSUSE Leap 42.2 |
Technology preview1 |
Technology preview1 |
|
OES 11 SP2 |
None |
Full2, 3 |
|
OES 2015 |
None |
Full2, 3 |
|
OES 2015 SP1 |
None |
Full2, 3 |
|
Netware 6.5 SP8 |
None |
Full (32-bit only)2 |
|
RHEL 5.11+ |
Full/best effort4 |
Full/best effort4 |
|
RHEL 6.7+ |
Full/best effort4 |
Full/best effort4 |
|
RHEL 7.2+ |
Full/best effort4 |
Full/best effort4 |
|
Windows Server 2008 SP2+ |
Full |
None |
|
Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1+ |
Full |
None |
|
Windows Server 2012+ |
Full |
None |
|
Windows Server 2012 R2+ |
Full |
None |
|
Windows Server 2016 |
Full |
None |
|
Windows Vista SP2+ |
Best effort |
None |
|
Windows 7 SP1+ |
Best effort |
None |
|
Windows 8+ |
Best effort |
None |
|
Windows 8.1+ |
Best effort |
None |
|
Windows 10+ |
Best effort |
None |
| 1 Technology preview: The operating system has been tested to install and run successfully. Bugs can be reported and will be tracked by SUSE Technical Services, but no support commitments or service level agreements apply. Potential fixes and patches will be evaluated for future inclusion. |
| 2 You need a static IP address for each virtual machine running NetWare or OES. |
| 3 OES can only be installed from a network installation source. |
| 4 RedHat* guest operating systems are fully supported with Expanded Support. Otherwise, they will be supported on a best-effort basis (fixes if reasonable). |
7.1.1 Availability of Paravirtualized Drivers #
To improve the performance of the guest operating system, paravirtualized drivers are provided when available. Although they are not required, it is strongly recommended to use them. The paravirtualized drivers are available as follows:
- openSUSE Leap 42.2
Included in kernel
- RedHat
Available in RedHat Enterprise Linux 5.4 and newer
- Windows
SUSE has developed virtio-based drivers for Windows, which are available in the Virtual Machine Driver Pack (VMDP). For more information, see http://www.suse.com/products/vmdriverpack/.
7.2 Supported VM Host Servers for openSUSE Leap 42.2 VM Guests #
This section lists the support status of openSUSE Leap 42.2 running as a guest on top of various virtualization hosts (Hypervisor). Both 32-bit and 64-bit versions are supported for the host if available. The support status is defined as follows:
Full support for all SUSE host systems and openSUSE Leap 42.2 VM Guests
Full support for openSUSE Leap 42.2 VM Guests on third-party host systems
The following SUSE host operating systems are supported:
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 SP4 (KVM/Xen)
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 SP1 (KVM/Xen)
openSUSE Leap 42.2 (KVM/Xen)
The following third party host operating systems are supported:
KVM for IBM z Systems 1.1.0
PowerKVM
VMware ESX 5.5
VMware ESXi 6.0
Windows 2008 SP2+
Windows 2008 R2 SP1+
Windows 2012+
Windows 2012 R2+
Microsoft Windows 2016
Citrix XenServer 6.5
Oracle VM 3.3
The following host operating systems will be supported when released:
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 SP3 (KVM/Xen)
VMware ESXi 2016
Citrix XenServer 6.5
7.3 KVM Hardware Requirements #
Currently, SUSE only supports KVM full virtualization on AMD64/Intel 64 hosts and on z Systems (only as Technology Preview). On the AMD64/Intel 64 architecture, KVM is designed around hardware virtualization features included in AMD* (AMD-V) and Intel* (VT-x) CPUs. It supports virtualization features of chipsets, and PCI devices, such as an I/O Memory Mapping Unit (IOMMU) and Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV).
On the AMD64/Intel 64 architecture, you can test whether your CPU supports hardware virtualization with the following command:
egrep '(vmx|svm)' /proc/cpuinfo
If this command returns no output, your processor either does not support hardware virtualization, or this feature has been disabled in the BIOS or Firmware.
The following Web sites identify AMD64/Intel 64 processors that support hardware virtualization: http://ark.intel.com/Products/VirtualizationTechnology (for Intel CPUs), and http://products.amd.com/ (for AMD CPUs).
Note: KVM Kernel Modules Not Loading
The KVM kernel modules only load if the CPU hardware virtualization features are available.
The general minimum hardware requirements for the VM Host Server are the same as for a physical machine. However, additional RAM for each virtualized guest is needed. It should at least be the same amount that is needed for a physical installation. It is also strongly recommended to have at least one processor core or hyper-thread for each running guest.
7.4 Feature Support #
7.4.1 Host (Dom0) #
Table 7.2: Feature Support—Host (Dom0) #
|
Features |
Xen |
|---|---|
|
Network and block device hotplugging |
Yes |
|
Physical CPU hotplugging |
No |
|
Virtual CPU hotplugging |
Yes |
|
Virtual CPU pinning |
Yes |
|
Virtual CPU capping |
Yes |
|
Intel* VT-x2: FlexPriority, FlexMigrate (migration constraints apply to dissimilar CPU architectures) |
Yes |
|
Intel* VT-d2 (DMA remapping with interrupt filtering and queued invalidation) |
Yes |
|
AMD* IOMMU (I/O page table with guest-to-host physical address translation) |
Yes |
Note: Adding or Removing Physical CPUs at Runtime Is Not Supported
The addition or removal of physical CPUs at runtime is not supported. However, virtual CPUs can be added or removed for each VM Guest.
7.4.2 Paravirtualized Guest #
Table 7.3: Feature Support—Paravirtualized Guest #
|
Features |
Xen |
|---|---|
|
Virtual network and virtual block device hotplugging |
Yes |
|
Virtual CPU hotplugging |
Yes |
|
Virtual CPU over-commitment |
Yes |
|
Dynamic virtual memory resize |
Yes |
|
VM save and restore |
Yes |
|
VM live migration |
Yes, between like virtual host systems with similar resources |
|
Advanced debugging with GDBC |
Yes |
|
Dom0 metrics visible to VM |
Yes |
|
Memory ballooning |
Yes |
|
PCI pass-through |
Yes (Netware guests are excluded) |
For live migration, both source and target system architectures need to match; that is, the processors (AMD* or Intel*) must be the same. Unless CPU ID masking is used, such as with Intel FlexMigration, the target should feature the same processor revision or a more recent processor revision than the source. If VMs are moved among different systems, the same rules apply for each move. To avoid failing optimized code at runtime or application start-up, source and target CPUs need to expose the same processor extensions. Xen exposes the physical CPU extensions to the VMs transparently. To summarize, guests can be 32-bit or 64-bit, but the VHS must be identical.
Note: Intel FlexMigration
For machines that support Intel FlexMigration, CPU-ID masking and faulting allow more flexibility in cross-CPU migration.
7.4.3 Fully Virtualized Guest #
Table 7.4: Feature Support—Fully Virtualized Guest #
|
Features |
Xen |
KVM |
|---|---|---|
|
Virtual network and virtual block device hotplugging |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Virtual CPU hotplugging |
No |
No |
|
Virtual CPU over-commitment |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Dynamic virtual memory resize |
Yes |
Yes |
|
VM save and restore |
Yes |
Yes |
|
VM Live Migration |
Yes between like virtual host systems with similar resources (that is, from 32-bit to 32-bit, 64-bit to 64-bit) |
Yes |
|
VM snapshot |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Advanced debugging with GDBC |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Dom0 metrics visible to VM |
Yes |
Yes |
|
PCI pass-through |
Yes |
Yes |
Note: Windows Guest
Hotplugging of virtual network and virtual block devices, and resizing, shrinking, and restoring dynamic virtual memory are supported in Xen and KVM only if PV drivers are being used (VMDP).
For KVM, a detailed description of supported limits, features,
recommended settings and scenarios, and other useful information is
maintained in kvm-supported.txt.
This file is part of the KVM package and can be found in
/usr/share/doc/packages/kvm.
Part II Managing Virtual Machines with libvirt #
- 8 Starting and Stopping
libvirtd The communication between the virtualization solutions (KVM, Xen, LXC) and the libvirt API is managed by the daemon libvirtd, which needs to run on the VM Host Server. libvirt client applications such as virt-manager, possibly running on a remote machine, communicate with libvirtd running on the VM …
- 9 Guest Installation
A VM Guest consists of an image containing an operating system and data files and a configuration file describing the VM Guest's virtual hardware resources. VM Guests are hosted on and controlled by the VM Host Server. This section provides generalized instructions for installing a VM Guest.
- 10 Basic VM Guest Management
Most management tasks, such as starting or stopping a VM Guest, can either be done using the graphical application Virtual Machine Manager or on the command line using
virsh. Connecting to the graphical console via VNC is only possible from a graphical user interface.- 11 Connecting and Authorizing
Managing several VM Host Servers, each hosting multiple VM Guests, quickly becomes difficult. One benefit of
libvirtis the ability to connect to several VM Host Servers at once, providing a single interface to manage all VM Guests and to connect to their graphical console.- 12 Managing Storage
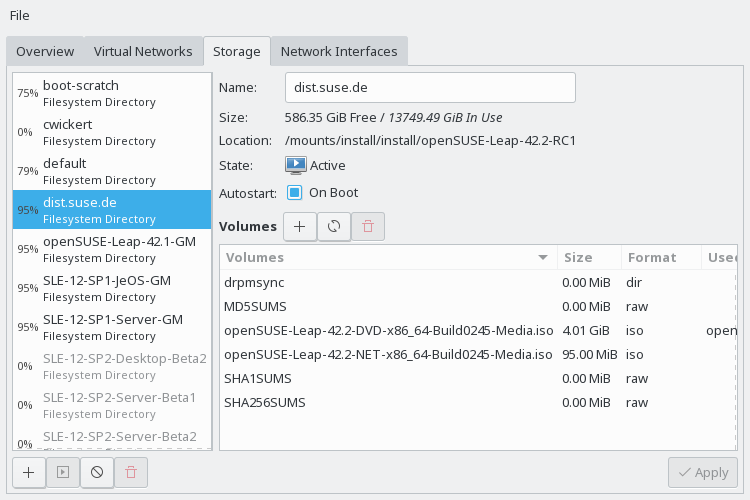
When managing a VM Guest on the VM Host Server itself, you can access the complete file system of the VM Host Server to attach or create virtual hard disks or to attach existing images to the VM Guest. However, this is not possible when managing VM Guests from a remote host. For this reason, libvirt…
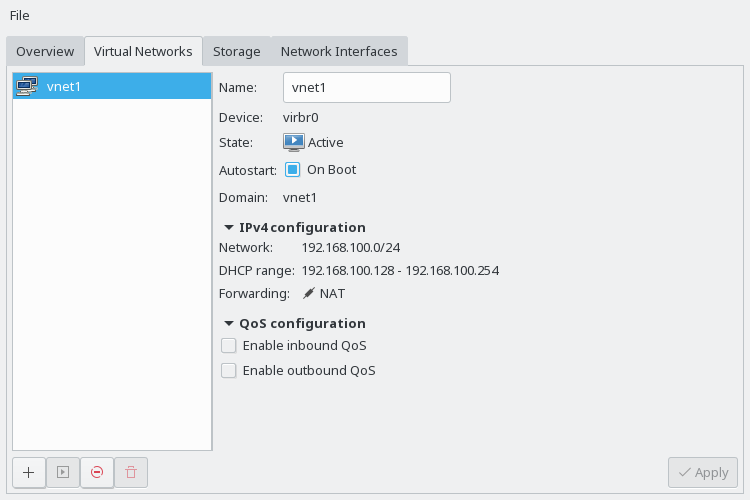
- 13 Managing Networks
This chapter introduces common networking configurations supported by
libvirt. It does not depend on the hypervisor used. It is valid for all hypervisors supported bylibvirt, such as KVM or Xen. These setups can be achieved using both the graphical interface of Virtual Machine Manager and the command line toolvirsh.- 14 Configuring Virtual Machines
Virtual Machine Manager's view offers in-depth information about the VM Guest's complete configuration and hardware equipment. Using this view, you can also change the guest configuration or add and modify virtual hardware. To access this view, open the guest's console in Virtual Machine Manager and either choose › from the menu, or click in the toolbar.
8 Starting and Stopping libvirtd #
The communication between the virtualization solutions (KVM, Xen, LXC)
and the libvirt API is managed by the daemon libvirtd, which needs to run
on the VM Host Server. libvirt client applications such as virt-manager, possibly
running on a remote machine, communicate with libvirtd running on the
VM Host Server, which services the request using native hypervisor APIs. Use the
following commands to start and stop libvirtd or check its status:
root #systemctl start libvirtdroot #systemctl status libvirtd libvirtd.service - Virtualization daemon Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/libvirtd.service; enabled) Active: active (running) since Mon 2014-05-12 08:49:40 EDT; 2s ago [...]root #systemctl stop libvirtdroot #systemctl status libvirtd [...] Active: inactive (dead) since Mon 2014-05-12 08:51:11 EDT; 4s ago [...]
To automatically start libvirtd at boot time, either activate it
using the YaST module or by
entering the following command:
root # systemctl enable libvirtd9 Guest Installation #
A VM Guest consists of an image containing an operating system and data files and a configuration file describing the VM Guest's virtual hardware resources. VM Guests are hosted on and controlled by the VM Host Server. This section provides generalized instructions for installing a VM Guest.
Virtual machines have few if any requirements above those required to run the operating system. If the operating system has not been optimized for the virtual machine host environment, it can only run on hardware-assisted virtualization computer hardware, in full virtualization mode, and requires specific device drivers to be loaded. The hardware that is presented to the VM Guest depends on the configuration of the host.
Note: Virtual Machine Architectures
The virtual machine host runs only on AMD64 and Intel 64. Additionally, KVM for z Systems is included on SUSE Linux Enterprise Server as a technology preview. It does not run on other system architectures such as POWER. A 64-bit virtual machine host can, however, run both 32-bit and 64-bit VM Guests.
You should be aware of any licensing issues related to running a single licensed copy of an operating system on multiple virtual machines. Consult the operating system license agreement for more information.
9.1 GUI-Based Guest Installation #
The wizard helps you through the steps required to create a virtual machine and install its operating system. There are two ways to start it: Within Virtual Machine Manager, either click or choose › . Alternatively, start YaST and choose › .
Start the wizard either from YaST or Virtual Machine Manager.
Choose an installation source—either a locally available media or a network installation source. If you want to set up your VM Guest from an existing image, choose .
On a VM Host Server running the Xen hypervisor, you can choose whether to install a paravirtualized or a fully virtualized guest. The respective option is available under . Depending on this choice, not all installation options may be available.
Depending on your choice in the previous step, you need to provide the following data:
Specify the path on the VM Host Server to an iso image containing the installation data. If it is available as a volume in a libvirt storage pool, you can also select it using . For more information, see Chapter 12, Managing Storage.
Alternatively, choose a physical CD-ROM or DVD inserted in the optical drive of the VM Host Server.
Provide the pointing to the installation source. Valid URL prefixes are, for example,
ftp://,http://,https://, andnfs://.Under , provide a path to an auto-installation file (AutoYaST or Kickstart, for example) and Kernel parameters. Having provided a URL, the operating system should be automatically detected correctly. If this is not the case, deselect and manually select the and .
When booting via PXE, you only need to provide the and the .
To set up the VM Guest from an existing image, you need to specify the path on the VM Host Server to the image. If it is available as a volume in a libvirt storage pool, you can also select it using . For more information, see Chapter 12, Managing Storage.
Choose the memory size and number of CPUs for the new virtual machine.
This step is omitted when is chosen in the first step.
Set up a virtual hard disk for the VM Guest. Either create a new disk image or choose an existing one from a storage pool (for more information, see Chapter 12, Managing Storage). If you choose to create a disk, a
qcow2image will be created. By default, it is stored under/var/lib/libvirt/images.Setting up a disk is optional. If you are running a live system directly from CD or DVD, for example, you can omit this step by deactivating .
On the last screen of the wizard, specify the name for the virtual machine. To be offered the possibility to review and make changes to the virtualized hardware selection, activate . Find options to specify the network device under .
Click .
(Optional) If you kept the defaults in the previous step, the installation will now start. If you selected , a VM Guest configuration dialog opens. For more information about configuring VM Guests, see Chapter 14, Configuring Virtual Machines.
When you are done configuring, click .
Tip: Passing Key Combinations to Virtual Machines
The installation starts in a Virtual Machine Manager console window. Some key combinations, such as Ctrl–Alt–F1, are recognized by the VM Host Server but are not passed to the virtual machine. To bypass the VM Host Server, Virtual Machine Manager provides the “sticky key” functionality. Pressing Ctrl, Alt, or Shift three times makes the key sticky, then you can press the remaining keys to pass the combination to the virtual machine.
For example, to pass Ctrl–Alt–F2 to a Linux virtual machine, press Ctrl three times, then press Alt–F2. You can also press Alt three times, then press Ctrl–F2.
The sticky key functionality is available in the Virtual Machine Manager during and after installing a VM Guest.
9.2 Installing from the Command Line with virt-install #
virt-install is a command line tool that helps you
create new virtual machines using the libvirt library. It is useful
if you cannot use the graphical user interface, or need to automatize the
process of creating virtual machines.
virt-install is a complex script with a lot of command
line switches. The following are required. For more information, see the
man page of virt-install (1).
- General Options
--name vm_guest_name: Specify the name of the new virtual machine. The name must be unique across all guests known to the hypervisor on the same connection. It is used to create and name the guest’s configuration file and you can access the guest with this name fromvirsh. Alphanumeric and_-.:+characters are allowed.--memory required_memory: Specify the amount of memory to allocate for the new virtual machine in megabytes.--vcpus number_of_cpus: Specify the number of virtual CPUs. For best performance, the number of virtual processors should be less than or equal to the number of physical processors.
- Virtualization Type
--paravirt: Set up a paravirtualized guest. This is the default if the VM Host Server supports paravirtualization and full virtualization.--hvm: Set up a fully virtualized guest.--virt-type hypervisor: Specify the hypervisor. Supported values arekvm,xen, orlxc.
- Guest Storage
Specify one of
--disk,--filesystemor--nodisksthe type of the storage for the new virtual machine. For example,--disk size=10creates 10 GB disk in the default image location for the hypervisor and uses it for the VM Guest.--filesystem /export/path/on/vmhostspecifies the directory on the VM Host Server to be exported to the guest. And--nodiskssets up a VM Guest without a local storage (good for Live CDs).- Installation Method
Specify the installation method using one of
--location,--cdrom,--pxe,--import, or--boot.- Accessing the Installation
Use the
--graphics valueoption to specify how to access the installation. openSUSE Leap supports the valuesvncornone.If using vnc
virt-installtries to launchvirt-viewer. If it is not installed or cannot be run, connect to the VM Guest manually with you preferred viewer. To explicitly preventvirt-installfrom launching the viewer use--noautoconsole. To define a password for accessing the VNC session, use the following syntax:--graphics vnc,password=PASSWORD.In case you are using
--graphics none, you can access the VM Guest through operating system supported services, such as SSH or VNC. Refer to the operating system installation manual on how to set up these services in the installation system.
Example 9.1: Example of a virt-install command line #
The following command line example creates a new SUSE Linux Enterprise Desktop 12 virtual machine with a virtio accelerated disk and network card. It creates a new 10 GB qcow2 disk image as a storage, the source installation media being the host CD-ROM drive. It will use VNC graphics, and it will auto-launch the graphical client.
- KVM
virt-install --connect qemu:///system --virt-type kvm --name sled12 \ --memory 1024 --disk size=10 --cdrom /dev/cdrom --graphics vnc \ --os-variant sled12
- Xen
virt-install --connect xen:// --virt-type xen --name sled12 \ --memory 1024 --disk size=10 --cdrom /dev/cdrom --graphics vnc \ --os-variant sled12
9.3 Advanced Guest Installation Scenarios #
This section provides instructions for operations exceeding the scope of a normal installation, such as including modules and extensions packages.
9.3.1 Memory Ballooning with Windows Guests #
Memory ballooning is a method to change the amount of memory used by VM Guest at runtime. Both the KVM and Xen hypervisors provide this method, but it needs to be supported by the guest as well.
While openSUSE and SLE-based guests support memory ballooning, Windows guests need the Virtual Machine Driver Pack (VMDP) to provide ballooning. To set the maximum memory greater than the initial memory configured for Windows guests, follow these steps:
Install the Windows guest with the maximum memory equal or less than the initial value.
Install the Virtual Machine Driver Pack in the Windows guest to provide required drivers.
Shut down the Windows guest.
Reset the maximum memory of the Windows guest to the required value.
Start the Windows guest again.
9.3.2 Including Add-On Products in the Installation #
Some operating systems such as SUSE Linux Enterprise Server offer to include add-on products in the installation process. In case the add-on product installation source is provided via network, no special VM Guest configuration is needed. If it is provided via CD/DVD or ISO image, it is necessary to provide the VM Guest installation system with both, the standard installation medium and an image for the add-on product.
In case you are using the GUI-based installation, select in the last step of the wizard and add the add-on product ISO image via › . Specify the path to the image and set the to .
If installing from the command line, you need to set up the virtual
CD/DVD drives with the --disk parameter rather than
with --cdrom. The device that is specified first is
used for booting. The following example will install SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 plus
SDK:
virt-install --name sles12+sdk --memory 1024 --disk size=10 \ --disk /virt/iso/SLES12.iso,device=cdrom \ --disk /virt/iso/SLES12_SDK.iso,device=cdrom \ --graphics vnc --os-variant sles12
10 Basic VM Guest Management #
Most management tasks, such as starting or stopping a VM Guest, can
either be done using the graphical application Virtual Machine Manager or on the command
line using virsh. Connecting to the graphical console
via VNC is only possible from a graphical user interface.
Note: Managing VM Guests on a Remote VM Host Server
If started on a VM Host Server, the libvirt tools Virtual Machine Manager,
virsh, and virt-viewer can be used to
manage VM Guests on the host. However, it is also possible to manage
VM Guests on a remote VM Host Server. This requires configuring remote
access for libvirt on the host. For instructions, see
Chapter 11, Connecting and Authorizing.
To connect to such a remote host with Virtual Machine Manager, you need to set
up a connection as explained in
Section 11.2.2, “Managing Connections with Virtual Machine Manager”. If connecting to a
remote host using virsh or
virt-viewer, you need to specify a connection URI with
the parameter -c (for example, virsh -c
qemu+tls://saturn.example.com/system or virsh -c
xen+ssh://). The form of connection URI depends on the
connection type and the hypervisor—see
Section 11.2, “Connecting to a VM Host Server” for details.
Examples in this chapter are all listed without a connection URI.
10.1 Listing VM Guests #
The VM Guest listing shows all VM Guests managed by libvirt
on a VM Host Server.
10.1.1 Listing VM Guests with Virtual Machine Manager #
The main window of the Virtual Machine Manager lists all VM Guests for each VM Host Server it is connected to. Each VM Guest entry contains the machine's name, its status (, , or ) displayed as an icon and literally, and a CPU usage bar.
10.1.2 Listing VM Guests with virsh #
Use the command virsh list to get a
list of VM Guests:
- List all running guests
virsh list
- List all running and inactive guests
virsh --all
For more information and further options, see virsh help
list or man 1 virsh.
10.2 Accessing the VM Guest via Console #
VM Guests can be accessed via a VNC connection (graphical console) or, if supported by the guest operating system, via a serial console.
10.2.1 Opening a Graphical Console #
Opening a graphical console to a VM Guest lets you interact with the machine like a physical host via a VNC connection. If accessing the VNC server requires authentication, you are prompted to enter a user name (if applicable) and a password.
When you click into the VNC console, the cursor is “grabbed” and cannot be used outside the console anymore. To release it, press Alt–Ctrl.
Tip: Seamless (Absolute) Cursor Movement
To prevent the console from grabbing the cursor and to enable seamless cursor movement, add a tablet input device to the VM Guest. See Section 14.5, “Enabling Seamless and Synchronized Mouse Pointer Movement” for more information.
Certain key combinations such as Ctrl–Alt–Del are
interpreted by the host system and are not passed to the VM Guest. To
pass such key combinations to a VM Guest, open the menu from the VNC window and choose the desired key
combination entry. The menu is only available
when using Virtual Machine Manager and virt-viewer. With Virtual Machine Manager, you can
alternatively use the “sticky key” feature as explained in
Tip: Passing Key Combinations to Virtual Machines.
Note: Supported VNC Viewers
Principally all VNC viewers can connect to the console of a
VM Guest. However, if you are using SASL authentication and/or TLS/SSL
connection to access the guest, the options are limited. Common VNC
viewers such as tightvnc or
tigervnc support neither SASL authentication nor
TLS/SSL. The only supported alternative to Virtual Machine Manager and
virt-viewer is vinagre.
10.2.1.1 Opening a Graphical Console with Virtual Machine Manager #
In the Virtual Machine Manager, right-click a VM Guest entry.
Choose from the pop-up menu.
10.2.1.2
Opening a Graphical Console with virt-viewer
#
virt-viewer is a simple VNC viewer with added
functionality for displaying VM Guest consoles. For example, it can be
started in “wait” mode, where it waits for a VM Guest to
start before it connects. It also supports automatically reconnecting to
a VM Guest that is rebooted.
virt-viewer addresses VM Guests by name, by ID or by
UUID. Use virsh list --all to get
this data.
To connect to a guest that is running or paused, use either the ID, UUID, or name. VM Guests that are shut off do not have an ID—you can only connect to them by UUID or name.
- Connect to guest with the ID
8 virt-viewer 8
- Connect to the inactive guest named
sles12; the connection window will open once the guest starts virt-viewer --wait sles12
With the
--waitoption, the connection will be upheld even if the VM Guest is not running at the moment. When the guest starts, the viewer will be launched.
For more information, see virt-viewer
--help or man 1 virt-viewer.
Note: Password Input on Remote connections with SSH
When using virt-viewer to open a connection to a
remote host via SSH, the SSH password needs to be entered twice. The
first time for authenticating with libvirt, the second time for
authenticating with the VNC server. The second password needs to be
provided on the command line where virt-viewer was started.
10.2.2 Opening a Serial Console #
Accessing the graphical console of a virtual machine requires a graphical
environment on the client accessing the VM Guest.
As an alternative, virtual machines
managed with libvirt can also be accessed from the shell via the serial
console and virsh. To open a serial console to a
VM Guest named “sles12”, run the following command:
virsh console sles12
virsh console takes two optional flags:
--safe ensures exclusive access to the console,
--force disconnects any existing sessions before
connecting. Both features need to be supported by the guest operating
system.
Being able to connect to a VM Guest via serial console requires that the guest operating system supports serial console access and is properly supported. Refer to the guest operating system manual for more information.
Tip: Enabling Serial Console Access for SUSE Linux Enterprise and openSUSE Guests
Serial console access in SUSE Linux Enterprise and openSUSE is disabled by default. To enable it, proceed as follows:
- SLES 12 / openSUSE
Launch the YaST Boot Loader module and switch to the tab. Add
console=ttyS0to the field .- SLES 11
Launch the YaST Boot Loader module and select the boot entry for which to activate serial console access. Choose and add
console=ttyS0to the field . Additionally, edit/etc/inittaband uncomment the line with the following content:#S0:12345:respawn:/sbin/agetty -L 9600 ttyS0 vt102
10.3 Changing a VM Guest's State: Start, Stop, Pause #
Starting, stopping or pausing a VM Guest can be done with either
Virtual Machine Manager or virsh. You can also configure a
VM Guest to be automatically started when booting the VM Host Server.
When shutting down a VM Guest, you may either shut it down gracefully, or force the shutdown. The latter is equivalent to pulling the power plug on a physical host and is only recommended if there are no alternatives. Forcing a shutdown may cause file system corruption and loss of data on the VM Guest.
Tip: Graceful Shutdown
To be able to perform a graceful shutdown, the VM Guest must be configured to support ACPI. If you have created the guest with the Virtual Machine Manager, ACPI should be available in the VM Guest.
Depending on the guest operating system, availability of ACPI may not be sufficient to perform a graceful shutdown. It is strongly recommended to test shutting down and rebooting a guest before using it in production. openSUSE or SUSE Linux Enterprise Desktop, for example, can require PolKit authorization for shutdown and reboot. Make sure this policy is turned off on all VM Guests.
If ACPI was enabled during a Windows XP/Windows Server 2003 guest installation, turning it on in the VM Guest configuration only is not sufficient. For more information, see:
Regardless of the VM Guest's configuration, a graceful shutdown is always possible from within the guest operating system.
10.3.1 Changing a VM Guest's State with Virtual Machine Manager #
Changing a VM Guest's state can be done either from Virtual Machine Manager's main window, or from a VNC window.
Procedure 10.1: State Change from the Virtual Machine Manager Window #
Right-click a VM Guest entry.
Choose , , or one of the from the pop-up menu.
Procedure 10.2: State change from the VNC Window #
Open a VNC Window as described in Section 10.2.1.1, “Opening a Graphical Console with Virtual Machine Manager”.
Choose , , or one of the options either from the toolbar or from the menu.
10.3.1.1 Automatically Starting a VM Guest #
You can automatically start a guest when the VM Host Server boots. This feature is not enabled by default and needs to be enabled for each VM Guest individually. There is no way to activate it globally.
Double-click the VM Guest entry in Virtual Machine Manager to open its console.
Choose › to open the VM Guest configuration window.
Choose and check .
Save the new configuration with .
10.3.2 Changing a VM Guest's State with virsh #
In the following examples, the state of a VM Guest named “sles12” is changed.
- Start
virsh start sles12
- Pause
virsh suspend sles12
- Reboot
virsh reboot sles12
- Graceful shutdown
virsh shutdown sles12
- Force shutdown
virsh destroy sles12
- Turn on automatic start
virsh autostart sles12
- Turn off automatic start
virsh autostart --disable sles12
10.4 Saving and Restoring the State of a VM Guest #
Saving a VM Guest preserves the exact state of the guest’s memory. The operation is similar to hibernating a computer. A saved VM Guest can be quickly restored to its previously saved running condition.
When saved, the VM Guest is paused, its current memory state is saved to disk, and then the guest is stopped. The operation does not make a copy of any portion of the VM Guest’s virtual disk. The amount of time taken to save the virtual machine depends on the amount of memory allocated. When saved, a VM Guest’s memory is returned to the pool of memory available on the VM Host Server.
The restore operation loads a VM Guest’s previously saved memory state file and starts it. The guest is not booted but instead resumed at the point where it was previously saved. The operation is similar to coming out of hibernation.
The VM Guest is saved to a state file. Make sure there is enough space on the partition you are going to save to. For an estimation of the file size in megabytes to be expected, issue the following command on the guest:
free -mh | awk '/^Mem:/ {print $3}'Warning: Always Restore Saved Guests
After using the save operation, do not boot or start the saved VM Guest. Doing so would cause the machine's virtual disk and the saved memory state to get out of synchronization. This can result in critical errors when restoring the guest.
To be able to work with a saved VM Guest again, use the restore operation.
If you used virsh to save a VM Guest, you cannot
restore it using Virtual Machine Manager. In this case, make sure to restore using
virsh.
Important:
Only for VM Guests with Disk Types raw,
qcow2, qed
Saving and restoring VM Guests is only possible if the
VM Guest is using a virtual disk of the type
raw (.img),
qcow2, or qed.
10.4.1 Saving/Restoring with Virtual Machine Manager #
Procedure 10.3: Saving a VM Guest #
Open a VNC connection window to a VM Guest. Make sure the guest is running.
Choose › › .
Procedure 10.4: Restoring a VM Guest #
Open a VNC connection window to a VM Guest. Make sure the guest is not running.
Choose › .
If the VM Guest was previously saved using Virtual Machine Manager, you will not be offered an option to the guest. However, note the caveats on machines saved with
virshoutlined in Warning: Always Restore Saved Guests.
10.4.2 Saving and Restoring with virsh #
Save a running VM Guest with the command virsh
save and specify the file which it is saved to.
- Save the guest named
opensuse13 virsh save opensuse13 /virtual/saves/opensuse13.vmsav
- Save the guest with the ID
37 virsh save 37 /virtual/saves/opensuse13.vmsave
To restore a VM Guest, use virsh restore:
virsh restore /virtual/saves/opensuse13.vmsave
10.5 Creating and Managing Snapshots #
VM Guest snapshots are snapshots of the complete virtual machine including the state of CPU, RAM, and the content of all writable disks. To use virtual machine snapshots, you must have at least one non-removable and writable block device using the qcow2 disk image format.
Note
Snapshots are supported on KVM VM Host Servers only.
Snapshots let you restore the state of the machine at a particular point in time. This is for example useful to undo a faulty configuration or the installation of a lot of packages. It is also helpful for testing purposes, as it allows you to go back to a defined state at any time.
Snapshots can be taken either from running guests or from a guest currently not running. Taking a screenshot from a guest that is shut down ensures data integrity. In case you want to create a snapshot from a running system, be aware that the snapshot only captures the state of the disk(s), not the state of the memory. Therefore you need to ensure that:
All running programs have written their data to the disk. If you are unsure, terminate the application and/or stop the respective service.
Buffers have been written to disk. This can be achieved by running the command
syncon the VM Guest.
Starting a snapshot reverts the machine back to the state it was in when the snapshot was taken. Any changes written to the disk after that point in time will be lost when starting the snapshot.
Starting a snapshot will restore the machine to the state (shut off or running) it was in when the snapshot was taken. After starting a snapshot that was created while the VM Guest was shut off, you will need to boot it.
10.5.1 Creating and Managing Snapshots with Virtual Machine Manager #
To open the snapshot management view in Virtual Machine Manager, open the VNC window as described in Section 10.2.1.1, “Opening a Graphical Console with Virtual Machine Manager”. Now either choose › or click in the toolbar.
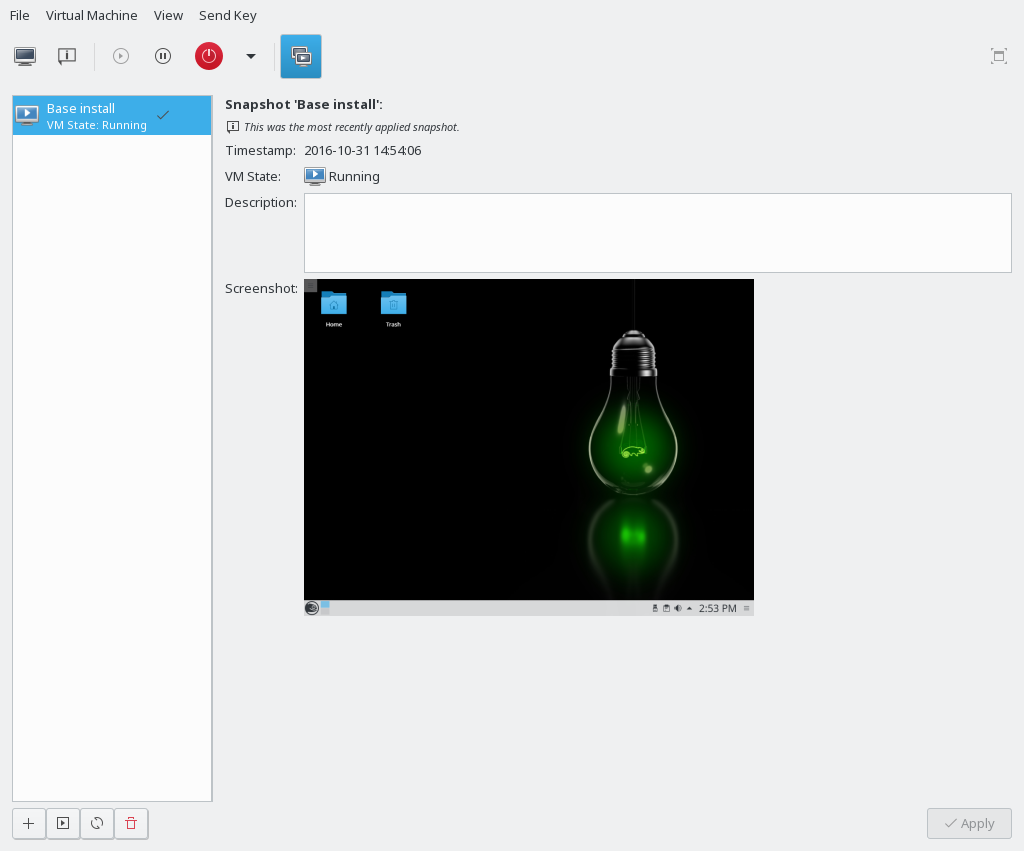
The list of existing snapshots for the chosen VM Guest is displayed in the left-hand part of the window. The snapshot that was last started is marked with a green tick. The right-hand part of the window shows details of the snapshot currently marked in the list. These details include the snapshot's title and time stamp, the state of the VM Guest at the time the snapshot was taken and a description. Snapshots of running guests also include a screenshot. The can be changed directly from this view. Other snapshot data cannot be changed.
10.5.1.1 Creating a Snapshot #
To take a new snapshot of a VM Guest, proceed as follows:
Shut down the VM Guest in case you want to create a snapshot from a guest that is not running.
Click in the bottom left corner of the VNC window.
The window opens.
Provide a and, optionally, a description. The name cannot be changed after the snapshot has been taken. To be able to identify the snapshot later easily, use a “speaking name”.
Confirm with .
10.5.1.2 Deleting a Snapshot #
To delete a snapshot of a VM Guest, proceed as follows:
Click in the bottom left corner of the VNC window.
Confirm the deletion with .
10.5.1.3 Starting a Snapshot #
To start a snapshot, proceed as follows:
Click in the bottom left corner of the VNC window.
Confirm the start with .
10.5.2 Creating and Managing Snapshots with virsh #
To list all existing snapshots for a domain
(admin_server in the following), run the
snapshot-list command:
tux > virsh snapshot-list
Name Creation Time State
------------------------------------------------------------
Basic installation incl. SMT finished 2013-09-18 09:45:29 +0200 shutoff
Basic installation incl. SMT for CLOUD3 2013-12-11 15:11:05 +0100 shutoff
Basic installation incl. SMT for CLOUD3-HA 2014-03-24 13:44:03 +0100 shutoff
Basic installation incl. SMT for CLOUD4 2014-07-07 11:27:47 +0200 shutoff
Beta1 Running 2013-07-12 12:27:28 +0200 shutoff
Beta2 prepared 2013-07-12 17:00:44 +0200 shutoff
Beta2 running 2013-07-29 12:14:11 +0200 shutoff
Beta3 admin node deployed 2013-07-30 16:50:40 +0200 shutoff
Beta3 prepared 2013-07-30 17:07:35 +0200 shutoff
Beta3 running 2013-09-02 16:13:25 +0200 shutoff
Cloud2 GM running 2013-12-10 15:44:58 +0100 shutoff
CLOUD3 RC prepared 2013-12-20 15:30:19 +0100 shutoff
CLOUD3-HA Build 680 prepared 2014-03-24 14:20:37 +0100 shutoff
CLOUD3-HA Build 796 installed (zypper up) 2014-04-14 16:45:18 +0200 shutoff
GMC2 post Cloud install 2013-09-18 10:53:03 +0200 shutoff
GMC2 pre Cloud install 2013-09-18 10:31:17 +0200 shutoff
GMC2 prepared (incl. Add-On Installation) 2013-09-17 16:22:37 +0200 shutoff
GMC_pre prepared 2013-09-03 13:30:38 +0200 shutoff
OS + SMT + eth[01] 2013-06-14 16:17:24 +0200 shutoff
OS + SMT + Mirror + eth[01] 2013-07-30 15:50:16 +0200 shutoff
The snapshot that was last started is shown with the
snapshot-current command:
tux > virsh snapshot-current --name admin_server
Basic installation incl. SMT for CLOUD4
Details about a particular snapshot can be obtained by running the
snapshot-info command:
tux > virsh snapshot-info sles "Basic installation incl. SMT for CLOUD4"
Name: Basic installation incl. SMT for CLOUD4
Domain: admin_server
Current: yes
State: shutoff
Location: internal
Parent: Basic installation incl. SMT for CLOUD3-HA
Children: 0
Descendants: 0
Metadata: yes10.5.2.1 Creating a Snapshot #
To take a new snapshot of a VM Guest currently not running, use the
snapshot-create-as command as follows:
virsh snapshot-create-as --domain admin_server1 --name "Snapshot 1"2 \ --description "First snapshot"3
Domain name. Mandatory. | |
Name of the snapshot. It is recommended to use a “speaking name”, since that makes it easier to identify the snapshot. Mandatory. | |
Description for the snapshot. Optional. |
To take a snapshot of a running VM Guest, you need to specify the
--live parameter:
virsh snapshot-create-as --domain admin_server --name "Snapshot 2" \ --description "First live snapshot" --live
Refer to the SNAPSHOT COMMANDS section in
man 1 virsh for more details.
10.5.2.2 Deleting a Snapshot #
To delete a snapshot of a VM Guest, use the
snapshot-delete command:
virsh snapshot-delete --domain admin_server --snapshotname "Snapshot 2"
10.5.2.3 Starting a Snapshot #
To start a snapshot, use the snapshot-revert
command:
virsh snapshot-revert --domain admin_server --snapshotname "Snapshot 1"
To start the current snapshot (the one the VM Guest was started
off), it is sufficient to use --current rather than
specifying the snapshot name:
virsh snapshot-revert --domain admin_server --current
10.6 Deleting a VM Guest #
By default, deleting a VM Guest using virsh removes only
its XML configuration. Since attached storage is not deleted by default, you
can reuse it with another VM Guest. With Virtual Machine Manager, you can also delete a
guest's storage files as well—this will completely erase the guest.
10.6.1 Deleting a VM Guest with Virtual Machine Manager #
In the Virtual Machine Manager, right-click a VM Guest entry.
From the context menu, choose .
A confirmation window opens. Clicking will permanently erase the VM Guest. The deletion is not recoverable.
You can also permanently delete the guest's virtual disk by activating . The deletion is not recoverable either.
10.6.2 Deleting a VM Guest with virsh #
To delete a VM Guest, it needs to be shut down first. It is not possible to delete a running guest. For information on shutting down, see Section 10.3, “Changing a VM Guest's State: Start, Stop, Pause”.
To delete a VM Guest with virsh, run
virsh undefine
VM_NAME.
virsh undefine sles12
There is no option to automatically delete the attached storage files. If they are managed by libvirt, delete them as described in Section 12.2.4, “Deleting Volumes from a Storage Pool”.
10.7 Migrating VM Guests #
One of the major advantages of virtualization is that VM Guests are portable. When a VM Host Server needs to go down for maintenance, or when the host gets overloaded, the guests can easily be moved to another VM Host Server. KVM and Xen even support “live” migrations during which the VM Guest is constantly available.
10.7.1 Migration Requirements #
To successfully migrate a VM Guest to another VM Host Server, the following requirements need to be met:
It is recommended that the source and destination systems have the same architecture. However, it is possible to migrate between hosts with AMD* and Intel* architectures.
Storage devices must be accessible from both machines (for example, via NFS or iSCSI) and must be configured as a storage pool on both machines. For more information, see Chapter 12, Managing Storage.
This is also true for CD-ROM or floppy images that are connected during the move. However, you can disconnect them prior to the move as described in Section 14.8, “Ejecting and Changing Floppy or CD/DVD-ROM Media with Virtual Machine Manager”.
libvirtdneeds to run on both VM Host Servers and you must be able to open a remotelibvirtconnection between the target and the source host (or vice versa). Refer to Section 11.3, “Configuring Remote Connections” for details.If a firewall is running on the target host, ports need to be opened to allow the migration. If you do not specify a port during the migration process,
libvirtchooses one from the range 49152:49215. Make sure that either this range (recommended) or a dedicated port of your choice is opened in the firewall on the target host.Host and target machine should be in the same subnet on the network, otherwise networking will not work after the migration.
No running or paused VM Guest with the same name must exist on the target host. If a shut-down machine with the same name exists, its configuration will be overwritten.
All CPU models except host cpu model are supported when migrating VM Guests.
SATA disk device type is not migratable.
File system pass-through feature is incompatible with migration.
The VM Host Server and VM Guest need to have proper timekeeping installed. See Chapter 16, VM Guest Clock Settings.
Section 29.3.1.2, “virtio-blk-data-plane” is not supported for migration.
No physical devices can be passed from host to guest. Live migration is currently not supported when using devices with PCI pass-through or SR-IOV. In case live migration needs to be supported, you need to use software virtualization (paravirtualization or full virtualization).
Cache mode setting is an important setting for migration. See: Section 15.5, “Effect of Cache Modes on Live Migration”.
The image directory should be located in the same path on both hosts.
10.7.2 Migrating with Virtual Machine Manager #
When using the Virtual Machine Manager to migrate VM Guests, it does not matter on which machine it is started. You can start Virtual Machine Manager on the source or the target host or even on a third host. In the latter case you need to be able to open remote connections to both the target and the source host.
Start Virtual Machine Manager and establish a connection to the target or the source host. If the Virtual Machine Manager was started neither on the target nor the source host, connections to both hosts need to be opened.
Right-click the VM Guest that you want to migrate and choose . Make sure the guest is running or paused—it is not possible to migrate guests that are shut down.

Tip: Increasing the Speed of the Migration
To increase the speed of the migration somewhat, pause the VM Guest. This is the equivalent of the former so-called “offline migration” option of Virtual Machine Manager.
Choose a for the VM Guest. If the desired target host does not show up, make sure that you are connected to the host.
To change the default options for connecting to the remote host, under , set the , and the target host's (IP address or host name) and . If you specify a , you must also specify an .
Under , choose whether the move should be permanent (default) or temporary, using .
Additionally, there is the option , which allows migrating without disabling the cache of the VM Host Server. This can speed up the migration but only works when the current configuration allows for a consistent view of the VM Guest storage without using
cache="none"/0_DIRECT.
Note: Bandwidth Option
In recent versions of Virtual Machine Manager, the option of setting a bandwidth for the migration has been removed. To set a specific bandwidth, use
virshinstead.To perform the migration, click .
When the migration is complete, the window closes and the VM Guest is now listed on the new host in the Virtual Machine Manager window. The original VM Guest will still be available on the target host (in shut down state).
10.7.3 Migrating with virsh #
To migrate a VM Guest with virsh
migrate, you need to have direct or remote shell access
to the VM Host Server, because the command needs to be run on the host. The
migration command looks like this:
virsh migrate [OPTIONS] VM_ID_or_NAME CONNECTION_URI [--migrateuri tcp://REMOTE_HOST:PORT]
The most important options are listed below. See virsh help
migrate for a full list.
--liveDoes a live migration. If not specified, the guest will be paused during the migration (“offline migration”).
--suspendDoes an offline migration and does not restart the VM Guest on the target host.
--persistentBy default a migrated VM Guest will be migrated temporarily, so its configuration is automatically deleted on the target host if it is shut down. Use this switch to make the migration persistent.
--undefinesourceWhen specified, the VM Guest definition on the source host will be deleted after a successful migration (however, virtual disks attached to this guest will not be deleted).
The following examples use mercury.example.com as the source system and
jupiter.example.com as the target system; the VM Guest's name is
opensuse131 with Id 37.
- Offline migration with default parameters
virsh migrate 37 qemu+ssh://tux@jupiter.example.com/system
- Transient live migration with default parameters
virsh migrate --live opensuse131 qemu+ssh://tux@jupiter.example.com/system
- Persistent live migration; delete VM definition on source
virsh migrate --live --persistent --undefinesource 37 \ qemu+tls://tux@jupiter.example.com/system
- Offline migration using port 49152
virsh migrate opensuse131 qemu+ssh://tux@jupiter.example.com/system \ --migrateuri tcp://@jupiter.example.com:49152
Note: Transient Compared to Persistent Migrations
By default virsh migrate creates a temporary
(transient) copy of the VM Guest on the target host. A shut down
version of the original guest description remains on the source host. A
transient copy will be deleted from the server after it is shut down.
To create a permanent copy of a guest on the target host, use
the switch --persistent. A shut down version of the
original guest description remains on the source host, too. Use the
option --undefinesource together with
--persistent for a “real” move where a
permanent copy is created on the target host and the version on the
source host is deleted.
It is not recommended to use --undefinesource without
the --persistent option, since this will result in the
loss of both VM Guest definitions when the guest is shut down on
the target host.
10.7.4 Step-by-Step Example #
10.7.4.1 Exporting the Storage #
First you need to export the storage, to share the Guest image between
host. This can be done by an NFS server. In the following example we
want to share the /volume1/VM directory for all
machines that are on the network 10.0.1.0/24. We will use a SUSE Linux Enterprise
NFS server. As root user, edit the /etc/exports
file and add:
/volume1/VM 10.0.1.0/24 (rw,sync,no_root_squash)
You need to restart the NFS server:
root #systemctl restart nfsserverroot #exportfs /volume1/VM 10.0.1.0/24
10.7.4.2 Defining the Pool on the Target Hosts #
On each host where you want to migrate the VM Guest, the pool must
be defined to be able to access the volume (that contains the Guest
image). Our NFS server IP address is 10.0.1.99, its share is the
/volume1/VM directory, and we want to get it
mounted in the /var/lib/libvirt/images/VM
directory. The pool name will be VM. To define
this pool, create a VM.xml file with the following
content:
<pool type='netfs'>
<name>VM</name>
<source>
<host name='10.0.1.99'/>
<dir path='/volume1/VM'/>
<format type='auto'/>
</source>
<target>
<path>/var/lib/libvirt/images/VM</path>
<permissions>
<mode>0755</mode>
<owner>-1</owner>
<group>-1</group>
</permissions>
</target>
</pool>
Then load it into libvirt using the pool-define
command:
root # virsh pool-define VM.xml
An alternative way to define this pool is to use the
virsh command:
root # virsh pool-define-as VM --type netfs --source-host 10.0.1.99 \
--source-path /volume1/VM --target /var/lib/libvirt/images/VM
Pool VM created
The following commands assume that you are in the interactive shell of
virsh which can also be reached by using the command
virsh without any arguments.
Then the pool can be set to start automatically at host boot (autostart
option):
virsh # pool-autostart VM
Pool VM marked as autostartedIf you want to disable the autostart:
virsh # pool-autostart VM --disable
Pool VM unmarked as autostartedCheck if the pool is present:
virsh #pool-list --all Name State Autostart ------------------------------------------- default active yes VM active yesvirsh #pool-info VM Name: VM UUID: 42efe1b3-7eaa-4e24-a06a-ba7c9ee29741 State: running Persistent: yes Autostart: yes Capacity: 2,68 TiB Allocation: 2,38 TiB Available: 306,05 GiB
Warning: Pool Needs to Exist on All Target Hosts
Remember: this pool must be defined on each host where you want to be able to migrate your VM Guest.
10.7.4.3 Creating the Volume #
The pool has been defined—now we need a volume which will contain the disk image:
virsh # vol-create-as VM sled12.qcow12 8G --format qcow2
Vol sled12.qcow12 createdThe volume names shown will be used later to install the guest with virt-install.
10.7.4.4 Creating the VM Guest #
Let's create a openSUSE Leap VM Guest with the
virt-install command. The VM
pool will be specified with the --disk option,
cache=none is recommended if you do not want to use
the --unsafe option while doing the migration.
root # virt-install --connect qemu:///system --virt-type kvm --name \
sled12 --memory 1024 --disk vol=VM/sled12.qcow2,cache=none --cdrom \
/mnt/install/ISO/SLE-12-Desktop-DVD-x86_64-Build0327-Media1.iso --graphics \
vnc --os-variant sled12
Starting install...
Creating domain...10.7.4.5 Migrate the VM Guest #
Everything is ready to do the migration now. Run the
migrate command on the VM Host Server that is currently
hosting the VM Guest, and choose the destination.
virsh # migrate --live sled12 --verbose qemu+ssh://IP/Hostname/system Password: Migration: [ 12 %]
10.8 Monitoring #
10.8.1 Monitoring with Virtual Machine Manager #
After starting Virtual Machine Manager and connecting to the VM Host Server, a CPU usage graph of all the running guests is displayed.
It is also possible to get information about disk and network usage with this tool, however, you must first activate this in :
Run
virt-manager.Select › .
Change the tab from to .
Activate the check boxes for the kind of activity you want to see: , , and .
If desired, also change the update interval using .
Close the dialog.
Activate the graphs that should be displayed under › .
Afterward, the disk and network statistics are also displayed in the main window of the Virtual Machine Manager.
More precise data is available from the VNC window. Open a VNC window as described in Section 10.2.1, “Opening a Graphical Console”. Choose from the toolbar or the menu. The statistics are displayed from the entry of the left-hand tree menu.
10.8.2 Monitoring with virt-top #
virt-top is a command line tool similar to the
well-known process monitoring tool
top. virt-top uses libvirt and
therefore is capable of showing statistics for VM Guests running on
different hypervisors. It is recommended to use
virt-top instead of hypervisor-specific tools like
xentop.
By default virt-top shows statistics for all running
VM Guests. Among the data that is displayed is the percentage of memory
used (%MEM) and CPU (%CPU) and the
uptime of the guest (TIME). The data is updated
regularly (every three seconds by default). The following shows the output
on a VM Host Server with seven VM Guests, four of them inactive:
virt-top 13:40:19 - x86_64 8/8CPU 1283MHz 16067MB 7.6% 0.5%
7 domains, 3 active, 3 running, 0 sleeping, 0 paused, 4 inactive D:0 O:0 X:0
CPU: 6.1% Mem: 3072 MB (3072 MB by guests)
ID S RDRQ WRRQ RXBY TXBY %CPU %MEM TIME NAME
7 R 123 1 18K 196 5.8 6.0 0:24.35 sled12_sp1
6 R 1 0 18K 0 0.2 6.0 0:42.51 sles12_sp1
5 R 0 0 18K 0 0.1 6.0 85:45.67 opensuse_leap
- (Ubuntu_1410)
- (debian_780)
- (fedora_21)
- (sles11sp3)By default the output is sorted by ID. Use the following key combinations to change the sort field:
| Shift–P: CPU usage |
| Shift–M: Total memory allocated by the guest |
| Shift–T: Time |
| Shift–I: ID |
To use any other field for sorting, press Shift–F and select a field from the list. To toggle the sort order, use Shift–R.
virt-top also supports different views on the
VM Guests data, which can be changed on-the-fly by pressing the following
keys:
| 0: default view |
| 1: show physical CPUs |
| 2: show network interfaces |
| 3: show virtual disks |
virt-top supports more hot keys to change the view of
the data and many command line switches that affect the behavior of
the program. For more information, see man 1 virt-top.
10.8.3 Monitoring with kvm_stat #
kvm_stat can be used to trace KVM performance
events. It monitors /sys/kernel/debug/kvm, so it
needs the debugfs to be mounted. On openSUSE Leap it should be
mounted by default. In case it is not mounted, use the following
command:
mount -t debugfs none /sys/kernel/debug
kvm_stat can be used in three different modes:
kvm_stat # update in 1 second intervals
kvm_stat -1 # 1 second snapshot
kvm_stat -l > kvmstats.log # update in 1 second intervals in log format
# can be imported to a spreadsheetExample 10.1: Typical Output of kvm_stat #
kvm statistics efer_reload 0 0 exits 11378946 218130 fpu_reload 62144 152 halt_exits 414866 100 halt_wakeup 260358 50 host_state_reload 539650 249 hypercalls 0 0 insn_emulation 6227331 173067 insn_emulation_fail 0 0 invlpg 227281 47 io_exits 113148 18 irq_exits 168474 127 irq_injections 482804 123 irq_window 51270 18 largepages 0 0 mmio_exits 6925 0 mmu_cache_miss 71820 19 mmu_flooded 35420 9 mmu_pde_zapped 64763 20 mmu_pte_updated 0 0 mmu_pte_write 213782 29 mmu_recycled 0 0 mmu_shadow_zapped 128690 17 mmu_unsync 46 -1 nmi_injections 0 0 nmi_window 0 0 pf_fixed 1553821 857 pf_guest 1018832 562 remote_tlb_flush 174007 37 request_irq 0 0 signal_exits 0 0 tlb_flush 394182 148
See http://clalance.blogspot.com/2009/01/kvm-performance-tools.html for further information on how to interpret these values.
11 Connecting and Authorizing #
Managing several VM Host Servers, each hosting multiple VM Guests, quickly
becomes difficult. One benefit of libvirt is the ability to connect to
several VM Host Servers at once, providing a single interface to manage all
VM Guests and to connect to their graphical console.
To ensure only authorized users can connect, libvirt offers
several connection types (via TLS, SSH, Unix sockets, and TCP) that can be
combined with different authorization mechanisms (socket, PolKit, SASL
and Kerberos).
11.1 Authentication #
The power to manage VM Guests and to access their graphical console is something that should be restricted to a well defined circle of persons. To achieve this goal, you can use the following authentication techniques on the VM Host Server:
Access control for Unix sockets with permissions and group ownership. This method is available for
libvirtdconnections only.Access control for Unix sockets with PolKit. This method is available for local
libvirtdconnections only.User name and password authentication with SASL (Simple Authentication and Security Layer). This method is available for both,
libvirtdand VNC connections. Using SASL does not require real user accounts on the server, since it uses its own database to store user names and passwords. Connections authenticated with SASL are encrypted.Kerberos authentication. This method, available for
libvirtdconnections only, is not covered in this manual. Refer to http://libvirt.org/auth.html#ACL_server_kerberos for details.Single password authentication. This method is available for VNC connections only.
Important: Authentication for libvirtd and VNC need to be configured separately
Access to the VM Guest's management functions (via libvirtd) on
the one hand, and to its graphical console on the other hand, always
needs to be configured separately. When restricting access to the
management tools, these restrictions do not
automatically apply to VNC connections!
When accessing VM Guests from remote via TLS/SSL connections, access can be indirectly controlled on each client by restricting read permissions to the certificate's key file to a certain group. See Section 11.3.2.5, “Restricting Access (Security Considerations)” for details.
11.1.1 libvirtd Authentication #
libvirtd authentication is configured in
/etc/libvirt/libvirtd.conf. The configuration made
here applies to all libvirt tools such as the Virtual Machine Manager or
virsh.
libvirt offers two sockets: a read-only socket for monitoring
purposes and a read-write socket to be used for management operations.
Access to both sockets can be configured independently. By default, both
sockets are owned by root.root. Default access
permissions on the read-write socket are restricted to the user
root (0700) and fully open on the read-only
socket (0777).
In the following instructions, you will learn how to configure access permissions for the read-write socket. The same instructions also apply to the read-only socket. All configuration steps need to be carried out on the VM Host Server.
Note: Default Authentication Settings on openSUSE Leap
The default authentication method on openSUSE Leap is access control
for Unix sockets. Only the user root may authenticate. When
accessing the libvirt tools as a non-root user directly on the
VM Host Server, you need to provide the root password through
PolKit once. You are then granted access for the current and for future
sessions.
Alternatively, you can configure libvirt to allow
“system” access to non-privileged users. See
Section 11.2.1, ““system” Access for Non-Privileged Users” for details.
Recommended Authorization Methods #
- Local Connections
Section 11.1.1.2, “Local Access Control for Unix Sockets with PolKit” Section 11.1.1.1, “Access Control for Unix Sockets with Permissions and Group Ownership” - Remote Tunnel over SSH
Section 11.1.1.1, “Access Control for Unix Sockets with Permissions and Group Ownership” - Remote TLS/SSL Connection
Section 11.1.1.3, “User name and Password Authentication with SASL” none (access controlled on the client side by restricting access to the certificates)
11.1.1.1 Access Control for Unix Sockets with Permissions and Group Ownership #
To grant access for non-root accounts, configure the
sockets to be owned and accessible by a certain group
(libvirt in the following
example). This authentication method can be used for local and remote
SSH connections.
In case it does not exist, create the group that should own the socket:
groupadd libvirt

Important: Group Needs to Exist
The group must exist prior to restarting
libvirtd. If not, the restart will fail.Add the desired users to the group:
usermod --append --groups libvirt tux
Change the configuration in
/etc/libvirt/libvirtd.confas follows:unix_sock_group = "libvirt"1 unix_sock_rw_perms = "0770"2 auth_unix_rw = "none"3
Restart
libvirtd:systemctl start libvirtd
11.1.1.2 Local Access Control for Unix Sockets with PolKit #
Access control for Unix sockets with PolKit is the default
authentication method on openSUSE Leap for non-remote connections.
Therefore, no libvirt configuration changes are needed. With
PolKit authorization enabled, permissions on both sockets default to
0777 and each application trying to access a socket
needs to authenticate via PolKit.
Important: PolKit Authentication for Local Connections Only
Authentication with PolKit can only be used for local connections on the VM Host Server itself, since PolKit does not handle remote authentication.
Two policies for accessing libvirt's sockets exist:
org.libvirt.unix.monitor: accessing the read-only socket
org.libvirt.unix.manage: accessing the read-write socket
By default, the policy for accessing the read-write socket is to
authenticate with the root password once and grant the
privilege for the current and for future sessions.
To grant users access to a socket without having to provide
the root password, you need to create a rule in
/etc/polkit-1/rules.d. Create the file
/etc/polkit-1/rules.d/10-grant-libvirt with the
following content to grant access to the read-write socket to all
members of the group
libvirt:
polkit.addRule(function(action, subject) {
if (action.id == "org.libvirt.unix.manage" && subject.isInGroup("libvirt")) {
return polkit.Result.YES;
}
});11.1.1.3 User name and Password Authentication with SASL #
SASL provides user name and password authentication and data encryption (digest-md5, by default). Since SASL maintains its own user database, the users do not need to exist on the VM Host Server. SASL is required by TCP connections and on top of TLS/SSL connections.
Important: Plain TCP and SASL with digest-md5 Encryption
Using digest-md5 encryption on an otherwise not encrypted TCP connection does not provide enough security for production environments. It is recommended to only use it in testing environments.
Tip: SASL Authentication on Top of TLS/SSL
Access from remote TLS/SSL connections can be indirectly controlled on the client side by restricting access to the certificate's key file. However, this might prove error-prone when dealing with many clients. Using SASL with TLS adds security by additionally controlling access on the server side.
To configure SASL authentication, proceed as follows:
Change the configuration in
/etc/libvirt/libvirtd.confas follows:To enable SASL for TCP connections:
auth_tcp = "sasl"
To enable SASL for TLS/SSL connections:
auth_tls = "sasl"
Restart
libvirtd:systemctl restart libvirtd
The libvirt SASL configuration file is located at
/etc/sasl2/libvirtd.conf. Normally, there is no need to change the defaults. However, if using SASL on top of TLS, you may turn off session encryption to avoid additional overhead (TLS connections are already encrypted) by commenting the line setting themech_listparameter. Only do this for TSL/SASL, for TCP connections this parameter must be set to digest-md5.#mech_list: digest-md5
By default, no SASL users are configured, so no logins are possible. Use the following commands to manage users:
- Add the user
tux saslpasswd2 -a libvirt tux
- Delete the user
tux saslpasswd2 -a libvirt -d tux
- List existing users
sasldblistusers2 -f /etc/libvirt/passwd.db
- Add the user
Tip: virsh and SASL Authentication
When using SASL authentication, you will be prompted for a user name
and password every time you issue a virsh command.
Avoid this by using virsh in shell mode.
11.1.2 VNC Authentication #
Since access to the graphical console of a VM Guest is not
controlled by libvirt, but rather by the specific hypervisor, it is
always necessary to additionally configure VNC authentication. The main
configuration file is
/etc/libvirt/<hypervisor>.conf. This
section describes the QEMU/KVM hypervisor, so the target
configuration file is /etc/libvirt/qemu.conf.
Note: VNC Authentication for Xen
In contrast to KVM and LXC, Xen does not yet offer more
sophisticated VNC authentication than setting a password on a per VM
basis. See the <graphics type='vnc'...
libvirt configuration option below.
Two authentication types are available: SASL and single password
authentication. If you are using SASL for libvirt authentication,
it is strongly recommended to use it for VNC authentication as
well—it is possible to share the same database.
A third method to restrict access to the VM Guest is to enable the use of TLS encryption on the VNC server. This requires the VNC clients to have access to x509 client certificates. By restricting access to these certificates, access can indirectly be controlled on the client side. Refer to Section 11.3.2.4.2, “VNC over TLS/SSL: Client Configuration” for details.
11.1.2.1 User name and Password Authentication with SASL #
SASL provides user name and password authentication and data
encryption. Since SASL maintains its own user database, the users do
not need to exist on the VM Host Server. As with SASL authentication for
libvirt, you may use SASL on top of TLS/SSL connections. Refer to
Section 11.3.2.4.2, “VNC over TLS/SSL: Client Configuration” for details
on configuring these connections.
To configure SASL authentication for VNC, proceed as follows:
Create a SASL configuration file. It is recommended to use the existing
libvirtfile. If you have already configured SASL forlibvirtand are planning to use the same settings including the same user name and password database, a simple link is suitable:ln -s /etc/sasl2/libvirt.conf /etc/sasl2/qemu.conf
If are setting up SASL for VNC only or you are planning to use a different configuration than for
libvirt, copy the existing file to use as a template:cp /etc/sasl2/libvirt.conf /etc/sasl2/qemu.conf
Then edit it according to your needs.
Change the configuration in
/etc/libvirt/qemu.confas follows:vnc_listen = "0.0.0.0" vnc_sasl = 1 sasldb_path: /etc/libvirt/qemu_passwd.db
The first parameter enables VNC to listen on all public interfaces (rather than to the local host only), and the second parameter enables SASL authentication.
By default, no SASL users are configured, so no logins are possible. Use the following commands to manage users:
- Add the user
tux saslpasswd2 -f /etc/libvirt/qemu_passwd.db -a qemu tux
- Delete the user
tux saslpasswd2 -f /etc/libvirt/qemu_passwd.db -a qemu -d tux
- List existing users
sasldblistusers2 -f /etc/libvirt/qemu_passwd.db
- Add the user
Restart
libvirtd:systemctl restart libvirtd
Restart all VM Guests that have been running prior to changing the configuration. VM Guests that have not been restarted will not use SASL authentication for VNC connects.
Note: Supported VNC Viewers
SASL authentication is currently supported by Virtual Machine Manager and
virt-viewer.
Both of these viewers also support TLS/SSL connections.
11.1.2.2 Single Password Authentication #
Access to the VNC server may also be controlled by setting a VNC password. You can either set a global password for all VM Guests or set individual passwords for each guest. The latter requires to edit the VM Guest's configuration files.
Note: Always Set a Global Password
If you are using single password authentication, it is good practice to set a global password even if setting passwords for each VM Guest. This will always leave your virtual machines protected with a “fallback” password if you forget to set a per-machine password. The global password will only be used if no other password is set for the machine.
Procedure 11.1: Setting a Global VNC Password #
Change the configuration in
/etc/libvirt/qemu.confas follows:vnc_listen = "0.0.0.0" vnc_password = "PASSWORD"
The first parameter enables VNC to listen on all public interfaces (rather than to the local host only), and the second parameter sets the password. The maximum length of the password is eight characters.
Restart
libvirtd:root #systemctl restart libvirtdRestart all VM Guests that have been running prior to changing the configuration. VM Guests that have not been restarted will not use password authentication for VNC connects.
Procedure 11.2: Setting a VM Guest Specific VNC Password #
Change the configuration in
/etc/libvirt/qemu.confas follows to enable VNC to listen on all public interfaces (rather than to the local host only).vnc_listen = "0.0.0.0"
Open the VM Guest's XML configuration file in an editor. Replace VM NAME in the following example with the name of the VM Guest. The editor that is used defaults to
$EDITOR. If that variable is not set,viis used.virsh edit VM NAME
Search for the element
<graphics>with the attributetype='vnc', for example:<graphics type='vnc' port='-1' autoport='yes'/>
Add the
passwd=PASSWORDattribute, save the file and exit the editor. The maximum length of the password is eight characters.<graphics type='vnc' port='-1' autoport='yes' passwd='PASSWORD'/>
Restart
libvirtd:root #systemctl restart libvirtdRestart all VM Guests that have been running prior to changing the configuration. VM Guests that have not been restarted will not use password authentication for VNC connects.
Warning: Security of the VNC Protocol
The VNC protocol is not considered to be safe. Although the password
is sent encrypted, it might be vulnerable when an attacker can
sniff both the encrypted password and the encryption key. Therefore,
it is recommended to use VNC with TLS/SSL or tunneled over SSH.
virt-viewer, Virtual Machine Manager and
vinagre from version 2.30 onward support both
methods.
11.2 Connecting to a VM Host Server #
To connect to a hypervisor with libvirt, you need to
specify a uniform resource identifier (URI). This URI is needed with
virsh and virt-viewer (except when
working as root on the VM Host Server) and is optional for the
Virtual Machine Manager. Although the latter can be called with a connection parameter
(for example, virt-manager -c qemu:///system), it also
offers a graphical interface to create connection URIs. See
Section 11.2.2, “Managing Connections with Virtual Machine Manager” for details.
HYPERVISOR1+PROTOCOL2://USER@REMOTE3/CONNECTION_TYPE4
Specify the hypervisor. openSUSE Leap currently supports the
following hypervisors: | |
When connecting to a remote host, specify the protocol here. It can be
one of: | |
When connecting to a remote host, specify the user name and the remote host
name. If no user name is specified, the user name that has called the
command ( | |
When connecting to the |
Example Hypervisor Connection URIs #
test:///defaultConnect to the local dummy hypervisor. Useful for testing.
qemu:///systemorxen:///systemConnect to the QEMU/Xen hypervisor on the local host having full access (type system).
qemu+ssh://tux@mercury.example.com/systemorxen+ssh://tux@mercury.example.com/systemConnect to the QEMU/Xen hypervisor on the remote host mercury.example.com. The connection is established via an SSH tunnel.
qemu+tls://saturn.example.com/systemorxen+tls://saturn.example.com/systemConnect to the QEMU/Xen hypervisor on the remote host mercury.example.com. The connection is established using TLS/SSL.
For more details and examples, refer to the libvirt documentation at
http://libvirt.org/uri.html.
Note: User Names in URIs
A user name needs to be specified when using Unix socket authentication (regardless of whether using the user/password authentication scheme or PolKit). This applies to all SSH and local connections.
There is no need to specify a user name when using SASL authentication (for TCP or TLS connections) or when doing no additional server-side authentication for TLS connections. With SASL the user name will not be evaluated—you will be prompted for an SASL user/password combination in any case.
11.2.1 “system” Access for Non-Privileged Users #
As mentioned above, a connection to the QEMU hypervisor can be
established using two different protocols: session
and system. A “session” connection is
spawned with the same privileges as the client program. Such a
connection is intended for desktop virtualization, since it is
restricted (for example no USB/PCI device assignments, no virtual
network setup, limited remote access to libvirtd).
The “system” connection intended for server virtualization
has no functional restrictions but is, by default, only accessible by
root. However, with the addition of the DAC (Discretionary
Access Control) driver to libvirt it is now possible to grant
non-privileged users “system” access. To grant
“system” access to the user tux, proceed as
follows:
Procedure 11.3: Granting “system” Access to a Regular User #
Enable access via Unix sockets as described in Section 11.1.1.1, “Access Control for Unix Sockets with Permissions and Group Ownership”. In that example access to libvirt is granted to all members of the group
libvirtandtuxmade a member of this group. This ensures thattuxcan connect usingvirshor Virtual Machine Manager.Edit
/etc/libvirt/qemu.confand change the configuration as follows:user = "tux" group = "libvirt" dynamic_ownership = 1
This ensures that the VM Guests are started by
tuxand that resources bound to the guest (for example virtual disks) can be accessed and modified bytux.Make
tuxa member of the groupkvm:usermod --append --groups kvm tux
This step is needed to grant access to
/dev/kvm, which is required to start VM Guests.Restart
libvirtd:root #systemctl restart libvirtd
11.2.2 Managing Connections with Virtual Machine Manager #
The Virtual Machine Manager uses a Connection for every VM Host Server
it manages. Each connection contains all VM Guests on the respective
host. By default, a connection to the local host is already configured
and connected.
All configured connections are displayed in the Virtual Machine Manager main window. Active connections are marked with a small triangle, which you can click to fold or unfold the list of VM Guests for this connection.
Inactive connections are listed gray and are marked with Not
Connected. Either double-click or right-click it and choose
from the context menu. You can also
an existing connection from this menu.
Note: Editing Existing Connections
It is not possible to edit an existing connection. To change a connection, create a new one with the desired parameters and delete the “old” one.
To add a new connection in the Virtual Machine Manager, proceed as follows:
Choose ›
Choose the host's ( or )
(Optional) To set up a remote connection, choose . For more information, see Section 11.3, “Configuring Remote Connections”.
In case of a remote connection, specify the of the remote machine in the format
USERNAME@REMOTE _HOST.
Important: Specifying a User Name
There is no need to specify a user name for TCP and TLS connections: In these cases, it will not be evaluated. However, in the case of SSH connections, specifying a user name is necessary when you want to connect as a user other than
root.If you do not want the connection to be automatically started when starting the Virtual Machine Manager, deactivate .
Finish the configuration by clicking .
11.3 Configuring Remote Connections #
A major benefit of libvirt is the ability to manage VM Guests on
different remote hosts from a central location. This section gives
detailed instructions on how to configure server and client to allow
remote connections.
11.3.1 Remote Tunnel over SSH (qemu+ssh or xen+ssh) #
Enabling a remote connection that is tunneled over SSH on the
VM Host Server only requires the ability to accept SSH connections. Make
sure the SSH daemon is started (systemctl status
sshd) and that the ports for service
SSH are opened in the firewall.
User authentication for SSH connections can be done using traditional
file user/group ownership and permissions as described in
Section 11.1.1.1, “Access Control for Unix Sockets with Permissions and Group Ownership”.
Connecting as user tux
(qemu+ssh://tuxsIVname;/system or
xen+ssh://tuxsIVname;/system) works out
of the box and does not require additional configuration on the
libvirt side.
When connecting via SSH
qemu+ssh://USER@SYSTEM
or
xen+ssh://USER@SYSTEM
you need to provide the password for USER.
This can be avoided by copying your public key to
~USER/.ssh/authorized_keys
on the VM Host Server as explained in
Book “Security Guide”, Chapter 14 “SSH: Secure Network Operations”, Section 14.5.2 “Copying an SSH Key”. Using an ssh-agent on the
machine from which you are connecting adds even more
convenience. For more information, see
Book “Security Guide”, Chapter 14 “SSH: Secure Network Operations”, Section 14.5.3 “Using the ssh-agent”.
11.3.2 Remote TLS/SSL Connection with x509 Certificate (qemu+tls or xen+tls) #
Using TCP connections with TLS/SSL encryption and authentication via x509 certificates is much more complicated to set up than SSH, but it is a lot more scalable. Use this method if you need to manage several VM Host Servers with a varying number of administrators.
11.3.2.1 Basic Concept #
TLS (Transport Layer Security) encrypts the communication between two computers by using certificates. The computer starting the connection is always considered the “client”, using a “client certificate”, while the receiving computer is always considered the “server”, using a “server certificate”. This scenario applies, for example, if you manage your VM Host Servers from a central desktop.
If connections are initiated from both computers, each needs to have a client and a server certificate. This is the case, for example, if you migrate a VM Guest from one host to another.
Each x509 certificate has a matching private key file. Only the combination of certificate and private key file can identify itself correctly. To assure that a certificate was issued by the assumed owner, it is signed and issued by a central certificate called certificate authority (CA). Both the client and the server certificates must be issued by the same CA.
Important: User Authentication
Using a remote TLS/SSL connection only ensures that two computers are allowed to communicate in a certain direction. Restricting access to certain users can indirectly be achieved on the client side by restricting access to the certificates. For more information, see Section 11.3.2.5, “Restricting Access (Security Considerations)”.
libvirt also supports user authentication on the server with
SASL. For more information, see
Section 11.3.2.6, “Central User Authentication with SASL for TLS Sockets”.
11.3.2.2 Configuring the VM Host Server #
The VM Host Server is the machine receiving connections. Therefore, the
server certificates need to be installed. The CA
certificate needs to be installed, too. When the certificates are
in place, TLS support can be turned on for libvirt.
Create the server certificate and export it together with the CA certificate as described in Section B.1, “Generating x509 Client/Server Certificates”.
Create the following directories on the VM Host Server:
mkdir -p /etc/pki/CA/ /etc/pki/libvirt/private/
Install the certificates as follows:
/etc/pki/CA/cacert.pem /etc/pki/libvirt/servercert.pem /etc/pki/libvirt/private/serverkey.pem

Important: Restrict Access to Certificates
Make sure to restrict access to certificates as explained in Section 11.3.2.5, “Restricting Access (Security Considerations)”.
Enable TLS support by editing
/etc/libvirt/libvirtd.confand settinglisten_tls = 1. Restartlibvirtd:root #systemctl restart libvirtdBy default,
libvirtuses the TCP port 16514 for accepting secure TLS connections. Open this port in the firewall.
Important: Restarting libvirtd with TLS enabled
If you enable TLS for libvirt, the server certificates need to be
in place, otherwise restarting libvirtd will fail. You also need
to restart libvirtd in case you change the certificates.
11.3.2.3 Configuring the Client and Testing the Setup #
The client is the machine initiating connections. Therefore the client certificates need to be installed. The CA certificate needs to be installed, too.
Create the client certificate and export it together with the CA certificate as described in Section B.1, “Generating x509 Client/Server Certificates”.
Create the following directories on the client:
mkdir -p /etc/pki/CA/ /etc/pki/libvirt/private/
Install the certificates as follows:
/etc/pki/CA/cacert.pem /etc/pki/libvirt/clientcert.pem /etc/pki/libvirt/private/clientkey.pem

Important: Restrict Access to Certificates
Make sure to restrict access to certificates as explained in Section 11.3.2.5, “Restricting Access (Security Considerations)”.
Test the client/server setup by issuing the following command. Replace mercury.example.com with the name of your VM Host Server. Specify the same fully qualified host name as used when creating the server certificate.
#QEMU/KVM virsh -c qemu+tls://mercury.example.com/system list --all #Xen virsh -c xen+tls://mercury.example.com/system list --all
If your setup is correct, you will see a list of all VM Guests registered with
libvirton the VM Host Server.
11.3.2.4 Enabling VNC for TLS/SSL connections #
Currently, VNC communication over TLS is only supported by a few tools.
Common VNC viewers such as tightvnc or
tigervnc do not support TLS/SSL. The only supported
alternative to Virtual Machine Manager and virt-viewer is
vinagre.
11.3.2.4.1 VNC over TLS/SSL: VM Host Server Configuration #
To access the graphical console via VNC over TLS/SSL, you need to configure the VM Host Server as follows:
Open ports for the service
VNCin your firewall.Create a directory
/etc/pki/libvirt-vncand link the certificates into this directory as follows:mkdir -p /etc/pki/libvirt-vnc && cd /etc/pki/libvirt-vnc ln -s /etc/pki/CA/cacert.pem ca-cert.pem ln -s /etc/pki/libvirt/servercert.pem server-cert.pem ln -s /etc/pki/libvirt/private/serverkey.pem server-key.pemEdit
/etc/libvirt/qemu.confand set the following parameters:vnc_listen = "0.0.0.0" vnc_tls = 1 vnc_tls_x509_verify = 1Restart the
libvirtd:root #systemctl restart libvirtd
Important: VM Guests Need to be Restarted
The VNC TLS setting is only set when starting a VM Guest. Therefore, you need to restart all machines that have been running prior to making the configuration change.
11.3.2.4.2 VNC over TLS/SSL: Client Configuration #
The only action needed on the client side is to place the x509 client
certificates in a location recognized by the client of choice.
Unfortunately, each supported client—Virtual Machine Manager,
virt-viewer, and
vinagre—expects the certificates in a
different location. However, Virtual Machine Manager and vinagre
can either read from a system-wide location applying to all users, or
from a per-user location.
-
Virtual Machine Manager (
virt-manager) To connect to the remote host, Virtual Machine Manager requires the setup explained in Section 11.3.2.3, “Configuring the Client and Testing the Setup”. To be able to connect via VNC, the client certificates also need to be placed in the following locations:
- System-wide location
/etc/pki/CA/cacert.pem/etc/pki/libvirt-vnc/clientcert.pem/etc/pki/libvirt-vnc/private/clientkey.pem- Per-user location
/etc/pki/CA/cacert.pem~/.pki/libvirt-vnc/clientcert.pem~/.pki/libvirt-vnc/private/clientkey.pem
virt-viewervirt-vieweronly accepts certificates from a system-wide location:/etc/pki/CA/cacert.pem/etc/pki/libvirt-vnc/clientcert.pem/etc/pki/libvirt-vnc/private/clientkey.pem
Important: Restrict Access to Certificates
Make sure to restrict access to certificates as explained in Section 11.3.2.5, “Restricting Access (Security Considerations)”.
11.3.2.5 Restricting Access (Security Considerations) #
Each x509 certificate consists of two pieces: the public certificate and a private key. A client can only authenticate using both pieces. Therefore, any user that has read access to the client certificate and its private key can access your VM Host Server. On the other hand, an arbitrary machine equipped with the full server certificate can pretend to be the VM Host Server. Since this is probably not desirable, access to at least the private key files needs to be restricted as much as possible. The easiest way to control access to a key file is to use access permissions.
- Server Certificates
Server certificates need to be readable for QEMU processes. On openSUSE Leap QEMU, processes started from
libvirttools are owned byroot, so it is sufficient if therootcan read the certificates:chmod 700 /etc/pki/libvirt/private/ chmod 600 /etc/pki/libvirt/private/serverkey.pem
If you change the ownership for QEMU processes in
/etc/libvirt/qemu.conf, you also need to adjust the ownership of the key file.- System Wide Client Certificates
To control access to a key file that is available system-wide, restrict read access to a certain group, so that only members of that group can read the key file. In the following example, a group
libvirtis created, and group ownership of theclientkey.pemfile and its parent directory is set tolibvirt. Afterward, the access permissions are restricted to owner and group. Finally the usertuxis added to the grouplibvirt, and thus can access the key file.CERTPATH="/etc/pki/libvirt/" # create group libvirt groupadd libvirt # change ownership to user root and group libvirt chown root.libvirt $CERTPATH/private $CERTPATH/clientkey.pem # restrict permissions chmod 750 $CERTPATH/private chmod 640 $CERTPATH/private/clientkey.pem # add user tux to group libvirt usermod --append --groups libvirt tux
- Per-User Certificates
User-specific client certificates for accessing the graphical console of a VM Guest via VNC need to be placed in the user's home directory in
~/.pki. Contrary to SSH, for example, the VNC viewer using these certificates do not check the access permissions of the private key file. Therefore, it is solely the user's responsibility to make sure the key file is not readable by others.
11.3.2.5.1 Restricting Access from the Server Side #
By default, every client that is equipped with appropriate client certificates may connect to a VM Host Server accepting TLS connections. Therefore, it is possible to use additional server-side authentication with SASL as described in Section 11.1.1.3, “User name and Password Authentication with SASL”.
It is also possible to restrict access with a whitelist of DNs (distinguished names), so only clients with a certificate matching a DN from the list can connect.
Add a list of allowed DNs to tls_allowed_dn_list in
/etc/libvirt/libvirtd.conf. This list may contain
wild cards. Do not specify an empty list, since that would result in
refusing all connections.
tls_allowed_dn_list = [ "C=US,L=Provo,O=SUSE Linux Products GmbH,OU=*,CN=venus.example.com,EMAIL=*", "C=DE,L=Nuremberg,O=SUSE Linux Products GmbH,OU=Documentation,CN=*"]
Get the distinguished name of a certificate with the following command:
certtool -i --infile /etc/pki/libvirt/clientcert.pem | grep "Subject:"
Restart libvirtd after having changed the configuration:
root # systemctl restart libvirtd11.3.2.6 Central User Authentication with SASL for TLS Sockets #
A direct user authentication via TLS is not possible—this is
handled indirectly on each client via the read permissions for the
certificates as explained in
Section 11.3.2.5, “Restricting Access (Security Considerations)”. However, if
a central, server-based user authentication is needed, libvirt
also allows to use SASL (Simple Authentication and Security Layer) on
top of TLS for direct user authentication. See
Section 11.1.1.3, “User name and Password Authentication with SASL” for
configuration details.
11.3.2.7 Troubleshooting #
11.3.2.7.1 Virtual Machine Manager/virsh Cannot Connect to Server #
Check the following in the given order:
| Is it a firewall issue (TCP port 16514 needs to be open on the server)? |
Is the client certificate (certificate and key) readable by the
user that has started
Virtual Machine Manager/virsh?
|
| Has the same full qualified host name as in the server certificate been specified with the connection? |
Is TLS enabled on the server (listen_tls =
1)? |
Has libvirtd been
restarted on the server? |
11.3.2.7.2 VNC Connection fails #
Ensure that you can connect to the remote server using Virtual Machine Manager. If so, check whether the virtual machine on the server has been started with TLS support. The virtual machine's name in the following example is “sles”.
ps ax | grep qemu | grep "\-name sles" | awk -F" -vnc " '{ print FS $2 }'If the output does not begin with a string similar to the following, the machine has not been started with TLS support and must be restarted.
-vnc 0.0.0.0:0,tls,x509verify=/etc/pki/libvirt
12 Managing Storage #
When managing a VM Guest on the VM Host Server itself, you can
access the complete file system of the VM Host Server to attach or
create virtual hard disks or to attach existing images to the
VM Guest. However, this is not possible when managing VM Guests
from a remote host. For this reason, libvirt supports so called
“Storage Pools”, which can be accessed from remote machines.
Tip: CD/DVD ISO images
To be able to access CD/DVD ISO images on the VM Host Server from remote, they also need to be placed in a storage pool.
libvirt knows two different types of storage: volumes and pools.
- Storage Volume
A storage volume is a storage device that can be assigned to a guest—a virtual disk or a CD/DVD/floppy image. Physically (on the VM Host Server) it can be a block device (a partition, a logical volume, etc.) or a file.
- Storage Pool
A storage pool is a storage resource on the VM Host Server that can be used for storing volumes, similar to network storage for a desktop machine. Physically it can be one of the following types:
- File System Directory ()
A directory for hosting image files. The files can be either one of the supported disk formats (raw, qcow2, or qed), or ISO images.
- Physical Disk Device ()
Use a complete physical disk as storage. A partition is created for each volume that is added to the pool.
- Pre-Formatted Block Device ()
Specify a partition to be used in the same way as a file system directory pool (a directory for hosting image files). The only difference to using a file system directory is that
libvirttakes care of mounting the device.- iSCSI Target (iscsi)
Set up a pool on an iSCSI target. You need to have been logged in to the volume once before, to use it with
libvirt(use the YaST to detect and log in to a volume). Volume creation on iSCSI pools is not supported, instead each existing Logical Unit Number (LUN) represents a volume. Each volume/LUN also needs a valid (empty) partition table or disk label before you can use it. If missing, usefdiskto add it:~ # fdisk -cu /dev/disk/by-path/ip-192.168.2.100:3260-iscsi-iqn.2010-10.com.example:[...]-lun-2 Device contains neither a valid DOS partition table, nor Sun, SGI or OSF disklabel Building a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0xc15cdc4e. Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them. After that, of course, the previous content won't be recoverable. Warning: invalid flag 0x0000 of partition table 4 will be corrected by w(rite) Command (m for help): w The partition table has been altered! Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table. Syncing disks.
- LVM Volume Group (logical)
Use an LVM volume group as a pool. You may either use a predefined volume group, or create a group by specifying the devices to use. Storage volumes are created as partitions on the volume.

Warning: Deleting the LVM-Based Pool
When the LVM-based pool is deleted in the Storage Manager, the volume group is deleted as well. This results in a non-recoverable loss of all data stored on the pool!
- Multipath Devices ()
At the moment, multipathing support is limited to assigning existing devices to the guests. Volume creation or configuring multipathing from within
libvirtis not supported.- Network Exported Directory ()
Specify a network directory to be used in the same way as a file system directory pool (a directory for hosting image files). The only difference to using a file system directory is that
libvirttakes care of mounting the directory. Supported protocols are NFS and GlusterFS.- SCSI Host Adapter ()
Use an SCSI host adapter in almost the same way as an iSCSI target. It is recommended to use a device name from
/dev/disk/by-*rather than/dev/sdX, since the latter can change (for example, when adding or removing hard disks). Volume creation on iSCSI pools is not supported; instead, each existing LUN (Logical Unit Number) represents a volume.
Warning: Security Considerations
To avoid data loss or data corruption, do not attempt to use
resources such as LVM volume groups, iSCSI targets, etc., that are also used
to build storage pools on the VM Host Server. There is no need to
connect to these resources from the VM Host Server or to mount them on the
VM Host Server—libvirt takes care of this.
Do not mount partitions on the VM Host Server by label. Under certain circumstances it is possible that a partition is labeled from within a VM Guest with a name already existing on the VM Host Server.
12.1 Managing Storage with Virtual Machine Manager #
The Virtual Machine Manager provides a graphical interface—the Storage Manager—to manage storage volumes and pools. To access it, either right-click a connection and choose , or highlight a connection and choose › . Select the tab.
12.1.1 Adding a Storage Pool #
To add a storage pool, proceed as follows:
Click in the bottom left corner. The dialog appears.
Provide a for the pool (consisting of alphanumeric characters and
_-.) and select a . Proceed with .Specify the required details in the following window. The data that needs to be entered depends on the type of pool you are creating:
- Type
: Specify an existing directory.
- Type
: The directory that hosts the devices. The default value
/devshould usually fit.: Format of the device's partition table. Using should usually work. If not, get the required format by running the command
parted-lon the VM Host Server.: Path to the device. It is recommended to use a device name from
/dev/disk/by-*rather than the simple/dev/sdX, since the latter can change (for example, when adding or removing hard disks). You need to specify the path that resembles the whole disk, not a partition on the disk (if existing).: Activating this option formats the device. Use with care—all data on the device will be lost!
- Type
: Mount point on the VM Host Server file system.
File system format of the device. The default value
autoshould work.: Path to the device file. It is recommended to use a device name from
/dev/disk/by-*rather than/dev/sdX, because the latter can change (for example, when adding or removing hard disks).
- Type
Get the necessary data by running the following command on the VM Host Server:
iscsiadm --mode node
It will return a list of iSCSI volumes with the following format. The elements in bold text are required:
IP_ADDRESS:PORT,TPGT TARGET_NAME_(IQN)
: The directory containing the device file. Use
/dev/disk/by-path(default) or/dev/disk/by-id.: Host name or IP address of the iSCSI server.
: The iSCSI target name (IQN).
- Type
: In case you use an existing volume group, specify the existing device path. When building a new LVM volume group, specify a device name in the
/devdirectory that does not already exist.: Leave empty when using an existing volume group. When creating a new one, specify its devices here.
: Only activate when creating a new volume group.
- Type
: Support for multipathing is currently limited to making all multipath devices available. Therefore, specify an arbitrary string here that will then be ignored. The path is required, otherwise the XML parser will fail.
- Type
: Mount point on the VM Host Server file system.
: IP address or host name of the server exporting the network file system.
: Directory on the server that is being exported.
- Type
: The directory containing the device file. Use
/dev/disk/by-path(default) or/dev/disk/by-id.: Name of the SCSI adapter.

Note: File Browsing
Using the file browser by clicking is not possible when operating from remote.
Click to add the storage pool.
12.1.2 Managing Storage Pools #
Virtual Machine Manager's Storage Manager lets you create or delete volumes in a pool. You may also temporarily deactivate or permanently delete existing storage pools. Changing the basic configuration of a pool is currently not supported by SUSE.
12.1.2.1 Starting, Stopping and Deleting Pools #
The purpose of storage pools is to provide block devices located on the VM Host Server that can be added to a VM Guest when managing it from remote. To make a pool temporarily inaccessible from remote, click in the bottom left corner of the Storage Manager. Stopped pools are marked with and are grayed out in the list pane. By default, a newly created pool will be automatically started of the VM Host Server.
To start an inactive pool and make it available from remote again, click in the bottom left corner of the Storage Manager.
Note: A Pool's State Does not Affect Attached Volumes
Volumes from a pool attached to VM Guests are always available, regardless of the pool's state ( (stopped) or (started)). The state of the pool solely affects the ability to attach volumes to a VM Guest via remote management.
To permanently make a pool inaccessible, click in the bottom left corner of the Storage Manager. You may only delete inactive pools. Deleting a pool does not physically erase its contents on VM Host Server—it only deletes the pool configuration. However, you need to be extra careful when deleting pools, especially when deleting LVM volume group-based tools:
Warning: Deleting Storage Pools
Deleting storage pools based on local file system directories, local partitions or disks has no effect on the availability of volumes from these pools currently attached to VM Guests.
Volumes located in pools of type iSCSI, SCSI, LVM group or Network Exported Directory will become inaccessible from the VM Guest if the pool is deleted. Although the volumes themselves will not be deleted, the VM Host Server will no longer have access to the resources.
Volumes on iSCSI/SCSI targets or Network Exported Directory will become accessible again when creating an adequate new pool or when mounting/accessing these resources directly from the host system.
When deleting an LVM group-based storage pool, the LVM group definition will be erased and the LVM group will no longer exist on the host system. The configuration is not recoverable and all volumes from this pool are lost.
12.1.2.2 Adding Volumes to a Storage Pool #
Virtual Machine Manager lets you create volumes in all storage pools, except in pools
of types Multipath, iSCSI, or SCSI. A volume in these pools is
equivalent to a LUN and cannot be changed from within libvirt.
A new volume can either be created using the Storage Manager or while adding a new storage device to a VM Guest. In either case, select a storage pool from the left panel, then click .
Specify a for the image and choose an image format.
Note that SUSE currently only supports
raw,qcow2, orqedimages. The latter option is not available on LVM group-based pools.Next to , specify the amount maximum size that the disk image is allowed to reach. Unless you are working with a
qcow2image, you can also set an amount for that should be allocated initially. If both values differ, a sparse image file will be created which grows on demand.For
qcow2images, you can use a (also called “backing file”) which constitutes a base image. The newly createdqcow2image will then only record the changes that are made to the base image.Start the volume creation by clicking .
12.1.2.3 Deleting Volumes From a Storage Pool #
Deleting a volume can only be done from the Storage Manager, by selecting a volume and clicking . Confirm with .
Warning: Volumes Can Be Deleted Even While in Use
Volumes can be deleted even if they are currently used in an active or inactive VM Guest. There is no way to recover a deleted volume.
Whether a volume is used by a VM Guest is indicated in the column in the Storage Manager.
12.2 Managing Storage with virsh #
Managing storage from the command line is also possible by using
virsh. However, creating storage pools is currently
not supported by SUSE. Therefore, this section is restricted to
documenting functions like starting, stopping and deleting pools and volume
management.
A list of all virsh subcommands for managing pools and
volumes is available by running virsh help pool and
virsh help volume, respectively.
12.2.1 Listing Pools and Volumes #
List all pools currently active by executing the following command. To
also list inactive pools, add the option --all:
virsh pool-list --details
Details about a specific pool can be obtained with the
pool-info subcommand:
virsh pool-info POOL
Volumes can only be listed per pool by default. To list all volumes from a pool, enter the following command.
virsh vol-list --details POOL
At the moment virsh offers no tools to show whether a
volume is used by a guest or not. The following procedure describes a
way to list volumes from all pools that are currently used by a
VM Guest.
Procedure 12.1: Listing all Storage Volumes Currently Used on a VM Host Server #
Create an XSLT style sheet by saving the following content to a file, for example, ~/libvirt/guest_storage_list.xsl:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <xsl:stylesheet version="1.0" xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"> <xsl:output method="text"/> <xsl:template match="text()"/> <xsl:strip-space elements="*"/> <xsl:template match="disk"> <xsl:text> </xsl:text> <xsl:value-of select="(source/@file|source/@dev|source/@dir)[1]"/> <xsl:text> </xsl:text> </xsl:template> </xsl:stylesheet>Run the following commands in a shell. It is assumed that the guest's XML definitions are all stored in the default location (
/etc/libvirt/qemu).xsltprocis provided by the packagelibxslt.SSHEET="$HOME/libvirt/guest_storage_list.xsl" cd /etc/libvirt/qemu for FILE in *.xml; do basename $FILE .xml xsltproc $SSHEET $FILE done
12.2.2 Starting, Stopping and Deleting Pools #
Use the virsh pool subcommands to start, stop or
delete a pool. Replace POOL with the pool's
name or its UUID in the following examples:
- Stopping a Pool
virsh pool-destroy POOL

Note: A Pool's State Does not Affect Attached Volumes
Volumes from a pool attached to VM Guests are always available, regardless of the pool's state ( (stopped) or (started)). The state of the pool solely affects the ability to attach volumes to a VM Guest via remote management.
- Deleting a Pool
virsh pool-delete POOL
- Starting a Pool
virsh pool-start POOL
- Enable Autostarting a Pool
virsh pool-autostart POOL
Only pools that are marked to autostart will automatically be started if the VM Host Server reboots.
- Disable Autostarting a Pool
virsh pool-autostart POOL --disable
12.2.3 Adding Volumes to a Storage Pool #
virsh offers two ways to add volumes to storage pools:
either from an XML definition with vol-create and
vol-create-from or via command line arguments with
vol-create-as. The first two methods are currently not
supported by SUSE, therefore this section focuses on the subcommand
vol-create-as.
To add a volume to an existing pool, enter the following command:
virsh vol-create-as POOL1NAME2 12G --format3raw|qcow2|qed4 --allocation 4G5
Name of the pool to which the volume should be added | |
Name of the volume | |
Size of the image, in this example 12 gigabytes. Use the suffixes k, M, G, T for kilobyte, megabyte, gigabyte, and terabyte, respectively. | |
Format of the volume. SUSE currently supports
| |
Optional parameter. By default
When not specifying this parameter, a sparse image file with no
allocation will be generated. To create a non-sparse
volume, specify the whole image size with this parameter (would be
|
12.2.3.1 Cloning Existing Volumes #
Another way to add volumes to a pool is to clone an existing volume. The new instance is always created in the same pool as the original.
virsh vol-clone NAME_EXISTING_VOLUME1NAME_NEW_VOLUME2 --pool POOL3
12.2.4 Deleting Volumes from a Storage Pool #
To permanently delete a volume from a pool, use the subcommand
vol-delete:
virsh vol-delete NAME --pool POOL
--pool is optional. libvirt tries to locate the
volume automatically. If that fails, specify this parameter.
Warning: No Checks Upon Volume Deletion
A volume will be deleted in any case, regardless of whether it is currently used in an active or inactive VM Guest. There is no way to recover a deleted volume.
Whether a volume is used by a VM Guest can only be detected by using by the method described in Procedure 12.1, “Listing all Storage Volumes Currently Used on a VM Host Server”.
12.3 Locking Disk Files and Block Devices with virtlockd #
Locking block devices and disk files prevents concurrent writes to these resources from different VM Guests. It provides protection against starting the same VM Guest twice, or adding the same disk to two different virtual machines. This will reduce the risk of a virtual machine's disk image becoming corrupted because of a wrong configuration.
The locking is controlled by a daemon called virtlockd. Since it operates independently from
the libvirtd daemon, locks will endure a crash or a restart of
libvirtd. Locks will even persist in the case of an update of the
virtlockd itself, since it can
re-execute itself. This ensures that VM Guests do not
need to be restarted upon a virtlockd update.
Note: KVM Only
virtlockd integration is only
supported on a KVM VM Host Server.
12.3.1 Enable Locking #
Locking virtual disks is not enabled by default on openSUSE Leap. To enable and automatically start it upon rebooting, perform the following steps:
Edit
/etc/libvirt/qemu.confand setlock_manager = "lockd"
Start the
virtlockddaemon with the following command:systemctl start virtlockd
Restart the
libvirtddaemon with:systemctl restart libvirtd
Make sure
virtlockdis automatically started when booting the system:systemctl enable virtlockd
12.3.2 Configure Locking #
By default virtlockd is
configured to automatically lock all disks configured for your
VM Guests. The default setting uses a "direct" lockspace, where the
locks are acquired against the actual file paths associated with the VM
Guest <disk> devices. For example, flock(2)
will be called directly on
/var/lib/libvirt/images/my-server/disk0.raw when
the VM Guest contains the following <disk> device:
<disk type='file' device='disk'> <driver name='qemu' type='raw'/> <source file='/var/lib/libvirt/images/my-server/disk0.raw'/> <target dev='vda' bus='virtio'/> </disk>
The virtlockd configuration can
be changed by editing the file
/etc/libvirt/qemu-lockd.conf. It also contains
detailed comments with further information. Make sure to activate
configuration changes by reloading
virtlockd:
systemctl reload virtlockd
Note: Locking Currently Only Available for All Disks
Currently, locking can only be activated globally, so that all virtual disks are locked. Support for locking selected disks is planned for future releases.
12.3.2.2 Enable Locking on LVM or iSCSI Volumes #
When wanting to lock virtual disks placed on LVM or iSCSI volumes shared by several hosts, locking needs to be done by UUID rather than by path (which is used by default). Furthermore, the lockspace directory needs to be placed on a shared file system accessible by all hosts sharing the volume. Set the following options for LVM and/or iSCSI:
lvm_lockspace_dir = "/MY_LOCKSPACE_DIRECTORY" iscsi_lockspace_dir = "/MY_LOCKSPACE_DIRECTORY"
12.4 Online Resizing of Guest Block Devices #
Sometimes you need to change—extend or shrink—the size
of the block device used by your guest system. For example, when the disk
space originally allocated is no longer enough, it is time to increase
its size. If the guest disk resides on a logical
volume, you can resize it while the guest system is running.
This is a big advantage over an offline disk resizing (see the
virt-resize command from the
Section 17.3, “Guestfs Tools” package) as the service provided by
the guest is not interrupted by the resizing process. To resize a
VM Guest disk, follow these steps:
Procedure 12.2: Online Resizing of Guest Disk #
Inside the guest system, check the current size of the disk (for example
/dev/vda).root #fdisk -l /dev/vda Disk /dev/sda: 160.0 GB, 160041885696 bytes, 312581808 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytesOn the host, resize the logical volume holding the
/dev/vdadisk of the guest to the required size, for example 200 GB.root #lvresize -L 2048M /dev/mapper/vg00-home Extending logical volume home to 2.00 GiB Logical volume home successfully resizedOn the host, resize the block device related to the disk
/dev/mapper/vg00-homeof the guest. Note that you can find the domain_id withvirsh list.root #virsh blockresize --path /dev/vg00/home --size 2048M domain_id Block device '/dev/vg00/home' is resizedCheck that the new disk size is accepted by the guest.
root #fdisk -l /dev/vda Disk /dev/sda: 200.0 GB, 200052357120 bytes, 390727260 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
13 Managing Networks #
Abstract#
This chapter introduces common networking configurations supported by
libvirt. It does not depend on the hypervisor used. It is valid for all
hypervisors supported by libvirt, such as KVM or Xen. These setups
can be achieved using both the graphical interface of Virtual Machine Manager and the command
line tool virsh.
There are two common network setups to provide a VM Guest with a network connection:
A virtual network for the guest
A network bridge over a host's physical network interface that the guest can use
13.1 Virtual Networks #
A virtual network is a computer network which does not consist of a physical network link, but rather uses a virtual network link. Each host can have several virtual networks defined. Virtual networks are based on virtual devices that connect virtual machines inside a hypervisor. They allow outgoing traffic translated to the LAN and are provided with DHCP and DNS services. Virtual networks can be either isolated, or forwarded to a physical network.
Guests inside an isolated virtual network can communicate with each other, but cannot communicate with guests outside the virtual network. Also, guests not belonging to the isolated virtual network cannot communicate with guests inside.
On the other hand, guests inside a forwarded (NAT,
network address translation) virtual network can make any outgoing network
connection they request. Incoming connections are allowed from VM Host Server, and
from other guests connected to the same virtual network. All other incoming
connections are blocked by iptables rules.
A standard libvirt installation on openSUSE Leap already comes with a predefined virtual network providing DHCP server and network address translation (NAT) named "default".
13.1.1 Managing Virtual Networks with Virtual Machine Manager #
You can define, configure, and operate both isolated and forwarded virtual networks with Virtual Machine Manager.
13.1.1.1 Defining Virtual Networks #
Start Virtual Machine Manager. In the list of available connections, right-click the name of the connection for which you need to configure the virtual network, and then select .
In the window, click the tab. You can see the list of all virtual networks available for the current connection. On the right, there are details of the selected virtual network.
Figure 13.1: Connection Details #
To add a new virtual network, click .
Specify a name for the new virtual network and click .
Figure 13.2: Create virtual network #
To specify an IPv4 network address space definition, activate the relevant option and type it into the text entry.
Figure 13.3: Create virtual network #
libvirtcan provide your virtual network with a DHCP server. If you need it, activate , then type the start and end IP address range of assignable addresses.To enable static routing for the new virtual network, activate the relevant option and type the network and gateway addresses.
Click to proceed.
To specify IPv6-related options—network address space, DHCPv6 server, or static route—activate and activate the relevant options and fill in the relevant boxes.
Click to proceed.
Select whether you want isolated or forwarded virtual network.
Figure 13.4: Create virtual network #
For forwarded networks, specify the network interface to which the requests will be forwarded, and one of the forwarding modes: While (network address translation) remaps the virtual network address space and allows sharing a single IP address, connects the virtual switch to the physical host LAN with no network translation.
If you did not specify IPv6 network address space definition earlier, you can enable IPv6 internal routing between virtual machines.
(Optional) Optionally, change the DNS domain name.
Click to create the new virtual network. On the VM Host Server, a new virtual network bridge
virbrXis available, which corresponds to the newly created virtual network. You can check withbrctl show.libvirtautomatically adds iptables rules to allow traffic to/from guests attached to the new virbrX device.
13.1.1.2 Starting Virtual Networks #
To start a virtual network that is temporarily stopped, follow these steps:
Start Virtual Machine Manager. In the list of available connections, right-click the name of the connection for which you need to configure the virtual network, and then select .
In the window, click the tab. You can see the list of all virtual networks available for the current connection.
To start the virtual network, click .
13.1.1.3 Stopping Virtual Networks #
To stop an active virtual network, follow these steps:
Start Virtual Machine Manager. In the list of available connections, right-click the name of the connection for which you need to configure the virtual network, and then select .
In the window, click the tab. You can see the list of all virtual networks available for the current connection.
Select the virtual network to be stopped, then click .
13.1.1.4 Deleting Virtual Networks #
To delete a virtual network from VM Host Server, follow these steps:
Start Virtual Machine Manager. In the list of available connections, right-click the name of the connection for which you need to configure the virtual network, and then select .
In the window, click the tab. You can see the list of all virtual networks available for the current connection.
Select the virtual network to be deleted, then click .
13.1.1.5 Obtaining IP Addresses with nsswitch for NAT Networks (in KVM) #
On VM Host Server, install libvirt-nss, which provides NSS support for libvirt:
zypper in libvirt-nss
Add
libvirtto/etc/nsswitch.conf:... hosts: files libvirt mdns_minimal [NOTFOUND=return] dns ...
If NSCD is running, restart it:
systemctl restart nscd
Now you can reach the guest system by name from the host.
The NSS module has limited functionality. It reads
/var/lib/libvirt/dnsmasq/*.status files to find the
host name and corresponding IP addresses in a JSON record describing each
lease provided by dnsmasq. Host name translation can
only be done on those VM Host Servers using a libvirt-managed bridged network
backed by dnsmasq.
For more information, see http://wiki.libvirt.org/page/NSS_module.
13.1.2 Managing Virtual Networks with virsh #
You can manage libvirt-provided virtual networks with the
virsh command line tool. To view all network related
virsh commands, run
# virsh help network
Networking (help keyword 'network'):
net-autostart autostart a network
net-create create a network from an XML file
net-define define (but don't start) a network from an XML file
net-destroy destroy (stop) a network
net-dumpxml network information in XML
net-edit edit XML configuration for a network
net-event Network Events
net-info network information
net-list list networks
net-name convert a network UUID to network name
net-start start a (previously defined) inactive network
net-undefine undefine an inactive network
net-update update parts of an existing network's configuration
net-uuid convert a network name to network UUID
To view brief help information for a specific virsh
command, run virsh help
virsh_command:
# virsh help net-create
NAME
net-create - create a network from an XML file
SYNOPSIS
net-create <file>
DESCRIPTION
Create a network.
OPTIONS
[--file] <string> file containing an XML network description13.1.2.1 Creating a Network #
To create a new running virtual network, run
root # virsh net-create vnet_definition.xml
The vnet_definition.xml XML file includes the
definition of the virtual network that libvirt accepts.
To define a new virtual network without activating it, run
root # virsh net-define vnet_definition.xmlThe following examples illustrate definitions of different types of virtual networks.
Example 13.1: NAT Based Network #
The following configuration allows VM Guests outgoing connectivity if it is available on VM Host Server. In the absence of VM Host Server networking, it allows guests to talk directly to each other.
<network> <name>vnet_nated</name>1 <bridge name="virbr1" />2 <forward mode="nat"/>3 <ip address="192.168.122.1" netmask="255.255.255.0">4 <dhcp> <range start="192.168.122.2" end="192.168.122.254" />5 <host mac="52:54:00:c7:92:da" name="host1.testing.com" \ ip="192.168.1.23.101" />6 <host mac="52:54:00:c7:92:db" name="host2.testing.com" \ ip="192.168.1.23.102" /> <host mac="52:54:00:c7:92:dc" name="host3.testing.com" \ ip="192.168.1.23.103" /> </dhcp> </ip> </network>
The name of the new virtual network. | |
The name of the bridge device used to construct the virtual network.
When defining a new network with a <forward> mode of "nat" or
"route" (or an isolated network with no <forward> element),
| |
Inclusion of the <forward> element indicates that the virtual
network will be connected to the physical LAN. The
| |
The IP address and netmask for the network bridge. | |
Enable DHCP server for the virtual network, offering IP addresses
ranging from the specified | |
The optional <host> elements specify hosts which will be given names
and predefined IP addresses by the built-in DHCP server. Any IPv4 host
element must specify the MAC address of the host to be assigned a given
name, the IP to be assigned to that host, and the name to be given that
host by the DHCP server. An IPv6 host element differs slightly from
that for IPv4: there is no |
Example 13.2: Routed Network #
The following configuration routes traffic from the virtual network to the LAN without applying any NAT. The IP address range must be preconfigured in the routing tables of the router on the VM Host Server network.
<network>
<name>vnet_routed</name>
<bridge name="virbr1" />
<forward mode="route" dev="eth1"/>1
<ip address="192.168.122.1" netmask="255.255.255.0">
<dhcp>
<range start="192.168.122.2" end="192.168.122.254" />
</dhcp>
</ip>
</network>
The guest traffic may only go out via the |
Example 13.3: Isolated Network #
This configuration provides a completely isolated private network. The guests can talk to each other, and to VM Host Server, but cannot reach any other machines on the LAN, as the <forward> element is missing in the XML description.
<network> <name>vnet_isolated</name> <bridge name="virbr3" /> <ip address="192.168.152.1" netmask="255.255.255.0"> <dhcp> <range start="192.168.152.2" end="192.168.152.254" /> </dhcp> </ip> </network>
Example 13.4: Using an Existing Bridge on VM Host Server #
This configuration shows how to use an existing VM Host Server's network bridge
br0. VM Guests are directly connected to the physical
network. Their IP addresses will all be on the subnet of the physical
network, and there will be no restrictions on incoming or outgoing
connections.
<network>
<name>host-bridge</name>
<forward mode="bridge"/>
<bridge name="br0"/>
</network>13.1.2.2 Listing Networks #
To list all virtual networks available to libvirt, run:
root # virsh net-list --all
Name State Autostart Persistent
----------------------------------------------------------
crowbar active yes yes
vnet_nated active yes yes
vnet_routed active yes yes
vnet_isolated inactive yes yesTo list available domains, run:
root # virsh list
Id Name State
----------------------------------------------------
1 nated_sles12sp1 running
...
To get a list of interfaces of a running domain, run domifaddr
DOMAIN, or optionally specify the
interface to limit the output to this interface. By default, it
additionally outputs their IP and MAC addresses:
root # virsh domifaddr nated_sles12sp1 --interface vnet0 --source lease
Name MAC address Protocol Address
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
vnet0 52:54:00:9e:0d:2b ipv6 fd00:dead:beef:55::140/64
- - ipv4 192.168.100.168/24To print brief information of all virtual interfaces associated with the specified domain, run:
root # virsh domiflist nated_sles12sp1
Interface Type Source Model MAC
---------------------------------------------------------
vnet0 network vnet_nated virtio 52:54:00:9e:0d:2b13.1.2.3 Getting Details about a Network #
To get detailed information about a network, run:
root # virsh net-info vnet_routed
Name: vnet_routed
UUID: 756b48ff-d0c6-4c0a-804c-86c4c832a498
Active: yes
Persistent: yes
Autostart: yes
Bridge: virbr513.1.2.4 Starting a Network #
To start an inactive network that was already defined, find its name (or unique identifier, UUID) with:
root # virsh net-list --inactive
Name State Autostart Persistent
----------------------------------------------------------
vnet_isolated inactive yes yesThen run:
root # virsh net-start vnet_isolated
Network vnet_isolated started13.1.2.5 Stopping a Network #
To stop an active network, find its name (or unique identifier, UUID) with:
root # virsh net-list --inactive
Name State Autostart Persistent
----------------------------------------------------------
vnet_isolated active yes yesThen run:
root # virsh net-destroy vnet_isolated
Network vnet_isolated destroyed13.1.2.6 Removing a Network #
To remove the definition of an inactive network from VM Host Server permanently, run:
root # virsh net-undefine vnet_isolated
Network vnet_isolated has been undefined13.2 Bridged Networking #
A network bridge is used to connect two or more network segments. It behaves like a virtual network switch, and guest machines treat it transparently as a physical network interface. Any physical or virtual device can be connected to the bridge.
If there is a network bridge present on VM Host Server, you can connect a VM Guest to it directly. This provides the VM Guest with full incoming and outgoing network access.
13.2.1 Managing Network Bridges with YaST #
This section includes procedures to add or remove network bridges with YaST.
13.2.1.1 Adding a Network Bridge #
To add a network bridge on VM Host Server, follow these steps:
Start › › .
Activate the tab and click .
Select from the list and enter the bridge device interface name in the entry. Proceed with .
In the tab, specify networking details such as DHCP/static IP address, subnet mask or host name.
Using is only useful when also assigning a device to a bridge that is connected to some DHCP server.
If you intend to create a virtual bridge that has no connection to a real Ethernet device, use . In this case, it is a good idea to use addresses from the private IP address ranges, for example,
192.168.x.xor10.x.x.x.To create a bridge that should only serve as a connection between the different guests without connection to the host system, set the IP address to
0.0.0.0and the subnet mask to255.255.255.255. The network scripts handle this special address as an unset IP address.Activate the tab and activate the network devices you want to include in the network bridge.
Click to return to the tab and confirm with . The new network bridge should be active on VM Host Server now.
13.2.1.2 Deleting a Network Bridge #
To delete an existing network bridge, follow these steps:
Start › › .
Select the bridge device you want to delete from the list in the tab.
Delete the bridge with and confirm with .
13.2.2 Managing Network Bridges with brctl #
This section includes procedures to add or remove network bridges with the
brctl command line tool.
13.2.2.1 Adding a Network Bridge #
To add a new network bridge device on VM Host Server with
brctl, follow these steps:
Log in as
rooton the VM Host Server where you want to create a new network bridge.Choose a name for the new bridge—virbr_test in our example— and run
root #brctl addbr virbr_testCheck if the bridge was created on VM Host Server:
root #brctl show bridge name bridge id STP enabled interfaces br0 8000.e06995ec09e8 no eth0 virbr0 8000.525400b37ec9 yes virbr0-nic virbr_test 8000.000000000000 novirbr_testis present, but is not associated with any physical network interface.Add a network interface to the bridge:
root #brctl addif eth1
Important: Network Interface Must Be Unused
You can only enslave a network interface that is not yet used by other network bridge.
Optionally, enable STP (see Spanning Tree Protocol):
root #brctl stp virbr_test on
13.2.2.2 Deleting a Network Bridge #
To delete an existing network bridge device on VM Host Server with
brctl, follow these steps:
Log in as
rooton the VM Host Server where you want to delete an existing network bridge.List existing network bridges to identify the name of the bridge to remove:
root #brctl show bridge name bridge id STP enabled interfaces br0 8000.e06995ec09e8 no eth0 virbr0 8000.525400b37ec9 yes virbr0-nic virbr_test 8000.000000000000 yes eth1Delete the bridge:
root #brctl delbr virbr_test
13.2.3 Using VLAN Interfaces #
Sometimes, it is necessary to create a private connection either between two VM Host Servers or between VM Guest systems. For example, to migrate VM Guest to hosts in a different network segment, or to create a private bridge that only VM Guest systems may connect to, even when running on different VM Host Server systems. An easy way to build such connections is to set up VLAN networks.
VLAN interfaces are commonly set up on the VM Host Server and either interconnect the different VM Host Server systems, or they may be set up as a physical interface to an otherwise virtual-only bridge. It is even possible to create a bridge with a VLAN as a physical interface that has no IP address in the VM Host Server. That way, the guest systems have no possibility to access the host over this network.
Run the YaST module › . Follow this procedure to set up the VLAN device:
Procedure 13.1: Setting up VLAN Interfaces with YaST #
Press to create a new network interface.
In the , select .
Change the value of to the ID of your VLAN. Note that VLAN ID
1is commonly used for management purposes.Press .
Select the interface that the VLAN device should connect to below . If the desired interface does not appear in the list, first set up this interface without an IP Address.
Select the desired method for assigning an IP address to the VLAN device.
Press to finish the configuration.
It is also possible to use the VLAN interface as a physical interface of a bridge. This makes it possible to connect several VM Host Server-only networks and allows to live-migrate VM Guest systems that are connected to such a network.
YaST does not always allow to set no IP address. However, this may be a
desired feature especially if VM Host Server-only networks should be connected.
In this case, use the special address 0.0.0.0 with
netmask 255.255.255.255. The system scripts handle this
address as no IP address set.
14 Configuring Virtual Machines #
Abstract#
Virtual Machine Manager's view offers in-depth information about the VM Guest's complete configuration and hardware equipment. Using this view, you can also change the guest configuration or add and modify virtual hardware. To access this view, open the guest's console in Virtual Machine Manager and either choose › from the menu, or click in the toolbar.
- 14.1 Machine Setup
- 14.2 Storage
- 14.3 Controllers
- 14.4 Networking
- 14.5 Enabling Seamless and Synchronized Mouse Pointer Movement
- 14.6 Adding a CD/DVD-ROM Device with Virtual Machine Manager
- 14.7 Adding a Floppy Device with Virtual Machine Manager
- 14.8 Ejecting and Changing Floppy or CD/DVD-ROM Media with Virtual Machine Manager
- 14.9 Changing the Machine Type with
virsh - 14.10 Adding a PCI Device to a VM Guest
- 14.11 Adding SR-IOV Devices
Figure 14.1: View of a VM Guest #
The left panel of the window lists VM Guest overview and already
installed hardware. After clicking an item in the list, you can access its
detailed settings in the details view. You can change the hardware
parameters to match your needs, then click to
confirm them. Some changes take effect immediately, while others need a
reboot of the machine—and virt-manager
warns you about that fact.
To remove installed hardware from a VM Guest, select the appropriate list entry in the left panel and then click in the bottom right of the window.
To add new hardware, click below the left panel, then select the type of the hardware you want to add in the window. Modify its parameters and confirm with .
The following sections describe configuration options for the specific hardware type being added. They do not focus on modifying an existing piece of hardware as the options are identical.
14.1 Machine Setup #
This section describes the setup of the virtualized processor and memory hardware. These components are vital to a VM Guest, therefore you cannot remove them. It also shows how to view the overview and performance information, and how to change boot options.
14.1.1 Overview #
shows basic details about VM Guest and the hypervisor.
Figure 14.2: Overview details #
, , and are editable and help you identify VM Guest in the list of machines.
Figure 14.3: VM Guest Title and Description #
shows the universally unique identifier of the virtual machine, while shows its current status—, , or .
The section shows the hypervisor type, CPU architecture, used emulator, and chipset type. None of the hypervisor parameters can be changed.
14.1.2 Performance #
shows regularly updated charts of CPU and memory usage, and disk and network I/O.
Figure 14.4: Performance #
Tip: Enabling Disabled Charts
Not all the charts in the view are enabled by default. To enable these charts, go to › , then select › › , and check the charts that you want to see regularly updated.
Figure 14.5: Statistics Charts #
14.1.3 Processor #
includes detailed information about VM Guest processor configuration.
Figure 14.6: Processor View #
In the section, you can configure several parameters related to the number of allocated CPUs.
The real number of CPUs installed on VM Host Server.
The number of currently allocated CPUs. You can hotplug more CPUs by increasing this value up to the value.
Maximum number of allocable CPUs for the current session. Any change to this value will take effect after the next VM Guest reboot.
The section lets you configure the CPU model and topology.
When activated, the option uses the host CPU model for VM Guest. Otherwise you need to specify the CPU model from the drop-down box.
After you activate , you can specify a custom number of sockets, cores and threads for the CPU.
14.1.4 Memory #
contains information about the memory that is available to VM Guest.
Figure 14.7: Memory View #
Total amount of memory installed on VM Host Server.
The amount of memory currently available to VM Guest. You can hotplug more memory by increasing this value up to the value of .
The maximum value to which you can hotplug the currently available memory. Any change to this value will take effect after the next VM Guest reboot.
14.1.5 Boot Options #
introduces options affecting the VM Guest boot process.
Figure 14.8: Boot Options #
In the section, you can specify whether the virtual machine should automatically start during the VM Host Server boot phase.
In the , activate the devices that will be used for booting VM Guest. You can change their order with the up and down arrow buttons on the right side of the list. To choose from a list of bootable devices on VM Guest start, activate .
To boot a different kernel than the one on the boot device, activate and specify the paths to the alternative kernel and initrd placed on the VM Host Server file system. You can also specify kernel arguments that will be passed to the loaded kernel.
14.2 Storage #
This section gives you a detailed description of configuration options for storage devices. It includes both hard disks and removable media, such as USB or CD-ROM drives.
Procedure 14.1: Adding a New Storage Device #
Click below the left panel, then select from the window.
Figure 14.9: Add a New Storage #
To create a
qcow2disk image in the default location, activate and specify its size in gigabytes.To gain more control over the disk image creation, activate and click to manage storage pools and images. The window opens which has almost identical functionality as the tab described in Section 12.1, “Managing Storage with Virtual Machine Manager”.

Tip: Supported Storage Formats
SUSE only supports the following storage formats:
raw,qcow2, andqed.After you manage to create and specify the disk image file, specify the . It can be one of the following options:
: Does not allow using .
: Does not allow using .
: Required to use an existing SCSI storage directly without adding it into a storage pool.
Select the for your device. The list of available options depends on the device type you selected in the previous step. The types based on use paravirtualized drivers.
In the section, select the preferred . For more information on cache modes, see Chapter 15, Disk Cache Modes.
Confirm your settings with . A new storage device appears in the left panel.
14.3 Controllers #
This section focuses on adding and configuring new controllers.
Procedure 14.2: Adding a New Controller #
Click below the left panel, then select from the window.
Figure 14.10: Add a New Controller #
Select the type of the controller. You can choose from , , , , (paravirtualized), , or (smart card devices).
Optionally, in the case of a USB or SCSI controller, select a controller model.
Confirm your settings with . A new controller appears in the left panel.
14.4 Networking #
This section describes how to add and configure new network devices.
Procedure 14.3: Adding a New Network Device #
Click below the left panel, then select from the window.
Figure 14.11: Add a New Controller #
From the list, select the source for the network connection. The list includes VM Host Server's available physical network interfaces, network bridges, or network bonds. You can also assign the VM Guest to an already defined virtual network. See Chapter 13, Managing Networks for more information on setting up virtual networks with Virtual Machine Manager.
Specify a for the network device. While Virtual Machine Manager pre-fills a random value for your convenience, it is recommended to supply a MAC address appropriate for your network environment to avoid network conflicts.
Select a device model from the list. You can either leave the , or specify one of , , or models. Note that virtio uses paravirtualized drivers.
Confirm your settings with . A new network device appears in the left panel.
14.5 Enabling Seamless and Synchronized Mouse Pointer Movement #
When you click within a VM Guest's console with the mouse, the pointer is captured by the console window and cannot be used outside the console unless it is explicitly released (by pressing Alt–Ctrl). To prevent the console from grabbing the key and to enable seamless pointer movement between host and guest instead, add a tablet to the VM Guest.
Adding a tablet has the additional advantage of synchronizing the mouse pointer movement between VM Host Server and VM Guest when using a graphical environment on the guest. With no tablet configured on the guest, you will often see two pointers with one dragging behind the other.
Double-click a VM Guest entry in the Virtual Machine Manager to open its console and switch to the view with › .
Click and choose and then in the pop-up window. Proceed with .
If the guest is running, you will be asked whether to enable the tablet after the next reboot. Confirm with .
When you start or restart the VM Guest, the tablet becomes available in the VM Guest.
14.6 Adding a CD/DVD-ROM Device with Virtual Machine Manager #
KVM supports CD or DVD-ROMs in VM Guest either by directly accessing a
physical drive on the VM Host Server or by accessing ISO images. To create an
ISO image from an existing CD or DVD, use dd:
dd if=/dev/cd_dvd_device of=my_distro.iso bs=2048
To add a CD/DVD-ROM device to your VM Guest, proceed as follows:
Double-click a VM Guest entry in the Virtual Machine Manager to open its console and switch to the view with › .
Click and choose in the pop-up window.
Change the to .
Select .
To assign the device to a physical medium, enter the path to the VM Host Server's CD/DVD-ROM device (for example,
/dev/cdrom) next to . Alternatively, use to open a file browser and then click to select the device. Assigning the device to a physical medium is only possible when the Virtual Machine Manager was started on the VM Host Server.To assign the device to an existing image, click to choose an image from a storage pool. If the Virtual Machine Manager was started on the VM Host Server, alternatively choose an image from another location on the file system by clicking . Select an image and close the file browser with .
Save the new virtualized device with .
Reboot the VM Guest to make the new device available. For more information, see Section 14.8, “Ejecting and Changing Floppy or CD/DVD-ROM Media with Virtual Machine Manager”.
14.7 Adding a Floppy Device with Virtual Machine Manager #
Currently KVM only supports the use of floppy disk images—using a
physical floppy drive is not supported. Create a floppy disk image from
an existing floppy using dd:
dd if=/dev/fd0 of=/var/lib/libvirt/images/floppy.img
To create an empty floppy disk image use one of the following commands:
- Raw Image
dd if=/dev/zero of=/var/lib/libvirt/images/floppy.img bs=512 count=2880
- FAT Formatted Image
mkfs.msdos -C /var/lib/libvirt/images/floppy.img 1440
To add a floppy device to your VM Guest, proceed as follows:
Double-click a VM Guest entry in the Virtual Machine Manager to open its console and switch to the view with › .
Click and choose in the pop-up window.
Change the to .
Choose and click to choose an existing image from a storage pool. If Virtual Machine Manager was started on the VM Host Server, alternatively choose an image from another location on the file system by clicking . Select an image and close the file browser with .
Save the new virtualized device with .
Reboot the VM Guest to make the new device available. For more information, see Section 14.8, “Ejecting and Changing Floppy or CD/DVD-ROM Media with Virtual Machine Manager”.
14.8 Ejecting and Changing Floppy or CD/DVD-ROM Media with Virtual Machine Manager #
Regardless of whether you are using the VM Host Server's physical CD/DVD-ROM
device or an ISO/floppy image, before you can change the media or image
of an existing device in the VM Guest, you first need to
disconnect the media from the guest.
Double-click a VM Guest entry in the Virtual Machine Manager to open its console and switch to the view with › .
Choose the Floppy or CD/DVD-ROM device and “eject” the medium by clicking .
To “insert” a new medium, click .
If using the VM Host Server's physical CD/DVD-ROM device, first change the media in the device (this may require unmounting it on the VM Host Server before it can be ejected). Then choose and select the device from the drop-down box.
If you are using an ISO image, choose and select an image by clicking . When connecting from a remote host, you may only choose images from existing storage pools.
Click to finish. The new media can now be accessed in the VM Guest.
14.9 Changing the Machine Type with virsh #
By default, when installing with the virt-install tool, the machine type for VM Guest is
pc-i440fx. The machine type is stored in the
VM Guest's xml configuration file in
/etc/libvirt/qemu/ in the tag type:
<type arch='x86_64' machine='pc-i440fx-2.3'>hvm</type>
As an example, the following procedure shows how to change this value to the
machine type q35. q35 is an Intel*
chipset. It includes PCIe, supports up to
12 USB ports, and has support for
SATA and
IOMMU. IRQ routing has also
been improved.
Check whether your VM Guest is inactive:
virsh list --inactive Id Name State ---------------------------------------------------- - sles11 shut off
Edit the configuration for this VM Guest:
virsh edit sles11
Change the value of the
machineattribute:<type arch='x86_64' machine='pc-q35-2.0'>hvm</type>
Restart the VM Guest.
root #virsh start sles11Check that the machine type has changed. Log in to the VM Guest as root and run the following command:
root #dmidecode | grep ProductProduct Name: Standard PC (Q35 + ICH9, 2009)
Tip: Machine Type Update Recommendations
Whenever the QEMU version on the host system is upgraded, for example,
when upgrading the VM Host Server to a new service pack, it is also
recommended to upgrade the machine type of the VM Guests to the latest
available version. To check, use the command qemu-system-x86_64 -M
help on the VM Host Server.
The default machine type pc-i440fx, for example, is
regularly updated. If your VM Guest still runs with a machine type of
pc-i440fx-1.x, an update
to pc-i440fx-2.x is
strongly recommended. This allows taking advantage of the most recent
updates and corrections in machine definitions, and ensures
better future compatibility.
14.10 Adding a PCI Device to a VM Guest #
You can directly assign host-PCI devices to guests (PCI pass-through). When the PCI device is assigned to one VM Guest, it cannot be used on the host or by another VM Guest unless it is re-assigned. A prerequisite for this feature is a VM Host Server configuration as described in Important: Requirements for VFIO and SR-IOV.
14.10.1 Adding a PCI Device with Virtual Machine Manager #
The following procedure describes how to add a PCI device to a VM Guest using Virtual Machine Manager:
Double-click a VM Guest entry in the Virtual Machine Manager to open its console and switch to the view with › .
Click and choose the category in the left panel. A list of available PCI devices appears in the right part of the window.
Figure 14.12: Adding a PCI Device #
From the list of available PCI devices, choose the one you want to pass to the guest. Confirm with .
Tip: Assigning a PCI Device Requires a VM Guest Shutdown
Although it is possible to assign a PCI device to a running VM Guest as described above, the device will not become available until you shut down the VM Guest and reboot it afterward.
14.10.2 Adding a PCI Device with virsh #
To assign a PCI device to VM Guest with virsh,
follow these steps:
Identify the host PCI device to assign to the guest. In the following example, we are assigning a DEC network card to the guest:
tux >sudo lspci -nn[...] 03:07.0 Ethernet controller [0200]: Digital Equipment Corporation DECchip \ 21140 [FasterNet] [1011:0009] (rev 22) [...]Note down the device ID (
03:07.0in this case).Gather detailed information about the device using
virsh nodedev-dumpxml ID. To get the ID, you need to replace colon and period in the device ID (03:07.0) with underscore and prefix the result with “pci_0000_” (pci_0000_03_07_0).tux >virsh nodedev-dumpxml pci_0000_03_07_0 <device> <name>pci_0000_03_07_0</name> <path>/sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:14.4/0000:03:07.0</path> <parent>pci_0000_00_14_4</parent> <driver> <name>tulip</name> </driver> <capability type='pci'> <domain>0</domain> <bus>3</bus> <slot>7</slot> <function>0</function> <product id='0x0009'>DECchip 21140 [FasterNet]</product> <vendor id='0x1011'>Digital Equipment Corporation</vendor> <numa node='0'/> </capability> </device>Note down the values for domain, bus, and function.
Detach the device from the host system prior to attaching it to VM Guest.
tux >virsh nodedev-detach pci_0000_03_07_0 Device pci_0000_03_07_0 detached
Tip: Multi-Function PCI Devices
When using a multi-function PCI device that does not support FLR (function level reset) or PM (power management) reset, you need to detach all its functions from the VM Host Server. The whole device must be reset for security reasons.
libvirtwill refuse to assign the device if one of its functions is still in use by the VM Host Server or another VM Guest.Convert the domain, bus, slot, and function value from decimal to hexadecimal, and prefix with
0xto tell the system that the value is hexadecimal. In our example, domain = 0, bus = 3, slot = 7, and function = 0. Their hexadecimal values are:tux >printf %x 0 0tux >printf %x 3 3tux >printf %x 7 7This results in domain = 0x0000, bus = 0x03, slot = 0x07 and function = 0x00.
Run
virsh editon your domain, and add the following device entry in the<devices>section using the values from the previous step:<hostdev mode='subsystem' type='pci' managed='yes'> <source> <address domain='0x0000' bus='0x03' slot='0x07' function='0x00'/> </source> </hostdev>
Tip:
managedCompared tounmanagedlibvirtrecognizes two modes for handling PCI devices: they can be eithermanagedorunmanaged. In the managed case,libvirtwill handle all the details of unbinding the device from the existing driver if needed, resetting the device, binding it tovfio-pcibefore starting the domain, etc. When the domain is terminated or the device is removed from the domain,libvirtwill unbind fromvfio-pciand rebind to the original driver in the case of a managed device. If the device is unmanaged, the user must take care to ensure all of these management aspects of the device are done before assigning it to a domain, and after the device is no longer used by the domain.In the example above, the
managed='yes'option means that the device is managed. To switch the device mode to unmanaged, setmanaged='no'in the listing above. If you do so, you need to take care of the related driver with thevirsh nodedev-detachandvirsh nodedev-reattachcommands. That means you need to runvirsh nodedev-detach pci_0000_03_07_0prior to starting the VM Guest to detach the device from the host. In case the VM Guest is not running, you can make the device available for the host by runningvirsh nodedev-reattach pci_0000_03_07_0.Shut down the VM Guest and restart it to make the assigned PCI device available.

Tip: SELinux
If you are running SELinux on your VM Host Server, you need to disable it prior to starting the VM Guest with
setsebool -P virt_use_sysfs 1
14.11 Adding SR-IOV Devices #
Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) capable PCIe devices can replicate their resources, so they appear to be multiple devices. Each of these "pseudo-devices" can be assigned to a VM Guest.
SR-IOV is an industry specification that was created by the Peripheral Component Interconnect Special Interest Group (PCI-SIG) consortium. It introduces physical functions (PF) and virtual functions (VF). PFs are full PCIe functions used to manage and configure the device. PFs also can move data. VFs lack the configuration and management part—they only can move data and a reduced set of configuration functions. Since VFs do not have all PCIe functions, the host operating system or the Hypervisor must support SR-IOV to be able to access and initialize VFs. The theoretical maximum for VFs is 256 per device (consequently the maximum for a dual-port Ethernet card would be 512). In practice this maximum is much lower, since each VF consumes resources.
14.11.1 Requirements #
The following requirements must be met to be able to use SR-IOV:
An SR-IOV-capable network card (as of openSUSE Leap 42.2, only network cards support SR-IOV)
An AMD64/Intel 64 host supporting hardware virtualization (AMD-V or Intel VT-x), see Section 7.3, “KVM Hardware Requirements” for more information
A chipset that supports device assignment (AMD-Vi or Intel VT-d)
libvirt-0.9.10 or better
SR-IOV drivers must be loaded and configured on the host system
A host configuration that meets the requirements listed at Important: Requirements for VFIO and SR-IOV
A list of the PCI addresses of the VF(s) that will be assigned to VM Guests
Tip: Checking if a Device is SR-IOV-Capable
The information whether a device is SR-IOV-capable can be obtained from
its PCI descriptor by running lspci. A device that
supports SR-IOV reports a capability similar to
the following:
Capabilities: [160 v1] Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV)
Note: Adding an SR-IOV Device at VM Guest Creation
Before adding an SR-IOV device to a VM Guest when initially setting it up, the VM Host Server already needs to be configured as described in Section 14.11.2, “Loading and Configuring the SR-IOV Host Drivers”.
14.11.2 Loading and Configuring the SR-IOV Host Drivers #
To be able to access and initialize VFs, an SR-IOV-capable driver needs to be loaded on the host system.
Before loading the driver, make sure the card is properly detected by running
lspci. The following example shows thelspcioutput for the dual-port Intel 82576NS network card:tux >sudo /sbin/lspci | grep 82576 01:00.0 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation 82576NS Gigabit Network Connection (rev 01) 01:00.1 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation 82576NS Gigabit Network Connection (rev 01) 04:00.0 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation 82576NS Gigabit Network Connection (rev 01) 04:00.1 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation 82576NS Gigabit Network Connection (rev 01)In case the card is not detected, it is likely that the hardware virtualization support in the BIOS/EFI has not been enabled.
Check whether the SR-IOV driver is already loaded by running
lsmod. In the following example a check for the igb driver (for the Intel 82576NS network card) returns a result. That means the driver is already loaded. If the command returns nothing, the driver is not loaded.tux >sudo /sbin/lsmod | egrep "^igb " igb 185649 0Skip this step if the driver is already loaded.
If the SR-IOV driver is not yet loaded, the non-SR-IOV driver needs to be removed first, before loading the new driver. Use
rmmodto unload a driver. The following example unloads the non-SR-IOV driver for the Intel 82576NS network card:sudo /sbin/rmmod igbvf
Load the SR-IOV driver subsequently using the
modprobecommand—the VF parameter (max_vfs) is mandatory:sudo /sbin/modprobe igb max_vfs=8
Or load the driver via SYSFS:
Find the PCI ID of the physical NIC by listing Ethernet devices:
tux >sudo lspci | grep Eth 06:00.0 Ethernet controller: Emulex Corporation OneConnect NIC (Skyhawk) (rev 10) 06:00.1 Ethernet controller: Emulex Corporation OneConnect NIC (Skyhawk) (rev 10)To enable VFs, echo the number of desired VFs to load to the
sriov_numvfsparameter:tux >sudo echo 1 > /sys/bus/pci/devices/0000:06:00.1/sriov_numvfsVerify that the VF NIC was loaded:
tux >sudo lspci | grep Eth 06:00.0 Ethernet controller: Emulex Corporation OneConnect NIC (Skyhawk) (rev 10) 06:00.1 Ethernet controller: Emulex Corporation OneConnect NIC (Skyhawk) (rev 10) 06:08.0 Ethernet controller: Emulex Corporation OneConnect NIC (Skyhawk) (rev 10)Obtain the maximum number of VFs available:
tux >sudo lspci -vvv -s 06:00.1 | grep 'Initial VFs' Initial VFs: 32, Total VFs: 32, Number of VFs: 0, Function Dependency Link: 01Create a
before.servicefile which loads VF via SYSFS on boot:[Unit] Before= [Service] Type=oneshot RemainAfterExit=true ExecStart=/bin/bash -c "echo 1 > /sys/bus/pci/devices/0000:06:00.1/sriov_numvfs" # beware, executable is run directly, not through a shell, check the man pages # systemd.service and systemd.unit for full syntax [Install] # target in which to start the service WantedBy=multi-user.target #WantedBy=graphical.target
And copy it to
/etc/systemd/system.Additionally, it is required to create another service file (
after-local.service) pointing to/etc/init.d/after.localscript that detaches the NIC prior to starting the VM, otherwise the VM would fail to start:[Unit] Description=/etc/init.d/after.local Compatibility After=libvirtd.service Requires=libvirtd.service [Service] Type=oneshot ExecStart=/etc/init.d/after.local RemainAfterExit=true [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
And copy it to
/etc/systemd/system.#! /bin/sh # # Copyright (c) 2010 SuSE LINUX Products GmbH, Germany. All rights reserved. # ... virsh nodedev-detach pci_0000_06_08_0
Then save it as
/etc/init.d/after.local.Reboot the machine and check if the SR-IOV driver is loaded by re-running the
lspcicommand from the first step of this procedure. If the SR-IOV driver was loaded successfully you should see additional lines for the VFs:01:00.0 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation 82576NS Gigabit Network Connection (rev 01) 01:00.1 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation 82576NS Gigabit Network Connection (rev 01) 01:10.0 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation 82576 Virtual Function (rev 01) 01:10.1 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation 82576 Virtual Function (rev 01) 01:10.2 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation 82576 Virtual Function (rev 01) [...] 04:00.0 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation 82576NS Gigabit Network Connection (rev 01) 04:00.1 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation 82576NS Gigabit Network Connection (rev 01) 04:10.0 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation 82576 Virtual Function (rev 01) 04:10.1 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation 82576 Virtual Function (rev 01) 04:10.2 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation 82576 Virtual Function (rev 01) [...]
14.11.3 Adding a VF Network Device to an Existing VM Guest #
When the SR-IOV hardware is properly set up on the VM Host Server, you can add VFs to VM Guests. To do so, you need to collect some data first.
Note: The following procedure is using example data. Make sure to replace it by appropriate data from your setup.
Use the
virsh nodedev-listcommand to get the PCI address of the VF you want to assign and its corresponding PF. Numerical values from thelspcioutput shown in Section 14.11.2, “Loading and Configuring the SR-IOV Host Drivers” (for example01:00.0or04:00.1) are transformed by adding the prefix "pci_0000_" and by replacing colons and dots with underscores. So a PCI ID listed as "04:00.0" bylspciis listed as "pci_0000_04_00_0" by virsh. The following example lists the PCI IDs for the second port of the Intel 82576NS network card:tux >sudo virsh nodedev-list | grep 0000_04_ pci_0000_04_00_0 pci_0000_04_00_1 pci_0000_04_10_0 pci_0000_04_10_1 pci_0000_04_10_2 pci_0000_04_10_3 pci_0000_04_10_4 pci_0000_04_10_5 pci_0000_04_10_6 pci_0000_04_10_7 pci_0000_04_11_0 pci_0000_04_11_1 pci_0000_04_11_2 pci_0000_04_11_3 pci_0000_04_11_4 pci_0000_04_11_5The first two entries represent the PFs, whereas the other entries represent the VFs.
Get more data that will be needed by running the command
virsh nodedev-dumpxmlon the PCI ID of the VF you want to add:tux >sudo virsh nodedev-dumpxml pci_0000_04_10_0 <device> <name>pci_0000_04_10_0</name> <parent>pci_0000_00_02_0</parent> <capability type='pci'> <domain>0</domain> <bus>4</bus> <slot>16</slot> <function>0</function> <product id='0x10ca'>82576 Virtual Function</product> <vendor id='0x8086'>Intel Corporation</vendor> <capability type='phys_function'> <address domain='0x0000' bus='0x04' slot='0x00' function='0x0'/> </capability> </capability> </device>The following data is needed for the next step:
<domain>0</domain>
<bus>4</bus>
<slot>16</slot>
<function>0</function>
Create a temporary XML file (for example
/tmp/vf-interface.xmlcontaining the data necessary to add a VF network device to an existing VM Guest. The minimal content of the file needs to look like the following:<interface type='hostdev'>1 <source> <address type='pci' domain='0' bus='11' slot='16' function='0'2/>2 </source> </interface>
VFs do not get a fixed MAC address; it changes every time the host reboots. When adding network devices the “traditional” way with <hostdev>, it would require to reconfigure the VM Guest's network device after each reboot of the host, because of the MAC address change. To avoid this kind of problem, libvirt introduced the “interface type='hostdev'” directive, which sets up network-specific data before assigning the device.
Specify the data you acquired in the previous step here.
In case a device is already attached to the host, it cannot be attached to a guest. To make it available for guests, detach it from the host first:
virsh nodedev-detach pci_0000_04_10_0
Last, add the VF interface to an existing VM Guest:
virsh attach-device GUEST /tmp/vf-interface.xml --OPTION
GUEST needs to be replaced by the domain name, id or uuid of the VM Guest and --OPTION can be one of the following:
--persistentThis option will always add the device to the domain's persistent XML. In addition, if the domain is running, it will be hotplugged.
--configThis option will only affect the persistent XML, even if the domain is running. The device will only show up in the guest on next boot.
--liveThis option will only affect a running domain. If the domain is inactive, the operation will fail. The device is not persisted in the XML and will not be available in the guest on next boot.
- --current
This option affects the current state of the domain. If the domain is inactive, the device is added to the persistent XML and will be available on next boot. If the domain is active, the device is hotplugged but not added to the persistent XML.
To detach a VF interface, use the
virsh detach-devicecommand, which also takes the options listed above.
14.11.4 Dynamic Allocation of VFs from a Pool #
If you define the PCI address of a VF into a guest's configuration statically as described in Section 14.11.3, “Adding a VF Network Device to an Existing VM Guest”, it is hard to migrate such guest to another host. The host must have identical hardware in the same location on the PCI bus, or the guest configuration must be modified prior to each start.
Another approach is to create a libvirt network with a device pool
that contains all the VFs of an SR-IOV device.
The guest then references this network, and each time it is started, a
single VF is dynamically allocated to it. When the guest is stopped, the
VF is returned to the pool, available for another guest.
14.11.4.1 Defining Network with Pool of VFs on VM Host Server #
The following example of network definition creates a pool of all VFs for the SR-IOV device with its physical function (PF) at the network interface eth0 on the host:
<network>
<name>passthrough</name>
<forward mode='hostdev' managed='yes'>
<pf dev='eth0'/>
</forward>
</network>
To use this network on the host, save the above code to a file, for
example /tmp/passthrough.xml, and execute the
following commands. Remember to replace eth0 with the real network
interface name of your SR-IOV device's PF:
virsh net-define /tmp/passthrough.xml virsh net-autostart passthrough virsh net-start passthrough
14.11.4.2 Configuring VM Guest to Use VF from the Pool #
The following example of guest device interface definition uses a VF of
the SR-IOV device from the pool created in
Section 14.11.4.1, “Defining Network with Pool of VFs on VM Host Server”. libvirt automatically
derives the list of all VFs associated with that PF the first time the
guest is started.
<interface type='network'> <source network='passthrough'> </interface>
To verify the list of associated VFs, run virsh net-dumpxml
passthrough on the host after the first guest that uses the
network with the pool of VFs starts.
<network connections='1'>
<name>passthrough</name>
<uuid>a6a26429-d483-d4ed-3465-4436ac786437</uuid>
<forward mode='hostdev' managed='yes'>
<pf dev='eth0'/>
<address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x02' slot='0x10' function='0x1'/>
<address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x02' slot='0x10' function='0x3'/>
<address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x02' slot='0x10' function='0x5'/>
<address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x02' slot='0x10' function='0x7'/>
<address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x02' slot='0x11' function='0x1'/>
<address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x02' slot='0x11' function='0x3'/>
<address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x02' slot='0x11' function='0x5'/>
</forward>
</network>Part III Hypervisor-Independent Features #
- 15 Disk Cache Modes
- 16 VM Guest Clock Settings
Keeping the correct time in a VM Guest is one of the more difficult aspects of virtualization. Keeping the correct time is especially important for network applications and is also a prerequisite to do a live migration of a VM Guest.
- 17 libguestfs
Virtual Machines consist of disk images and definition files. Manually accessing and manipulating these guest components (outside of normal hypervisor processes) is possible, but inherently dangerous and risks compromising data integrity. libguestfs is a C library and corresponding set of tools designed for safely accessing and modifying Virtual Machine disk images - outside of normal hypervisor processes, but without the risk normally associated with manual editing.
15 Disk Cache Modes #
15.1 Disk Interface Cache Modes #
Hypervisors allow for various storage caching strategies to be specified when configuring a VM Guest. Each guest disk interface can have one of the following cache modes specified: writethrough, writeback, none, directsync, or unsafe. If no cache mode is specified, an appropriate default cache mode is used. These cache modes influence how host-based storage is accessed, as follows:
Read/write data may be cached in the host page cache.
The guest's storage controller is informed whether a write cache is present, allowing for the use of a flush command.
Synchronous write mode may be used, in which write requests are reported complete only when committed to the storage device.
Flush commands (generated by the guest storage controller) may be ignored for performance reasons.
If a disorderly disconnection between the guest and its storage occurs, the cache mode in use will affect whether data loss occurs. The cache mode can also affect disk performance significantly. Additionally, some cache modes are incompatible with live migration, depending on several factors. There are no simple rules about what combination of cache mode, disk image format, image placement, or storage sub-system is best. The user should plan each guest's configuration carefully and experiment with various configurations to determine the optimal performance.
15.2 Description of Cache Modes #
- cache mode unspecified
In QEMU versions older than v1.2 (for example, openSUSE Leap 42.2), not specifying a cache mode meant that writethrough would be used as the default. Since that version, the various guest storage interfaces have been fixed to handle writeback or writethrough semantics more correctly, allowing for the default caching mode to be switched to writeback. The guest driver for each of
ide,scsi, andvirtiohave within their power to disable the write back cache, causing the caching mode used to revert to writethrough. The typical guest's storage drivers will maintain the default caching mode as writeback, however.- writethrough
This mode causes the hypervisor to interact with the disk image file or block device with
O_DSYNCsemantics, where writes are reported as completed only when the data has been committed to the storage device. The host page cache is used in what can be termed a writethrough caching mode. The guest's virtual storage adapter is informed that there is no writeback cache, so the guest would not need to send down flush commands to manage data integrity. The storage behaves as if there is a writethrough cache.- writeback
This mode causes the hypervisor to interact with the disk image file or block device with neither
O_DSYNCnorO_DIRECTsemantics, so the host page cache is used and writes are reported to the guest as completed when they are placed in the host page cache. The normal page cache management will handle commitment to the storage device. Additionally, the guest's virtual storage adapter is informed of the writeback cache, so the guest would be expected to send down flush commands as needed to manage data integrity. Analogous to a raid controller with RAM cache.- none
This mode causes the hypervisor to interact with the disk image file or block device with
O_DIRECTsemantics, so the host page cache is bypassed and I/O happens directly between the hypervisor user space buffers and the storage device. Because the actual storage device may report a write as completed when placed in its write queue only, the guest's virtual storage adapter is informed that there is a writeback cache. The guest would be expected to send down flush commands as needed to manage data integrity. Performance-wise, it is equivalent to direct access to your host's disk.- unsafe
This mode is similar to the
writebackmode discussed above. The key aspect of this “unsafe” mode, is that all flush commands from the guests are ignored. Using this mode implies that the user has accepted the trade-off of performance over risk of data loss in case of a host failure. Useful, for example, during guest installation, but not for production workloads.- directsync
This mode causes the hypervisor to interact with the disk image file or block device with both
O_DSYNCandO_DIRECTsemantics. This means, writes are reported as completed only when the data has been committed to the storage device, and when it is also desirable to bypass the host page cache. Like writethrough, it is helpful to guests that do not send flushes when needed. It was the last cache mode added, completing the possible combinations of caching and direct access semantics.
15.3 Data Integrity Implications of Cache Modes #
- writethrough, none, directsync
These are the safest modes, and considered equally safe, given that the guest operating system is “modern and well behaved”, which means that it uses flushes as needed. If you have a suspect guest, use writethough, or directsync. Note that some file systems are not compatible with
noneordirectsync, as they do not support O_DIRECT, which these cache modes rely on.- writeback
This mode informs the guest of the presence of a write cache, and relies on the guest to send flush commands as needed to maintain data integrity within its disk image. This is a common storage design which is completely accounted for within modern file systems. But it should be noted that because there is a window of time between the time a write is reported as completed, and that write being committed to the storage device, this mode exposes the guest to data loss in the unlikely case of a host failure.
- unsafe
This mode is similar to writeback caching except the guest flush commands are ignored, nullifying the data integrity control of these flush commands, and resulting in a higher risk of data loss because of host failure. The name “unsafe” should serve as a warning that there is a much higher potential for data loss because of a host failure than with the other modes. Note that as the guest terminates, the cached data is flushed at that time.
15.4 Performance Implications of Cache Modes #
The choice to make full use of the page cache, or to write through it, or
to bypass it altogether can have dramatic performance implications. Other
factors that influence disk performance include the capabilities of the
actual storage system, what disk image format is used, the potential size
of the page cache and the IO scheduler used. Additionally, not flushing
the write cache increases performance, but with risk, as noted above. As
a general rule, high-end systems typically perform best with the cache mode
none, because of the reduced data copying that
occurs. The potential benefit of having multiple guests share the common
host page cache, the ratio of reads to writes, and the use of AIO mode
native (see below) should also be considered.
15.5 Effect of Cache Modes on Live Migration #
The caching of storage data and metadata restricts the configurations
that support live migration. Currently, only raw,
qcow2 and qed image formats can be
used for live migration. If a clustered file system is used, all cache
modes support live migration. Otherwise the only cache mode that supports
live migration on read/write shared storage is none.
The libvirt management layer includes checks for
migration compatibility based on several factors. If the guest
storage is hosted on a clustered file system, is read-only or is marked
shareable, then the cache mode is ignored when determining if migration
can be allowed. Otherwise libvirt will not allow
migration unless the cache mode is set to none.
However, this restriction can be overridden with the
“unsafe” option to the migration APIs, which is also
supported by virsh, as for example in
virsh migrate --live --unsafe
Tip
The cache mode none is required for the AIO mode setting
native. If another cache mode is used, then the
AIO mode will silently be switched back to the default threads. The
guest flush within the host is implemented using
fdatasync().
Tip: Timekeeping on the VM Host Server
It is strongly recommended to ensure the VM Host Server keeps the correct time as well, for example, by using NTP (see Book “Reference”, Chapter 18 “Time Synchronization with NTP” for more information).
16.1 KVM: Using kvm_clock #
KVM provides a paravirtualized clock which is currently supported by
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10 SP3 and newer and RedHat Enterprise Linux 5.4 and newer via
the kvm_clock driver. It is strongly recommended
to use kvm_clock when available.
Use the following command inside a VM Guest running Linux to check
whether the driver kvm_clock has been loaded:
tux > sudo dmesg | grep kvm-clock
[ 0.000000] kvm-clock: cpu 0, msr 0:7d3a81, boot clock
[ 0.000000] kvm-clock: cpu 0, msr 0:1206a81, primary cpu clock
[ 0.012000] kvm-clock: cpu 1, msr 0:1306a81, secondary cpu clock
[ 0.160082] Switching to clocksource kvm-clock
To check which clock source is currently used, run the following command
in the VM Guest. It should output kvm-clock:
cat /sys/devices/system/clocksource/clocksource0/current_clocksource
Important: kvm-clock and NTP
When using kvm-clock, it is recommended to use
NTP in the VM Guest, as well. Using NTP on the VM Host Server
is also recommended.
16.1.1 Other Timekeeping Methods #
The paravirtualized kvm-clock is currently not for
Windows* operating systems. For Windows*, use the Windows Time
Service Tools for time synchronization (see
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc773263%28WS.10%29.aspx
for more information).
16.2 Xen Virtual Machine Clock Settings #
When booting, virtual machines get their initial clock time from their host. After getting their initial clock time, fully virtual machines manage their time independently from the host. Paravirtual machines manage clock time according to their independent wallclock setting. If the independent wallclock is enabled, the virtual machine manages its time independently and does not synchronize with the host. If the independent wallclock is disabled, the virtual machine periodically synchronizes its time with the host clock.
Note
OES 2 NetWare virtual machines manage clock time independently after booting. They do not synchronize with the host clock time.
If a guest operating system is configured for NTP and the virtual
machine's independent wallclock setting is disabled, it will still
periodically synchronize its time with the host time. This dual type of
configuration can result in time drift between virtual machines that need
to be synchronized. To effectively use an external time source, such as
NTP, for time synchronization on a virtual machine, the virtual machine's
independent wallclock setting must be enabled (set to
1). Otherwise, it will continue to synchronize its
time with its host.
Procedure 16.1: Viewing the Independent Wallclock Setting #
Log in to the virtual machine’s operating system as
root.In the virtual machine environment, enter
cat /proc/sys/xen/independent_wallclock0means that the virtual machine is getting its time from the host and is not using independent wallclock.1means that the virtual machine is using independent wallclock and managing its time independently from the host.
Procedure 16.2: Permanently Changing the Independent Wallclock Setting #
Log in to the virtual machine environment as
root.Edit the virtual machine’s
/etc/sysctl.conffile.Add or change the following entry:
xen.independent_wallclock=1
Enter
1to enable or0to disable the wallclock setting.Save the file and reboot the virtual machine operating system.
While booting, a virtual machine gets its initial clock time from the host. Then, if the wallclock setting is set to 1 in the
sysctl.conffile, it manages its clock time independently and does not synchronize with the host clock time.
Procedure 16.3: Temporarily Changing the Independent Wallclock Setting #
Log in to the virtual machine environment as
root.Enter the following command:
echo "1" > /proc/sys/xen/independent_wallclock
Enter
1to enable or0to disable the wallclock setting.Add or change the following entry:
xen.independent_wallclock=1
Enter
1to enable or0to disable the wallclock setting.Although the current status of the independent wallclock changes immediately, its clock time might not be immediately synchronized. The setting persists until the virtual machine reboots. Then, it gets its initial clock time from the host and uses the independent wallclock according to the setting specified in the
sysctl.conffile.
17 libguestfs #
Abstract#
Virtual Machines consist of disk images and definition files. Manually accessing and manipulating these guest components (outside of normal hypervisor processes) is possible, but inherently dangerous and risks compromising data integrity. libguestfs is a C library and corresponding set of tools designed for safely accessing and modifying Virtual Machine disk images - outside of normal hypervisor processes, but without the risk normally associated with manual editing.
17.1 VM Guest Manipulation Overview #
17.1.1 VM Guest Manipulation Risk #
As disk images and definition files are simply another type of file in a Linux environment, it is possible to use many tools to access, edit and write to these files. When used correctly, such tools can be an important part of guest administration. However, even correct usage of these tools is not without risk. Risks that should be considered when manually manipulating guest disk images include:
Data Corruption: Concurrently accessing images, by the host machine or another node in a cluster, can cause changes to be lost or data corruption to occur if virtualization protection layers are bypassed.
Security: Mounting disk images as loop devices requires root access. While an image is loop mounted, other users and processes can potentially access the disk contents.
Administrator Error: Bypassing virtualization layers correctly requires advanced understanding of virtual components and tools. Failing to isolate the images or failing to clean up properly after changes have been made can lead to further problems once back in virtualization control.
17.1.2 libguestfs Design #
libguestfs C library has been designed to safely and securely create, access and modify virtual machine (VM Guest) disk images. It also provides additional language bindings: for Perl, Python, PHP (only for 64-bit machines), and Ruby. libguestfs can access VM Guest disk images without needing root and with multiple layers of defense against rogue disk images.
libguestfs provides many tools designed for accessing and modifying VM Guest disk images and contents. These tools provide such capabilities as: viewing and editing files inside guests, scripting changes to VM Guests, monitoring disk used/free statistics, creating guests, doing V2V or P2V migrations, performing backups, cloning VM Guests, formatting disks, and resizing disks.
Warning: Best Practices
You must not use libguestfs tools on live virtual machines. Doing so will probably result in disk corruption in the VM Guest. libguestfs tools try to stop you from doing this, but cannot catch all cases.
However most command have the --ro (read-only) option.
With this option, you can attach a command to a live virtual machine.
The results might be strange or inconsistent at times but you will not
risk disk corruption.
17.2 Package Installation #
libguestfs is shipped through 4 packages:
libguestfs0: which provides the main C libraryguestfs-data: which contains the appliance files used when launching images (stored in/usr/lib64/guestfs)guestfs-tools: the core guestfs tools, man pages, and the/etc/libguestfs-tools.confconfiguration file.guestfs-winsupport: provides support for Windows file guests in the guestfs tools. This package only needs to be installed to handle Windows guests, for example when converting a Windows guest to KVM.
To install guestfs tools on your system run:
zypper in guestfs-tools
17.3 Guestfs Tools #
17.3.1 Modifying Virtual Machines #
The set of tools found within the guestfs-tools package is used for
accessing and modifying virtual machine disk images. This functionality
is provided through a familiar shell interface with built-in safeguards
which ensure image integrity. Guestfs tools shells expose all
capabilities of the guestfs API, and create an appliance on the fly
using the packages installed on the machine and the files found in
/usr/lib4/guestfs.
17.3.2 Supported File Systems and Disk Images #
Guestfs tools support various file systems including:
Ext2, Ext3, Ext4
Xfs
Btrfs
Multiple disk image formats are also supported:
raw
qcow2
Warning: Unsupported File System
Guestfs may also support Windows* file systems (VFAT, NTFS), BSD* and Apple* file systems, and other disk image formats (VMDK, VHDX...). However, these file systems and disk image formats are unsupported on SUSE Linux Enterprise.
17.3.3 virt-rescue #
virt-rescue is similar to a rescue CD, but for
virtual machines, and without the need for a CD. virt-rescue presents
users with a rescue shell and some simple recovery tools which can be
used to examine and correct problems within a virtual machine or disk
image.
tux > virt-rescue -a sles.qcow2
Welcome to virt-rescue, the libguestfs rescue shell.
Note: The contents of / are the rescue appliance.
You need to mount the guest's partitions under /sysroot
before you can examine them. A helper script for that exists:
mount-rootfs-and-do-chroot.sh /dev/sda2
><rescue>
[ 67.194384] EXT4-fs (sda1): mounting ext3 file system
using the ext4 subsystem
[ 67.199292] EXT4-fs (sda1): mounted filesystem with ordered data
mode. Opts: (null)
mount: /dev/sda1 mounted on /sysroot.
mount: /dev bound on /sysroot/dev.
mount: /dev/pts bound on /sysroot/dev/pts.
mount: /proc bound on /sysroot/proc.
mount: /sys bound on /sysroot/sys.
Directory: /root
Thu Jun 5 13:20:51 UTC 2014
(none):~ #You are now running the VM Guest in rescue mode:
(none):~ # cat /etc/fstab devpts /dev/pts devpts mode=0620,gid=5 0 0 proc /proc proc defaults 0 0 sysfs /sys sysfs noauto 0 0 debugfs /sys/kernel/debug debugfs noauto 0 0 usbfs /proc/bus/usb usbfs noauto 0 0 tmpfs /run tmpfs noauto 0 0 /dev/disk/by-id/ata-QEMU_HARDDISK_QM00001-part1 / ext3 defaults 1 1
17.3.4 virt-resize #
virt-resize is used to resize a virtual machine disk,
making it larger or smaller overall, and resizing or deleting any
partitions contained within.
Procedure 17.1: Expanding a Disk #
Full step-by-step example: How to expand a virtual machine disk
First, with virtual machine powered off, determine the size of the partitions available on this virtual machine:
tux >virt-filesystems --long --parts --blkdevs -h -a sles.qcow2 Name Type MBR Size Parent /dev/sda1 partition 83 16G /dev/sda /dev/sda device - 16G -virt-resizecannot do in-place disk modifications—there must be sufficient space to store the resized output disk. Use thetruncatecommand to create a file of suitable size:tux >truncate -s 32G outdisk.imgUse
virt-resizeto resize the disk image.virt-resizerequires two mandatory parameters for the input and output images:tux >virt-resize --expand /dev/sda1 sles.qcow2 outdisk.img Examining sles.qcow2 ... ********** Summary of changes: /dev/sda1: This partition will be resized from 16,0G to 32,0G. The filesystem ext3 on /dev/sda1 will be expanded using the 'resize2fs' method. ********** Setting up initial partition table on outdisk.img ... Copying /dev/sda1 ... ◐ 84% ⟦▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒════════⟧ 00:03 Expanding /dev/sda1 using the 'resize2fs' method ... Resize operation completed with no errors. Before deleting the old disk, carefully check that the resized disk boots and works correctly.Confirm the image was resized properly:
tux >virt-filesystems --long --parts --blkdevs -h -a outdisk.img Name Type MBR Size Parent /dev/sda1 partition 83 32G /dev/sda /dev/sda device - 32G -Bring up the VM Guest using the new disk image and confirm correct operation before deleting the old image.
17.3.5 Other virt-* Tools #
There are guestfs tools to simplify administrative tasks—such as viewing and editing files, or obtaining information on the virtual machine.
17.3.5.1 virt-filesystems #
This tool is used to report information regarding file systems, partitions, and logical volumes in a disk image or virtual machine.
tux > virt-filesystems -l -a sles.qcow2
Name Type VFS Label Size Parent
/dev/sda1 filesystem ext3 - 17178820608 -17.3.5.2 virt-ls #
virt-ls lists file names, file sizes, checksums,
extended attributes and more from a virtual machine or disk image.
Multiple directory names can be given, in which case the output from
each is concatenated. To list directories from a libvirt guest, use the
-d option to specify the name of the guest. For a disk
image, use the -a option.
tux > virt-ls -h -lR -a sles.qcow2 /var/log/
d 0755 4,0K /var/log/
d 0700 4,0K /var/log//YaST2
- 0644 1,9K /var/log//YaST2/mkinitrd.log
- 0644 496 /var/log//YaST2/perl-BL-standalone-log
- 0600 3,2K /var/log//faillog
d 0700 4,0K /var/log//krb5
- 0644 29K /var/log//lastlog
- 0644 496 /var/log//pbl.log
- 0664 0 /var/log//wtmp
d 0755 4,0K /var/log//zypp17.3.5.3 virt-cat #
virt-cat is a command line tool to display the
contents of a file that exists in the named virtual machine (or disk
image). Multiple file names can be given, in which case they are
concatenated together. Each file name must be a full path, starting at
the root directory (starting with '/').
tux > virt-cat -a sles.qcow2 /etc/fstab
devpts /dev/pts devpts mode=0620,gid=5 0 0
proc /proc proc defaults 0 017.3.5.4 virt-df #
virt-df is a command line tool to display free space
on virtual machine file systems. Unlike other tools, it does not just
display the size of disk allocated to a virtual machine, but can look
inside disk images to show how much space is actually being used.
tux > virt-df -a sles.qcow2
Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use%
sles.qcow2:/dev/sda1 16381864 520564 15022492 4%17.3.5.5 virt-edit #
virt-edit is a command line tool capable of editing
files that reside in the named virtual machine (or disk image).
17.3.5.6 virt-tar-in/out #
virt-tar-in unpacks an uncompressed TAR archive into a
virtual machine disk image or named libvirt domain.
virt-tar-out packs a virtual machine disk image
directory into a TAR archive.
tux > virt-tar-out -a sles.qcow2 /home homes.tar17.3.5.7 virt-copy-in/out #
virt-copy-in copies files and directories from the
local disk into a virtual machine disk image or named libvirt domain.
virt-copy-out copies files and directories out of a
virtual machine disk image or named libvirt domain.
tux > virt-copy-in -a sles.qcow2 data.tar /tmp/
virt-ls -a sles.qcow2 /tmp/
.ICE-unix
.X11-unix
data.tar17.3.5.8 virt-log #
virt-log shows the log files of the named libvirt
domainvirtual machine or disk image. If the package
guestfs-winsupport is installed
it can also show the events log of a Windows virtual machine disk image.
tux > virt-log -a windows8.qcow2
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" standalone="yes" ?>
<Events>
<Event xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/win/2004/08/events/event"><System><Provider Name="EventLog"></Provider>
<EventID Qualifiers="32768">6011</EventID>
<Level>4</Level>
<Task>0</Task>
<Keywords>0x0080000000000000</Keywords>
<TimeCreated SystemTime="2014-09-12 05:47:21"></TimeCreated>
<EventRecordID>1</EventRecordID>
<Channel>System</Channel>
<Computer>windows-uj49s6b</Computer>
<Security UserID=""></Security>
</System>
<EventData><Data><string>WINDOWS-UJ49S6B</string>
<string>WIN-KG190623QG4</string>
</Data>
<Binary></Binary>
</EventData>
</Event>
...17.3.6 guestfish #
guestfish is a shell and command line tool for
examining and modifying virtual machine file systems. It uses libguestfs
and exposes all of the functionality of the guestfs API.
Examples of usage:
tux > guestfish -a disk.img <<EOF
run
list-filesystems
EOFguestfish
Welcome to guestfish, the guest filesystem shell for
editing virtual machine filesystems and disk images.
Type: 'help' for help on commands
'man' to read the manual
'quit' to quit the shell
><fs> add sles.qcow2
><fs> run
><fs> list-filesystems
/dev/sda1: ext3
><fs> mount /dev/sda1 /
cat /etc/fstab
devpts /dev/pts devpts mode=0620,gid=5 0 0
proc /proc proc defaults 0 0
sysfs /sys sysfs noauto 0 0
debugfs /sys/kernel/debug debugfs noauto 0 0
usbfs /proc/bus/usb usbfs noauto 0 0
tmpfs /run tmpfs noauto 0 0
/dev/disk/by-id/ata-QEMU_HARDDISK_QM00001-part1 / ext3 defaults 1 117.3.7 Converting a Physical Machine into a KVM Guest #
Libguestfs provides tools to help converting Xen virtual machines or physical machines into KVM guests. The Xen to KVM conversion scenario is covered by the . The following section will cover a special use case: converting a bare metal machine into a KVM one.
Converting a physical machine into a KVMone is not yet supported in openSUSE Leap. This feature is released as a technology preview only.
Converting a physical machine requires collecting information about
it and transmitting this to a conversion server. This is achieved by
running a live system prepared with virt-p2v and
kiwi tools on the machine.
Procedure 17.2: Using virt-p2v #
Install the needed packages with the command:
root #zypper in virt-p2v kiwi-desc-isoboot
Note
These steps will document how to create an ISO image to create a bootable DVD. Alternatively, you can create a PXE boot image instead; for more information about building PXE images with kiwi, see
man virt-p2v-make-kiwi.Create a kiwi configuration:
tux >virt-p2v-make-kiwi -o /tmp/p2v.kiwiThe
-odefines where to create the kiwi configuration.Edit the
config.xmlfile in the generated configuration if needed. For example, inconfig.xmladjust the keyboard layout of the live system.Build the ISO image with
kiwi:tux >kiwi --build /tmp/p2v.kiwi1 \ -d /tmp/build2 \ --ignore-repos \ --add-repo http://url/to/SLE/repositories3 \ --type isoBurn the ISO on a DVD or a USB stick. With such a medium, boot the machine to be converted.
Once the system is started, you will be asked for the connection details of the conversion server. This server is a machine with the
virt-v2vpackage installed.If the network setup is more complex than a DHCP client, click the button to open the YaST network configuration dialog.
Click the button to allow moving to the next page of the wizard.
Select the disks and network interfaces to be converted and define the VM data like the amount of allocated CPUs, memory and the Virtual Machine name.

Note
If not defined, the created disk image format will be raw by default. This can be changed by entering the desired format in the field.
There are two possibilities to generate the virtual machine: either using the local or the libvirt output. The first one will place the Virtual Machine disk image and configuration in the path defined in the field. These can then be used to define a new libvirt-handled guest using
virsh. The second method will create a new libvirt-handled guest with the disk image placed in the pool defined in the field.Click the to start it.
17.4 Troubleshooting #
17.4.1 Btrfs-related Problems #
When using the guestfs tools on an image with Btrfs root partition (the default with SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12) the following error message could be provided:
tux > virt-ls -a /path/to/sles12sp2.qcow2 /
virt-ls: multi-boot operating systems are not supported
If using guestfish '-i' option, remove this option and instead
use the commands 'run' followed by 'list-filesystems'.
You can then mount filesystems you want by hand using the
'mount' or 'mount-ro' command.
If using guestmount '-i', remove this option and choose the
filesystem(s) you want to see by manually adding '-m' option(s).
Use 'virt-filesystems' to see what filesystems are available.
If using other virt tools, multi-boot operating systems won't work
with these tools. Use the guestfish equivalent commands
(see the virt tool manual page).
This is usually caused by the presence of snapshots in the guests. In this
case guestfs does not know what snapshot to bootstrap. To force the
use of a snapshot, use the -m parameter as following:
tux > virt-ls -m /dev/sda2:/:subvol=@/.snapshots/2/snapshot -a /path/to/sles12sp2.qcow2 /17.4.2 Environment #
When troubleshooting problems within a libguestfs appliance, the environment variable LIBGUESTFS_DEBUG=1 can be used to enable debug messages. To output each command/API call in a format that is similar to guestfish commands, use the environment variable LIBGUESTFS_TRACE=1.
17.4.3 libguestfs-test-tool #
libguestfs-test-tool is a test program that checks if
basic libguestfs functionality is working. It will print a large amount
of diagnostic messages and details of the guestfs environment, then
create a test image and try to start it. If it runs to completion
successfully, the following message should be seen near the end:
===== TEST FINISHED OK =====
17.5 External References #
Part IV Managing Virtual Machines with Xen #
- 18 Setting Up a Virtual Machine Host
This section documents how to set up and use openSUSE Leap 42.2 as a virtual machine host.
- 19 Virtual Networking
A VM Guest system needs some means to communicate either with other VM Guest systems or with a local network. The network interface to the VM Guest system is made of a split device driver, which means that any virtual Ethernet device has a corresponding network interface in Dom0. This interface is s…
- 20 Managing a Virtualization Environment
Apart from using the recommended
libvirtlibrary (Part II, “Managing Virtual Machines withlibvirt”), you can manage Xen guest domains with thexltool from the command line.- 21 Block Devices in Xen
- 22 Virtualization: Configuration Options and Settings
The documentation in this section, describes advanced management tasks and configuration options that might help technology innovators implement leading-edge virtualization solutions. It is provided as a courtesy and does not imply that all documented options and tasks are supported by Novell, Inc.
- 23 Administrative Tasks
- 24 XenStore: Configuration Database Shared between Domains
This section introduces basic information about XenStore, its role in the Xen environment, the directory structure of files used by XenStore, and the description of XenStore's commands.
- 25 Xen as a High-Availability Virtualization Host
Setting up two Xen hosts as a failover system has several advantages compared to a setup where every server runs on dedicated hardware.
18 Setting Up a Virtual Machine Host #
This section documents how to set up and use openSUSE Leap 42.2 as a virtual machine host.
Usually, the hardware requirements for the Dom0 are the same as those for the openSUSE Leap operating system, but additional CPU, disk, memory, and network resources should be added to accommodate the resource demands of all planned VM Guest systems.
Tip: Resources
Remember that VM Guest systems, like physical machines, perform better when they run on faster processors and have access to more system memory.
The virtual machine host requires several software packages and their dependencies to be installed. To install all necessary packages, run YaST , select › and choose for installation. The installation can also be performed with YaST using the module › .
After the Xen software is installed, restart the computer and, on the boot screen, choose the newly added option with the Xen kernel.
Updates are available through your update channel. To be sure to have the latest updates installed, run YaST after the installation has finished.
18.1 Best Practices and Suggestions #
When installing and configuring the SUSE Linux Enterprise operating system on the host, be aware of the following best practices and suggestions:
If the host should always run as Xen host, run YaST › and activate the Xen boot entry as default boot section.
In YaST, click .
Change the default boot to the label, then click .
Click .
For best performance, only the applications and processes required for virtualization should be installed on the virtual machine host.
When using both iSCSI and OCFS2 to host Xen images, the latency required for OCFS2 default timeouts in SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 may not be met. To reconfigure this timeout, run
systemctl configure o2cbor editO2CB_HEARTBEAT_THRESHOLDin the system configuration.If you intend to use a watchdog device attached to the Xen host, use only one at a time. It is recommended to use a driver with actual hardware integration over a generic software one.
Note: Hardware Monitoring
The Dom0 Kernel is running virtualized, so tools like
irqbalance or lscpu will not reflect
the real hardware characteristics.
18.2 Managing Dom0 Memory #
When the host is set up, a percentage of system memory is reserved for the hypervisor, and all remaining memory is automatically allocated to Dom0.
A better solution is to set a default amount of memory for Dom0, so the memory can be allocated appropriately to the hypervisor. An adequate amount would be 20 percent of the total system memory up to 4 GiB. A recommended minimum amount would be 512 MiB
Warning: Minimum amount of Memory
The minimum amount of memory heavily depends on how many VM Guest(s) the host should handle. So be sure you have enough memory to support all your VM Guests. If the value is too low, the host system may hang when multiple VM Guests use most of the memory.
18.2.1 Setting a Maximum Amount of Memory #
Determine the amount of memory to set for Dom0.
At Dom0, type
xl infoto view the amount of memory that is available on the machine. The memory that is currently allocated by Dom0 can be determined with the commandxl list.Run › .
Select the Xen section.
In , add
dom0_mem=mem_amountwhere mem_amount is the maximum amount of memory to allocate to Dom0. AddK,M, orG, to specify the size, for example,dom0_mem=768M.Restart the computer to apply the changes.
Warning: Xen Dom0 Memory
When using the XL tool stack and the dom0_mem= option
for the Xen hypervisor in GRUB 2 you need to disable xl
autoballoon in etc/xen/xl.conf,
otherwise launching VMs will fail with errors about not being able to
balloon down Dom0. So add autoballoon=0 to
xl.conf if you have the dom0_mem=
option specified for Xen. Also see
Xen
dom0 memory
18.3 Network Card in Fully Virtualized Guests #
In a fully virtualized guest, the default network card is an emulated Realtek network card. However, it also possible to use the split network driver to run the communication between Dom0 and a VM Guest. By default, both interfaces are presented to the VM Guest, because the drivers of some operating systems require both to be present.
When using SUSE Linux Enterprise, only the paravirtualized network cards are available for the VM Guest by default. The following network options are available:
- emulated
To use an emulated network interface like an emulated Realtek card, specify
type=ioemuin thevifdevice section of the domain xl configuration. An example configuration would look like:vif = [ 'type=ioemu,mac=00:16:3e:5f:48:e4,bridge=br0' ]
Find more details about the xl configuration in the
xl.confmanual pageman 5 xl.conf.- paravirtualized
When you specify
type=vifand do not specify a model or type, the paravirtualized network interface is used:vif = [ 'type=vif,mac=00:16:3e:5f:48:e4,bridge=br0,backen=0' ]
- emulated and paravirtualized
If the administrator should be offered both options, simply specify both type and model. The xl configuration would look like:
vif = [ 'type=ioemu,mac=00:16:3e:5f:48:e4,model=rtl8139,bridge=br0' ]
In this case, one of the network interfaces should be disabled on the VM Guest.
18.4 Starting the Virtual Machine Host #
If virtualization software is correctly installed, the computer boots to display the GRUB 2 boot loader with a option on the menu. Select this option to start the virtual machine host.
Note: Xen and Kdump
In Xen, the hypervisor manages the memory resource. If you need to
reserve system memory for a recovery kernel in Dom0, this memory need to
be reserved by the hypervisor. Thus, it is necessary to add the parameter
crashkernel=size to the kernel
line instead of using the line with the other boot options.
For more information on the crashkernel parameter, see
Book “System Analysis and Tuning Guide”, Chapter 17 “Kexec and Kdump”, Section 17.4 “Calculating crashkernel Allocation Size”.
If the option is not on the GRUB 2 menu, review the steps for installation and verify that the GRUB 2 boot loader has been updated. If the installation has been done without selecting the Xen pattern, run the YaST , select the filter and choose for installation.
After booting the hypervisor, the Dom0 virtual machine starts and displays its graphical desktop environment. If you did not install a graphical desktop, the command line environment appears.
Tip: Graphics Problems
Sometimes it may happen that the graphics system does not work properly. In
this case, add vga=ask to the boot parameters. To
activate permanent settings, use vga=mode-0x??? where
??? is calculated as 0x100 + VESA
mode from
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/VESA_BIOS_Extensions, for
example vga=mode-0x361.
Before starting to install virtual guests, make sure that the system time is correct. To do this, configure NTP (Network Time Protocol) on the controlling domain:
In YaST select › .
Select the option to automatically start the NTP daemon during boot. Provide the IP address of an existing NTP time server, then click .
Note: Time Services on Virtual Guests
Hardware clocks commonly are not very precise. All modern operating systems
try to correct the system time compared to the hardware time by means of an
additional time source. To get the correct time on all VM Guest systems,
also activate the network time services on each respective guest or make
sure that the guest uses the system time of the host. For more about
Independent Wallclocks in openSUSE Leap see
Section 16.2, “Xen Virtual Machine Clock Settings”.
For more information about managing virtual machines, see Chapter 20, Managing a Virtualization Environment.
18.5 PCI Pass-Through #
To take full advantage of VM Guest systems, it is sometimes necessary to assign specific PCI devices to a dedicated domain. When using fully virtualized guests, this functionality is only available if the chipset of the system supports this feature, and if it is activated from the BIOS.
This feature is available from both AMD* and Intel*. For AMD machines, the feature is called IOMMU; in Intel speak, this is VT-d. Note that Intel-VT technology is not sufficient to use this feature for fully virtualized guests. To make sure that your computer supports this feature, ask your supplier specifically to deliver a system that supports PCI Pass-Through.
Limitations #
Some graphics drivers use highly optimized ways to access DMA. This is not supported, and thus using graphics cards may be difficult.
When accessing PCI devices behind a PCIe bridge, all of the PCI devices must be assigned to a single guest. This limitation does not apply to PCIe devices.
Guests with dedicated PCI devices cannot be migrated live to a different host.
The configuration of PCI Pass-Through is twofold. First, the hypervisor must be informed at boot time that a PCI device should be available for reassigning. Second, the PCI device must be assigned to the VM Guest.
18.5.1 Configuring the Hypervisor for PCI Pass-Through #
Select a device to reassign to a VM Guest. To do this, run
lspciand read the device number. For example, iflspcicontains the following line:06:01.0 Ethernet controller: Digital Equipment Corporation DECchip 21142/43 (rev 41)
In this case, the PCI number is
(06:01.0).Run › › .
Select the
Xensection and press .Add the PCI number to the line:
pciback.hide=(06:01.0)
Press and exit YaST.
Reboot the system.
Check if the device is in the list of assignable devices with the command
xl pci-assignable-list
18.5.1.1 Dynamic Assignment with xl #
To avoid restarting the host system, you can use dynamic assignment with xl to use PCI Pass-Through.
Begin by making sure that dom0 has the pciback module loaded:
modprobe pciback
Then make a device assignable by using xl
pci-assignable-add. For example, to make the
device 06:01.0 available for guests, run the command:
xl pci-assignable-add 06:01.0
18.5.2 Assigning PCI Devices to VM Guest Systems #
There are several possibilities to dedicate a PCI device to a VM Guest:
- Adding the device while installing:
During installation, add the
pciline to the configuration file:pci=['06:01.0']
- Hotplugging PCI devices to VM Guest systems
The command
xlcan be used to add or remove PCI devices on the fly. To add the device with number06:01.0to a guest with namesles12use:xl pci-attach sles12 06:01.0
- Adding the PCI device to Xend
To add the device to the guest permanently, add the following snippet to the guest configuration file:
pci = [ '06:01.0,power_mgmt=1,permissive=1' ]
After assigning the PCI device to the VM Guest, the guest system must care for the configuration and device drivers for this device.
18.5.3 VGA Pass-Through #
Xen 4.0 and newer supports VGA graphics adapter pass-through on fully virtualized VM Guests. The guest can take full control of the graphics adapter with high-performance full 3D and video acceleration.
Limitations #
VGA Pass-Through functionality is similar to PCI Pass-Through and as such also requires IOMMU (or Intel VT-d) support from the mainboard chipset and BIOS.
Only the primary graphics adapter (the one that is used when you power on the computer) can be used with VGA Pass-Through.
VGA Pass-Through is supported only for fully virtualized guests. Paravirtual guests (PV) are not supported.
The graphics card cannot be shared between multiple VM Guests using VGA Pass-Through — you can dedicate it to one guest only.
To enable VGA Pass-Through, add the following settings to your fully virtualized guest configuration file:
gfx_passthru=1 pci=['yy:zz.n']
where yy:zz.n is the PCI controller ID of the VGA
graphics adapter as found with lspci -v on Dom0.
18.5.4 Troubleshooting #
In some circumstances, problems may occur during the installation of the VM Guest. This section describes some known problems and their solutions.
- During boot, the system hangs
The software I/O translation buffer allocates a large chunk of low memory early in the bootstrap process. If the requests for memory exceed the size of the buffer it usually results in a hung boot process. To check if this is the case, switch to console 10 and check the output there for a message similar to
kernel: PCI-DMA: Out of SW-IOMMU space for 32768 bytes at device 000:01:02.0
In this case you need to increase the size of the
swiotlb. Addswiotlb=128on the cmdline of Dom0. Note that the number can be adjusted up or down to find the optimal size for the machine.
Note: swiotlb a PV guest
The swiotlb=force kernel parameter is required for DMA
access to work for PCI devices on a PV guest. For more information about
IOMMU and the swiotlb option see the file
boot-options.txt from the package
kernel-source.
18.5.5 For More Information #
There are several resources on the Internet that provide interesting information about PCI Pass-Through:
18.6 USB Pass-Through with PVUSB #
PVUSB is a new high performance method for USB Pass-Through from dom0 to the virtualized guests. PVUSB supports both, USB 2.0 and USB 1.1 devices. PVUSB uses a paravirtualized front- and back-end interface. With PVUSB, there are two ways to add USB devices to a guest:
via the config file at domain creation time
via hot-plug while the VM is running
PVUSB uses a paravirtualized front- and back-end interface. PVUSB supports USB 1.1 and USB 2.0, and it works for both, PV and HVM guests. In order to use PVUSB, you need usbfront in your guest OS, and usbback in dom0 or usb backend in qemu. With SUSE Linux Enterprise Server, usb backend comes with qemu.
Use lsusb to list the USB devices on the system:
root # lsusb
Bus 001 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0002 Linux Foundation 2.0 root hub
Bus 002 Device 003: ID 0461:4d15 Primax Electronics, Ltd Dell Optical Mouse
Bus 002 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0001 Linux Foundation 1.1 root hub
To pass through the Dell mouse, for instance, specify either
0461:4d15 or 2.3 (you must remove leading zeros, otherwise
xl would interpret the numbers as octal values).
As of Xen 4.7, xl PVUSB support and hot-plug
support is introduced.
In the configuration file, specify USB controllers and USB host
devices with usbctrl and usbdev. For
example, in case of HVM guests:
usbctrl=['type=qubs,version=2,ports=4', 'type=qubs,version=1,ports=4', ] usbdev=['hostbus=2, hostaddr=1, controller=0,port=1', ]
Note
It is important to specify type=qusb for the
controller of HVM guests.
To manage hot-pluggin PVUSB devices, use the
usbctrl-attach, usbctrl-detach,
usb-list, usbdev-attach and
usb-detach subcommands. For example:
Create a USB controller which is version USB 1.1 and has 8 ports:
root # xl usbctrl-attach test_vm version=1 ports=8 type=qusb
Find the first available controller:port in the domain, and attach USB
device whose busnum:devnum is 2:3 to it; you can also specify
controller and port:
root # xl usbdev-attach test_vm hostbus=2 hostaddr=3Show all USB controllers and USB devices in the domain:
root # xl usb-list test_vm
Devid Type BE state usb-ver ports
0 qusb 0 1 1 8
Port 1: Bus 002 Device 003
Port 2:
Port 3:
Port 4:
Port 5:
Port 6:
Port 7:
Port 8:Detach the USB device under controller 0 port 1:
root # xl usbdev-detach test_vm 0 1
Remove the USB controller with the indicated dev_id,
and all USB devices under it:
root # xl usbctrl-detach test_vm dev_idFor more information, see https://wiki.xenproject.org/wiki/Xen_USB_Passthrough.
19 Virtual Networking #
A VM Guest system needs some means to communicate either with other VM Guest systems or with a local network. The network interface to the VM Guest system is made of a split device driver, which means that any virtual Ethernet device has a corresponding network interface in Dom0. This interface is set up to access a virtual network that is run in Dom0. The bridged virtual network is fully integrated into the system configuration of openSUSE Leap and can be configured with YaST.
When installing a Xen VM Host Server, a bridged network configuration will be proposed during normal network configuration. The user can choose to change the configuration during the installation and customize it to the local needs.
If desired, Xen VM Host Server can be installed after performing a
default Physical Server installation using the Install
Hypervisor and Tools module in YaST. This module will
prepare the system for hosting virtual machines, including invocation of
the default bridge networking proposal.
In case the necessary packages for a Xen VM Host Server are installed
manually with rpm or
zypper, the remaining system configuration needs to
be done by the administrator manually or with YaST.
The network scripts that are provided by Xen are not used by default in openSUSE Leap. They are only delivered for reference but disabled. The network configuration that is used in openSUSE Leap is done by means of the YaST system configuration similar to the configuration of network interfaces in openSUSE Leap.
For more general information about managing network bridges, see Section 13.2, “Bridged Networking”.
19.1 Network Devices for Guest Systems #
The Xen hypervisor can provide different types of network interfaces to the VM Guest systems. The preferred network device should be a paravirtualized network interface. This yields the highest transfer rates with the lowest system requirements. Up to eight network interfaces may be provided for each VM Guest.
Systems that are not aware of paravirtualized hardware may not have this option. To connect systems to a network that can only run fully virtualized, several emulated network interfaces are available. The following emulations are at your disposal:
Realtek 8139 (PCI). This is the default emulated network card.
AMD PCnet32 (PCI)
NE2000 (PCI)
NE2000 (ISA)
Intel e100 (PCI)
Intel e1000 and its variants e1000-82540em, e1000-82544gc, e1000-82545em (PCI)
All these network interfaces are software interfaces. Because every network interface must have a unique MAC address, an address range has been assigned to Xensource that can be used by these interfaces.
Tip: Virtual Network Interfaces and MAC Addresses
The default configuration of MAC addresses in virtualized environments creates a random MAC address that looks like 00:16:3E:xx:xx:xx. Normally, the amount of available MAC addresses should be big enough to get only unique addresses. However, if you have a very big installation, or to make sure that no problems arise from random MAC address assignment, you can also manually assign these addresses.
For debugging or system management purposes, it may be useful to know
which virtual interface in Dom0 is connected to which Ethernet
device in a running guest. This information may be read from the device
naming in Dom0. All virtual devices follow the rule
vif<domain
number>.<interface_number>.
For example, if you want to know the device name for the third interface
(eth2) of the VM Guest with id 5, the device in Dom0 would be
vif5.2. To obtain a list of all available interfaces,
run the command ip a.
The device naming does not contain any information about which bridge
this interface is connected to. However, this information is available in
Dom0. To get an overview about which interface is connected to which
bridge, run the command brctl show. The output may
look like the following:
# brctl show
bridge name bridge id STP enabled interfaces
br0 8000.001cc0309083 no eth0
vif2.1
br1 8000.000476f060cc no eth1
vif2.0
br2 8000.000000000000 no
In this example, there are three configured bridges:
br0, br1 and
br2. Currently, br0 and
br1 each have a real Ethernet device added:
eth0 and eth1, respectively. There is
one VM Guest running with the ID 2 that has two Ethernet devices available.
eth0 on the VM Guest is bridged with
eth1 on the VM Host Server and eth1 on the VM Guest is
connected to eth0 on the VM Host Server. The third bridge with
the name br2 is not connected to any VM Guest nor any
real Ethernet device.
19.2 Host-Based Routing in Xen #
Xen can be set up to use host-based routing in the controlling Dom0. Unfortunately, this is not yet well supported from YaST and requires quite an amount of manual editing of configuration files. Thus, this is a task that requires an advanced administrator.
The following configuration will only work when using fixed IP addresses. Using DHCP is not practicable with this procedure, because the IP address must be known to both, the VM Guest and the VM Host Server system.
The easiest way to create a routed guest is to change the networking from a bridged to a routed network. As a requirement to the following procedures, a VM Guest with a bridged network setup must be installed. For example, the VM Host Server is named earth with the IP 192.168.1.20, and the VM Guest has the name alice with the IP 192.168.1.21.
Procedure 19.1: Configuring a routed IPv4 VM Guest #
Make sure that alice is shut down. Use
xlcommands to shut down and check.Prepare the network configuration on the VM Host Server earth:
Create a hotplug interface that will be used to route the traffic. To accomplish this, create a file named
/etc/sysconfig/network/ifcfg-alice.0with the following content:NAME="Xen guest alice" BOOTPROTO="static" STARTMODE="hotplug"
Edit the file
/etc/sysconfig/SuSEfirewall2and add the following configurations:Add alice.0 to the devices in FW_DEV_EXT:
FW_DEV_EXT="br0 alice.0"
Switch on the routing in the firewall:
FW_ROUTE="yes"
Tell the firewall which address should be forwarded:
FW_FORWARD="192.168.1.21/32,0/0"
Finally, restart the firewall with the command:
sudo systemctl restart SuSEfirewall2
Add a static route to the interface of alice. To accomplish this, add the following line to the end of
/etc/sysconfig/network/routes:192.168.1.21 - - alice.0
To make sure that the switches and routers that the VM Host Server is connected to know about the routed interface, activate
proxy_arpon earth. Add the following lines to/etc/sysctl.conf:net.ipv4.conf.default.proxy_arp = 1 net.ipv4.conf.all.proxy_arp = 1
Activate all changes with the commands:
sudo systemctl restart systemd-sysctl wicked
Proceed with configuring the Xen configuration of the VM Guest by changing the vif interface configuration for alice as described in Section 20.1, “XL—Xen Management Tool”. Make the following changes to the text file you generate during the process:
Remove the snippet
bridge=br0
And add the following one:
vifname=vifalice.0
or
vifname=vifalice.0=emu
for a fully virtualized domain.
Change the script that is used to set up the interface to the following:
script=/etc/xen/scripts/vif-route-ifup
Activate the new configuration and start the VM Guest.
The remaining configuration tasks must be accomplished from inside the VM Guest.
Open a console to the VM Guest with
xl consoledomain and log in.Check that the guest IP is set to 192.168.1.21.
Provide VM Guest with a host route and a default gateway to the VM Host Server. Do this by adding the following lines to
/etc/sysconfig/network/routes:192.168.1.20 - - eth0 default 192.168.1.20 - -
Finally, test the network connection from the VM Guest to the world outside and from the network to your VM Guest.
19.3 Creating a Masqueraded Network Setup #
Creating a masqueraded network setup is quite similar to the routed
setup. However, there is no proxy_arp needed, and some firewall rules are
different. To create a masqueraded network to a guest dolly
with the IP address 192.168.100.1 where the host has its external
interface on br0, proceed as follows. For easier
configuration, only the already installed guest is modified to use a
masqueraded network:
Procedure 19.2: Configuring a masqueraded IPv4 VM Guest #
Shut down the VM Guest system with
xl shutdowndomain.Prepare the network configuration on the VM Host Server:
Create a hotplug interface that will be used to route the traffic. To accomplish this, create a file named
/etc/sysconfig/network/ifcfg-dolly.0with the following content:NAME="Xen guest dolly" BOOTPROTO="static" STARTMODE="hotplug"
Edit the file
/etc/sysconfig/SuSEfirewall2and add the following configurations:Add dolly.0 to the devices in FW_DEV_DMZ:
FW_DEV_DMZ="dolly.0"
Switch on the routing in the firewall:
FW_ROUTE="yes"
Switch on masquerading in the firewall:
FW_MASQUERADE="yes"
Tell the firewall which network should be masqueraded:
FW_MASQ_NETS="192.168.100.1/32"
Remove the networks from the masquerading exceptions:
FW_NOMASQ_NETS=""
Finally, restart the firewall with the command:
sudo systemctl restart SuSEfirewall2
Add a static route to the interface of dolly. To accomplish this, add the following line to the end of
/etc/sysconfig/network/routes:192.168.100.1 - - dolly.0
Activate all changes with the command:
sudo systemctl restart wicked
Proceed with configuring the Xen configuration of the VM Guest.
Change the vif interface configuration for dolly as described in Section 20.1, “XL—Xen Management Tool”.
Remove the entry:
bridge=br0
And add the following one:
vifname=vifdolly.0
Change the script that is used to set up the interface to the following:
script=/etc/xen/scripts/vif-route-ifup
Activate the new configuration and start the VM Guest.
The remaining configuration tasks need to be accomplished from inside the VM Guest.
Open a console to the VM Guest with
xl consoledomain and log in.Check whether the guest IP is set to 192.168.100.1.
Provide VM Guest with a host route and a default gateway to the VM Host Server. Do this by adding the following lines to
/etc/sysconfig/network/routes:192.168.1.20 - - eth0 default 192.168.1.20 - -
Finally, test the network connection from the VM Guest to the outside world.
19.4 Special Configurations #
There are many network configuration possibilities available to Xen. The following configurations are not activated by default:
19.4.1 Bandwidth Throttling in Virtual Networks #
With Xen, you may limit the network transfer rate a virtual guest may use to access a bridge. To configure this, you need to modify the VM Guest configuration as described in Section 20.1, “XL—Xen Management Tool”.
In the configuration file, first search for the device that is connected to the virtual bridge. The configuration looks like the following:
vif = [ 'mac=00:16:3e:4f:94:a9,bridge=br0' ]
To add a maximum transfer rate, add a parameter
rate to this configuration as in:
vif = [ 'mac=00:16:3e:4f:94:a9,bridge=br0,rate=100Mb/s' ]
Note that the rate is either Mb/s (megabits per
second) or MB/s (megabytes per second). In the above
example, the maximum transfer rate of the virtual interface is 100
megabits. By default, there is no limitation to the bandwidth of a guest
to the virtual bridge.
It is even possible to fine-tune the behavior by specifying the time window that is used to define the granularity of the credit replenishment:
vif = [ 'mac=00:16:3e:4f:94:a9,bridge=br0,rate=100Mb/s@20ms' ]
19.4.2 Monitoring the Network Traffic #
To monitor the traffic on a specific interface, the little application
iftop is a nice program that displays the
current network traffic in a terminal.
When running a Xen VM Host Server, you need to define the interface
that is monitored. The interface that Dom0 uses to get access to
the physical network is the bridge device, for example
br0. This, however, may vary on your system. To
monitor all traffic to the physical interface, run a terminal as
root and use the command:
iftop -i br0
To monitor the network traffic of a special network interface of a specific VM Guest, supply the correct virtual interface. For example, to monitor the first Ethernet device of the domain with id 5, use the command:
ftop -i vif5.0
To quit iftop, press the key Q. More
options and possibilities are available in the manual page man
8 iftop.
20 Managing a Virtualization Environment #
Apart from using the recommended libvirt library
(Part II, “Managing Virtual Machines with libvirt”), you can manage Xen guest
domains with the xl tool from the command line.
20.1 XL—Xen Management Tool #
The xl program is a tool for managing Xen guest
domains. It is part of the xen-tools package.
xl is based on the LibXenlight library, and can be
used for general domain management, such as domain creation, listing,
pausing, or shutting down. Usually you need to be root to
execute xl commands.
Note
xl can only manage running guest domains specified by
their configuration file. If a guest domain is not running, you cannot
manage it with xl.
Tip
To allow users to continue to have managed guest domains in the way the
obsolete xm command allowed, we now recommend using
libvirt's virsh and
virt-manager tools. For more information, see
Part II, “Managing Virtual Machines with libvirt”.
xl operations rely upon
xenstored and
xenconsoled services. Make sure you start
systemctl start xencommons
at boot time to initialize all the daemons required by
xl.
Tip: Set up a xenbr0 Network Bridge in the Host Domain
In the most common network configuration, you need to set up a bridge in
the host domain named xenbr0 to have a
working network for the guest domains.
The basic structure of every xl command is:
xl <subcommand> [options] domain_id
where <subcommand> is the xl command to run, domain_id is the ID
number assigned to a domain or the name of the virtual machine, and
OPTIONS indicates subcommand-specific options.
For a complete list of the available xl subcommands,
run xl help. For each command, there is a more
detailed help available that is obtained with the extra parameter
--help. More information about the respective
subcommands is available in the manual page of xl.
For example, the xl list --help displays all options
that are available to the list command. As an example, the xl
list command displays the status of all virtual machines.
# xl list Name ID Mem VCPUs State Time(s) Domain-0 0 457 2 r----- 2712.9 sles12 7 512 1 -b---- 16.3 opensuse 512 1 12.9
The information indicates if a machine is
running, and in which state it is. The most common flags are
r (running) and b (blocked) where
blocked means it is either waiting for IO, or sleeping because there is
nothing to do. For more details about the state flags, see man 1
xl.
Other useful xl commands include:
xl createcreates a virtual machine from a given configuration file.xl rebootreboots a virtual machine.xl destroyimmediately terminates a virtual machine.xl block-listdisplays all virtual block devices attached to a virtual machine.
20.1.1 Guest Domain Configuration File #
When operating domains, xl requires a domain
configuration file for each domain. The default directory to store such
configuration files is /etc/xen/.
A domain configuration file is a plain text file. It consists of
several
key=value
pairs. Some keys are mandatory, some are general and apply to any
guest, and some apply only to a specific guest type (para or fully
virtualized). A value can either be a "string"
surrounded by single or double quotes, a number, a boolean value, or
a list of several values enclosed in brackets [ value1,
value2, ... ].
Example 20.1: Guest Domain Configuration File: /etc/xen/sled12.cfg #
name= "sled12" builder = "hvm" vncviewer = 1 memory = 512 disk = [ '/var/lib/xen/images/sled12.raw,,hda', '/dev/cdrom,,hdc,cdrom' ] vif = [ 'mac=00:16:3e:5f:48:e4,model=rtl8139,bridge=br0' ] boot = "n"
To start such domain, run xl create
/etc/xen/sled12.cfg.
20.2 Automatic Start of Guest Domains #
To make a guest domain start automatically after the host system boots, follow these steps:
Create the domain configuration file if it does not exist, and save it in the
/etc/xen/directory, for example/etc/xen/domain_name.cfg.Make a symbolic link of the guest domain configuration file in the
auto/subdirectory.ln -s /etc/xen/domain_name.cfg /etc/xen/auto/domain_name.cfg
On the next system boot, the guest domain defined in
domain_name.cfgwill be started.
20.3 Event Actions #
In the guest domain configuration file, you can define actions to be performed on a predefined set of events. For example, to tell the domain to restart itself after it is powered off, include the following line in its configuration file:
on_poweroff="restart"
A list of predefined events for a guest domain follows:
List of Events #
- on_poweroff
Specifies what should be done with the domain if it shuts itself down.
- on_reboot
Action to take if the domain shuts down with a reason code requesting a reboot.
- on_watchdog
Action to take if the domain shuts down because of a Xen watchdog timeout.
- on_crash
Action to take if the domain crashes.
For these events, you can define one of the following actions:
List of Related Actions #
- destroy
Destroy the domain.
- restart
Destroy the domain and immediately create a new domain with the same configuration.
- rename-restart
Rename the domain that terminated, and then immediately create a new domain with the same configuration as the original.
- preserve
Keep the domain. It can be examined, and later destroyed with
xl destroy.- coredump-destroy
Write a core dump of the domain to
/var/xen/dump/NAMEand then destroy the domain.- coredump-restart
Write a core dump of the domain to
/var/xen/dump/NAMEand then restart the domain.
20.4 Time Stamp Counter #
The Time Stamp Counter (TSC) may be specified for each domain in the guest domain configuration file (for more information, see Section 20.1.1, “Guest Domain Configuration File”).
With the tsc_mode setting, you specify whether
rdtsc instructions are executed “natively” (fast, but
TSC-sensitive applications may sometimes run incorrectly) or emulated
(always run correctly, but performance may suffer).
tsc_mode=0(default)Use this to ensure correctness while providing the best performance possible—for more information, see https://xenbits.xen.org/docs/4.3-testing/misc/tscmode.txt.
tsc_mode=1(always emulate)Use this when TSC-sensitive apps are running and worst-case performance degradation is known and acceptable.
tsc_mode=2(never emulate)Use this when all applications running in this VM are TSC-resilient and highest performance is required.
tsc_mode=3(PVRDTSCP)High-TSC-frequency applications may be paravirtualized (modified) to obtain both correctness and highest performance—any unmodified applications must be TSC-resilient.
For background information, see https://xenbits.xen.org/docs/4.3-testing/misc/tscmode.txt.
20.5 Saving Virtual Machines #
Procedure 20.1: Save a Virtual Machine’s Current State #
Make sure the virtual machine to be saved is running.
In the host environment, enter
xl save ID state-file
where ID is the virtual machine ID you want to save, and state-file is the name you specify for the memory state file. By default, the domain will no longer be running after you create its snapshot. Use
-cto keep it running even after you create the snapshot.
20.6 Restoring Virtual Machines #
Procedure 20.2: Restore a Virtual Machine’s Current State #
Make sure the virtual machine to be restored has not been started since you ran the save operation.
In the host environment, enter
xl restore state-file
where state-file is the previously saved memory state file. By default, the domain will be running after it is restored. To pause it after the restore, use
-p.
20.7 Virtual Machine States #
A virtual machine’s state can be displayed by viewing the results of
the xl list command, which abbreviates the state using
a single character.
r- running - The virtual machine is currently running and consuming allocated resources.b- blocked - The virtual machine’s processor is not running and not able to run. It is either waiting for I/O or has stopped working.p- paused - The virtual machine is paused. It does not interact with the hypervisor but still maintains its allocated resources, such as memory.s- shutdown - The guest operating system is in the process of being shut down, rebooted, or suspended, and the virtual machine is being stopped.c- crashed - The virtual machine has crashed and is not running.d- dying - The virtual machine is in the process of shutting down or crashing.
21 Block Devices in Xen #
21.1 Mapping Physical Storage to Virtual Disks #
The disk(s) specification for a Xen domain in the domain configuration file is as straightforward as the following example:
disk = [ 'format=raw,vdev=hdc,access=ro,devtype=cdrom,target=/root/image.iso' ]
It defines a disk block device based on the
/root/image.iso disk image file. The disk will be seen
as hdc by the guest, with read-only
(ro) access. The type of the device is
cdrom with raw format.
The following example defines an identical device, but using simplified positional syntax:
disk = [ '/root/image.iso,raw,hdc,ro,cdrom' ]
You can include more disk definitions in the same line, each one separated by a comma. If a parameter is not specified, then its default value is taken:
disk = [ '/root/image.iso,raw,hdc,ro,cdrom','/dev/vg/guest-volume,,hda','...' ]
List of Parameters #
- target
Source block device or disk image file path.
- format
The format of the image file. Default is
raw.- vdev
Virtual device as seen by the guest. Supported values are hd[x], xvd[x], sd[x] etc. See
/usr/share/doc/packages/xen/misc/vbd-interface.txtfor more details. This parameter is mandatory.- access
Whether the block device is provided to the guest in read-only or read-write mode. Supported values are
roorrfor read-only, andrworwfor read/write access. Default isrofordevtype=cdrom, andrwfor other device types.- devtype
Qualifies virtual device type. Supported value is
cdrom.- backendtype
The back-end implementation to use. Supported values are
phy,tap, andqdisk. Normally this option should not be specified as the back-end type is automatically determined.- script
Specifies that
targetis not a normal host path, but rather information to be interpreted by the executable program. The specified script file is looked for in/etc/xen/scriptsif it does not point to an absolute path. These scripts are normally calledblock-<script_name>.
For more information about specifying virtual disks, see
/usr/share/doc/packages/xen/misc/xl-disk-configuration.txt.
21.2 Mapping Network Storage to Virtual Disk #
Similar to mapping a local disk image (see Section 21.1, “Mapping Physical Storage to Virtual Disks”), you can map a network disk as a virtual disk as well.
The following example shows mapping of an RBD (RADOS Block Device) disk with multiple Ceph monitors and cephx authentication enabled:
disk = [ 'vdev=hdc, backendtype=qdisk, \ target=rbd:libvirt-pool/new-libvirt-image:\ id=libvirt:key=AQDsPWtW8JoXJBAAyLPQe7MhCC+JPkI3QuhaAw==:auth_supported=cephx;none:\ mon_host=137.65.135.205\\:6789;137.65.135.206\\:6789;137.65.135.207\\:6789' ]
Following is an example of an NBD (Network Block Device) disk mapping:
disk = [ 'vdev=hdc, backendtype=qdisk, target=nbd:151.155.144.82:5555' ]
21.3 File-Backed Virtual Disks and Loopback Devices #
When a virtual machine is running, each of its file-backed virtual disks consumes a loopback device on the host. By default, the host allows up to 64 loopback devices to be consumed.
To simultaneously run more file-backed virtual disks on a host, you can
increase the number of available loopback devices by adding the following
option to the host’s /etc/modprobe.conf.local file.
options loop max_loop=x
where x is the maximum number of loopback devices to
create.
Changes take effect after the module is reloaded.
Tip
Enter rmmod loop and modprobe loop to
unload and reload the module. In case rmmod does not
work, unmount all existing loop devices or reboot the computer.
21.4 Resizing Block Devices #
While it is always possible to add new block devices to a VM Guest system, it is sometimes more desirable to increase the size of an existing block device. In case such a system modification is already planned during deployment of the VM Guest, some basic considerations should be done:
Use a block device that may be increased in size. LVM devices and file system images are commonly used.
Do not partition the device inside the VM Guest, but use the main device directly to apply the file system. For example, use
/dev/xvdbdirectly instead of adding partitions to/dev/xvdb.Make sure that the file system to be used can be resized. Sometimes, for example with Ext3, some features must be switched off to be able to resize the file system. A file system that can be resized online and mounted is
XFS. Use the commandxfs_growfsto resize that file system after the underlying block device has been increased in size. For more information aboutXFS, seeman 8 xfs_growfs.
When resizing an LVM device that is assigned to a VM Guest, the new size is automatically known to the VM Guest. No further action is needed to inform the VM Guest about the new size of the block device.
When using file system images, a loop device is used to attach the image file to the guest. For more information about resizing that image and refreshing the size information for the VM Guest, see Section 23.2, “Sparse Image Files and Disk Space”.
21.5 Scripts for Managing Advanced Storage Scenarios #
There are scripts that can help with managing advanced storage scenarios
such as disk environments provided by
dmmd (“device mapper—multi
disk”) including LVM environments built upon a software RAID set, or
a software RAID set built upon an LVM environment. These scripts are part of
the xen-tools package. After installation, they can be
found in /etc/xen/scripts:
block-dmmdblock-drbd-probeblock-npiv
The scripts allow for external commands to perform some action, or series of actions of the block devices prior to serving them up to a guest.
These scripts could formerly only be used with xl
or libxl using the disk configuration syntax
script=. They can now be used with libvirt by
specifying the base name of the block script in the
<source> element of the disk. For example:
<source dev='dmmd:md;/dev/md0;lvm;/dev/vgxen/lv-vm01'/>
22 Virtualization: Configuration Options and Settings #
The documentation in this section, describes advanced management tasks and configuration options that might help technology innovators implement leading-edge virtualization solutions. It is provided as a courtesy and does not imply that all documented options and tasks are supported by Novell, Inc.
22.1 Virtual CD Readers #
Virtual CD readers can be set up when a virtual machine is created or added to an existing virtual machine. A virtual CD reader can be based on a physical CD/DVD, or based on an ISO image. Virtual CD readers work differently depending on whether they are paravirtual or fully virtual.
22.1.1 Virtual CD Readers on Paravirtual Machines #
A paravirtual machine can have up to 100 block devices composed of virtual CD readers and virtual disks. On paravirtual machines, virtual CD readers present the CD as a virtual disk with read-only access. Virtual CD readers cannot be used to write data to a CD.
After you have finished accessing a CD on a paravirtual machine, it is recommended that you remove the virtual CD reader from the virtual machine.
Paravirtualized guests can use the device type
devtype=cdrom. This partly emulates the behavior of a
real CD reader, and allows CDs to be changed. It is even possible to use
the eject command to open the tray of the CD reader.
22.1.2 Virtual CD Readers on Fully Virtual Machines #
A fully virtual machine can have up to four block devices composed of
virtual CD readers and virtual disks. A virtual CD reader on a fully
virtual machine interacts with an inserted CD in the way you would
expect a physical CD reader to interact. For example, in a Windows* XP*
virtual machine, the inserted CD appears in the Devices with
Removable Storage section of My Computer.
When a CD is inserted in the physical CD reader on the host computer,
all virtual machines with virtual CD readers based on the physical CD
reader, such as /dev/cdrom/, can read the
inserted CD. Assuming the operating system has automount functionality,
the CD should automatically appear in the file system. Virtual CD
readers cannot be used to write data to a CD. They are configured as
read-only devices.
22.1.3 Adding Virtual CD Readers #
Virtual CD readers can be based on a CD inserted into the CD reader or on an ISO image file.
Make sure that the virtual machine is running and the operating system has finished booting.
Insert the desired CD into the physical CD reader or copy the desired ISO image to a location available to Dom0.
Select a new, unused block device in your VM Guest, such as
/dev/xvdb.Choose the CD reader or ISO image that you want to assign to the guest.
When using a real CD reader, use the following command to assign the CD reader to your VM Guest. In this example, the name of the guest is alice:
xl block-attach alice target=/dev/sr0,vdev=xvdb,access=ro
When assigning an image file, use the following command:
xl block-attach alice target=/path/to/file.iso,vdev=xvdb,access=ro
A new block device, such as
/dev/xvdb, is added to the virtual machine.If the virtual machine is running Linux, complete the following:
Open a terminal in the virtual machine and enter
fdisk -lto verify that the device was properly added. You can also enterls /sys/blockto see all disks available to the virtual machine.The CD is recognized by the virtual machine as a virtual disk with a drive designation, for example:
/dev/xvdb
Enter the command to mount the CD or ISO image using its drive designation. For example,
mount -o ro /dev/xvdb /mnt
mounts the CD to a mount point named
/mnt.The CD or ISO image file should be available to the virtual machine at the specified mount point.
If the virtual machine is running Windows, reboot the virtual machine.
Verify that the virtual CD reader appears in its
My Computersection.
22.1.4 Removing Virtual CD Readers #
Make sure that the virtual machine is running and the operating system has finished booting.
If the virtual CD reader is mounted, unmount it from within the virtual machine.
Enter
xl block-list aliceon the host view of the guest block devices.Enter
xl block-detach aliceblock_dev_id to remove the virtual device from the guest. If that fails, try to add-fto force the removal.Press the hardware eject button to eject the CD.
22.2 Remote Access Methods #
Some configurations, such as those that include rack-mounted servers,
require a computer to run without a video monitor, keyboard, or mouse.
This type of configuration is often called headless and
requires the use of remote administration technologies.
Typical configuration scenarios and technologies include:
- Graphical Desktop with X Window Server
If a graphical desktop, such as GNOME, is installed on the virtual machine host, you can use a remote viewer, such as a VNC viewer. On a remote computer, log in and manage the remote guest environment by using graphical tools, such as
tigervncorvirt-viewer.- Text Only
You can use the
sshcommand from a remote computer to log in to a virtual machine host and access its text-based console. You can then use thexlcommand to manage virtual machines, and thevirt-installcommand to create new virtual machines.
22.3 VNC Viewer #
VNC viewer is used to view the environment of the running guest system in a graphical way. You can use it from Dom0 (known as local access or on-box access), or from a remote computer.
You can use the IP address of a VM Host Server and a VNC viewer to view the display of this VM Guest. When a virtual machine is running, the VNC server on the host assigns the virtual machine a port number to be used for VNC viewer connections. The assigned port number is the lowest port number available when the virtual machine starts. The number is only available for the virtual machine while it is running. After shutting down, the port number might be assigned to other virtual machines.
For example, if ports 1 and 2 and 4 and 5 are assigned to the running virtual machines, the VNC viewer assigns the lowest available port number, 3. If port number 3 is still in use the next time the virtual machine starts, the VNC server assigns a different port number to the virtual machine.
To use the VNC viewer from a remote computer, the firewall must permit access to as many ports as VM Guest systems run from. This means from port 5900 and up. For example, to run 10 VM Guest systems, you need to open the TCP ports 5900:5910.
To access the virtual machine from the local console running a VNC viewer client, enter one of the following commands:
vncviewer ::590#vncviewer :#
# is the VNC viewer port number assigned to the virtual machine.
When accessing the VM Guest from a machine other than Dom0, use the following syntax:
vncviewer 192.168.1.20::590#
In this case, the IP address of Dom0 is 192.168.1.20.
22.3.1 Assigning VNC Viewer Port Numbers to Virtual Machines #
Although the default behavior of VNC viewer is to assign the first available port number, you should assign a specific VNC viewer port number to a specific virtual machine.
To assign a specific port number on a VM Guest, edit the xl setting
of the virtual machine and change the vnclisten to
the desired value. Note that for example for port number 5902, specify 2
only, as 5900 is added automatically:
vfb = [ 'vnc=1,vnclisten="localhost:2"' ]
For more information regarding editing the xl settings of a guest domain, see Section 20.1, “XL—Xen Management Tool”.
Tip
Assign higher port numbers to avoid conflict with port numbers assigned by the VNC viewer, which uses the lowest available port number.
22.3.2 Using SDL instead of a VNC Viewer #
If you access a virtual machine's display from the virtual machine host console (known as local or on-box access), you should use SDL instead of VNC viewer. VNC viewer is faster for viewing desktops over a network, but SDL is faster for viewing desktops from the same computer.
To set the default to use SDL instead of VNC, change the virtual machine's configuration information to the following. For instructions, see Section 20.1, “XL—Xen Management Tool”.
vfb = [ 'sdl=1' ]
Remember that, unlike a VNC viewer window, closing an SDL window terminates the virtual machine.
22.4 Virtual Keyboards #
When a virtual machine is started, the host creates a virtual keyboard
that matches the keymap entry according to the virtual
machine's settings. If there is no keymap entry
specified, the virtual machine's keyboard defaults to English (US).
To view a virtual machine's current keymap entry,
enter the following command on the Dom0:
xl list -l vm_name | grep keymap
To configure a virtual keyboard for a guest, use the following snippet:
vfb = [ 'keymap="de"' ]
For a complete list of supported keyboard layouts, see the
Keymaps section of the xl.cfg
manual page man 5 xl.cfg.
22.5 Dedicating CPU Resources #
In Xen it is possible to specify how many and which CPU cores the Dom0 or VM Guest should use to retain its performance. The performance of Dom0 is important for the overall system, as the disk and network drivers are running on it. Also I/O intensive guests' workloads may consume lots of Dom0s' CPU cycles. On the other hand, the performance of VM Guests is also important, to be able to accomplish the task they were set up for.
22.5.1 Dom0 #
Dedicating CPU resources to Dom0 results in a better overall performance of the virtualized environment because Dom0 has free CPU time to process I/O requests from VM Guests. Failing to dedicate exclusive CPU resources to Dom0 usually results in a poor performance and can cause the VM Guests to function incorrectly.
Dedicating CPU resources involves three basic steps: modifying Xen boot line, binding Dom0's VCPUs to a physical processor, and configuring CPU-related options on VM Guests:
First you need to append the
dom0_max_vcpus=Xto the Xen boot line. Do so by adding the following line to/etc/default/grub:GRUB_CMDLINE_XEN="dom0_max_vcpus=X"
If
/etc/default/grubalready contains a line settingGRUB_CMDLINE_XEN, rather appenddom0_max_vcpus=Xto this line.Xneeds to be replaced by the number of VCPUs dedicated to Dom0.Update the GRUB 2 configuration file by running the following command:
grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
Reboot for the change to take effect.
The next step is to bind (or “pin”) each Dom0's VCPU to a physical processor.
xl vcpu-pin Domain-0 0 0 xl vcpu-pin Domain-0 1 1
The first line binds Dom0's VCPU number 0 to the physical processor number 0, while the second line binds Dom0's VCPU number 1 to the physical processor number 1.
Lastly, you need to make sure no VM Guest uses the physical processors dedicated to VCPUs of Dom0. Assuming you are running an 8-CPU system, you need to add
cpus="2-8"
to the configuration file of the relevant VM Guest.
22.5.2 VM Guests #
It is often necessary to dedicate specific CPU resources to a virtual machine. By default, a virtual machine uses any available CPU core. Its performance can be improved by assigning a reasonable number of physical processors to it as other VM Guests are not allowed to use them after that. Assuming a machine with 8 CPU cores while a virtual machine needs to use 2 of them, change its configuration file as follows:
vcpus=2 cpus="2,3"
The above example dedicates 2 processors to the
VM Guest, and these being the 3rd and 4th one, (2
and 3 counted from zero). If you need to assign more
physical processors, use the cpus="2-8" syntax.
If you need to change the CPU assignment for a guest named “alice” in a hotplug manner, do the following on the related Dom0:
xl vcpu-set alice 2 xl vcpu-pin alice 0 2 xl vcpu-pin alice 1 3
The example will dedicate 2 physical processors to the guest, and bind its VCPU 0 to physical processor 2 and VCPU 1 to physical processor 3. Now check the assignment:
xl vcpu-list alice Name ID VCPUs CPU State Time(s) CPU Affinity alice 4 0 2 -b- 1.9 2-3 alice 4 1 3 -b- 2.8 2-3
22.6 HVM Features #
In Xen some features are only available for fully virtualized domains. They are not very often used, but still may be interesting in some environments.
22.6.1 Specify Boot Device on Boot #
Just as with physical hardware, it is sometimes desirable to boot a
VM Guest from a different device than its own boot device. For fully
virtual machines, it is possible to select a boot device with the
boot parameter in a domain xl configuration file:
boot = boot_device
boot_device can be one of
c for hard disk, d for CD-ROM, or
n for Network/PXE. You can specify multiple options,
and they will be attempted in the given order. For example,
boot = dc
boots from CD-ROM, and falls back to the hard disk if CD-ROM is not bootable.
22.6.2 Changing CPUIDs for Guests #
To be able to migrate a VM Guest from one VM Host Server to a different
VM Host Server, it is mandatory, that the VM Guest system only uses CPU
features that are available on both VM Host Server systems. If the actual CPUs
are different on both hosts, it may be necessary to hide some features
before the VM Guest is started to maintain the possibility to
migrate the VM Guest between both hosts. For fully virtualized guests,
this can be achieved by configuring the cpuid that is
available to the guest.
To gain an overview of the current CPU, have a look at
/proc/cpuinfo. This contains all the important
information that defines the current CPU.
To redefine a CPU, first have a look at the respective cpuid definitions of the CPU vendor. These are available from:
cpuid = "host,tm=0,sse3=0"
The syntax is a comma-separated list of key=value pairs, preceded by the
word "host". A few keys take a numerical value, while all others take a
single character which describes what to do with the feature bit. See
man 5 xl.cfg for a complete list of cpuid keys. The
respective bits may be changed by using the following values:
- 1
Force the corresponding bit to
1- 0
Force the corresponding bit to
0- x
Use the values of the default policy
- k
Use the values defined by the host
- s
Like
k, but preserve the value over migrations
Note that counting bits is done from right to left, starting with bit
0.
22.6.3 Increasing the Number of PCI-IRQs #
In case you need to increase the default number of PCI-IRQs available to
Dom0 and/or VM Guest, you can do so by modifying the Xen
kernel command line. Use the command
extra_guest_irqs=
domu_irgs,dom0_irgs. The optional first
number domu_irgs is common for all
VM Guests, while the optional second number
dom0_irgs (preceded by a comma) is for
Dom0. Changing the setting for VM Guest has no impact on
Dom0 and vice versa. For example to change Dom0 without
changing VM Guest, use
extra_guest_irqs=,512
23 Administrative Tasks #
23.1 The Boot Loader Program #
The boot loader controls how the virtualization software boots and runs. You can modify the boot loader properties by using YaST, or by directly editing the boot loader configuration file.
The YaST boot loader program is located at › › . Click the tab and select the line containing the Xen kernel as the .
Figure 23.1: Boot Loader Settings #
Confirm with . Next time you boot the host, it will be ready to provide the Xen virtualization environment.
You can use the Boot Loader program to specify functionality, such as:
Pass kernel command line parameters.
Specify the kernel image and initial RAM disk.
Select a specific hypervisor.
Pass additional parameters to the hypervisor. See http://xenbits.xen.org/docs/unstable/misc/xen-command-line.html for their complete list.
You can customize your virtualization environment by editing the
/etc/default/grub file. Add the following line to
this file:
GRUB_CMDLINE_XEN="<boot_parameters>". Do not
forget to run grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
after editing the file.
23.2 Sparse Image Files and Disk Space #
If the host’s physical disk reaches a state where it has no available space, a virtual machine using a virtual disk based on a sparse image file cannot write to its disk. Consequently, it reports I/O errors.
If this situation occurs, you should free up available space on the physical disk, remount the virtual machine’s file system, and set the file system back to read-write.
To check the actual disk requirements of a sparse image file, use the
command du -h <image file>.
To increase the available space of a sparse image file, first increase the file size and then the file system.
Warning: Back Up Before Resizing
Touching the sizes of partitions or sparse files always bears the risk of data failure. Do not work without a backup.
The resizing of the image file can be done online, while the VM Guest is running. Increase the size of a sparse image file with:
dd if=/dev/zero of=<image file> count=0 bs=1M seek=<new size in MB>
For example, to increase the file
/var/lib/xen/images/sles/disk0 to a size of 16GB,
use the command:
dd if=/dev/zero of=/var/lib/xen/images/sles/disk0 count=0 bs=1M seek=16000
Note: Increasing Non-Sparse Images
It is also possible to increase the image files of devices that are not sparse files. However, you must know exactly where the previous image ends. Use the seek parameter to point to the end of the image file and use a command similar to the following:
dd if=/dev/zero of=/var/lib/xen/images/sles/disk0 seek=8000 bs=1M count=2000
Be sure to use the right seek, else data loss may happen.
If the VM Guest is running during the resize operation, also resize the loop device that provides the image file to the VM Guest. First detect the correct loop device with the command:
losetup -j /var/lib/xen/images/sles/disk0
Then resize the loop device, for example /dev/loop0,
with the following command:
losetup -c /dev/loop0
Finally check the size of the block device inside the guest system with
the command fdisk -l /dev/xvdb. The device name
depends on the actually increased device.
The resizing of the file system inside the sparse file involves tools that are depending on the actual file system.
23.3 Migrating Xen VM Guest Systems #
With Xen it is possible to migrate a VM Guest system from one VM Host Server to another with almost no service interruption. This could be used for example to move a busy VM Guest to a VM Host Server that has stronger hardware or is not yet loaded. Or, if a service of a VM Host Server is required, all VM Guest systems running on this machine can be migrated to other machines to avoid interruption of service. These are only two examples—many more reasons may apply to your personal situation.
Before starting, some preliminary considerations regarding the VM Host Server should be taken into account:
All VM Host Server systems should use a similar CPU. The frequency is not so important, but they should be using the same CPU family. To get more information about the used CPU, see
cat /proc/cpuinfo.All resources that are used by a specific guest system must be available on all involved VM Host Server systems—for example all used block devices must exist on both VM Host Server systems.
If the hosts included in the migration process run in different subnets, make sure that either DHCP relay is available to the guests, or for guests with static network configuration, set up the network manually.
Using special features like
PCI Pass-Throughmay be problematic. Do not implement these when deploying for an environment that should migrate VM Guest systems between different VM Host Server systems.For fast migrations, a fast network is mandatory. If possible, use GB Ethernet and fast switches. Deploying VLAN might also help avoid collisions.
23.3.1 Preparing Block Devices for Migrations #
The block devices needed by the VM Guest system must be available on all involved VM Host Server systems. This is done by implementing some kind of shared storage that serves as container for the root file system of the migrated VM Guest system. Common possibilities include:
iSCSIcan be set up to give access to the same block devices from different systems at the same time.NFSis a widely used root file system that can easily be accessed from different locations. For more information, see Book “Reference”, Chapter 22 “Sharing File Systems with NFS”.DRBDcan be used if only two VM Host Server systems are involved. This gives some extra data security, because the used data is mirrored over the network. .SCSIcan also be used if the available hardware permits shared access to the same disks.NPIVis a special mode to use Fibre channel disks. However, in this case all migration hosts must be attached to the same Fibre channel switch. For more information about NPIV, see Section 21.1, “Mapping Physical Storage to Virtual Disks”. Commonly, this works if the Fibre channel environment supports 4 Gbit or faster connections.
23.3.2 Migrating VM Guest Systems #
The actual migration of the VM Guest system is done with the command:
xl migrate <domain_name> <host>
The speed of the migration depends on how fast the memory print can be saved to disk, sent to the new VM Host Server and loaded there. This means that small VM Guest systems can be migrated faster than big systems with a lot of memory.
23.4 Monitoring Xen #
For a regular operation of many virtual guests, having a possibility to check the sanity of all the different VM Guest systems is indispensable. Xen offers several tools besides the system tools to gather information about the system.
Tip: Monitoring the VM Host Server
Basic monitoring of the VM Host Server (I/O and CPU) is available via the Virtual Machine Manager. Refer to Section 10.8.1, “Monitoring with Virtual Machine Manager” for details.
23.4.1 Monitor Xen with xentop #
The preferred terminal application to gather information about Xen
virtual environment is xentop. Unfortunately, this
tool needs a rather broad terminal, else it inserts line breaks into the
display.
xentop has several command keys that can give you
more information about the system that is monitored. Some of the more
important are:
- D
Change the delay between the refreshes of the screen.
- N
Also display network statistics. Note, that only standard configurations will be displayed. If you use a special configuration like a routed network, no network will be displayed.
- B
Display the respective block devices and their cumulated usage count.
For more information about xentop see the manual page
man 1 xentop.
Tip: virt-top
libvirt offers the hypervisor-agnostic tool virt-top,
which is recommended for monitoring VM Guests. See Section 10.8.2, “Monitoring with virt-top” for details.
23.4.2 Additional Tools #
There are many system tools that also help monitoring or debugging a running SUSE Linux Enterprise system. Many of these are covered in the official SUSE Linux Enterprise documentation. Especially useful for monitoring a virtualization environment are the following tools:
- ip
The command line utility
ipmay be used to monitor arbitrary network interfaces. This is especially useful if you have set up a network that is routed or applied a masqueraded network. To monitor a network interface with the namealice.0, run the following command:watch ip -s link show alice.0
- brctl
In a standard setup, all the Xen VM Guest systems are attached to a virtual network bridge.
brctlallows you to determine the connection between the bridge and the virtual network adapter in the VM Guest system. For example, the output ofbrctl showmay look like the following:bridge name bridge id STP enabled interfaces br0 8000.000476f060cc no eth0 vif1.0 br1 8000.00001cb5a9e7 no vlan22This shows that there are two virtual bridges defined on the system. One is connected to the physical Ethernet device
eth0, the other one is connected to a VLAN interfacevlan22.There is only one guest interface active in this setup,
vif1.0. This means that the guest with ID 1 has an Ethernet interfaceeth0assigned, that is connected tobr0in the VM Host Server.- iptables-save
Especially when using masquerade networks, or if several Ethernet interfaces are set up together with a firewall setup, it may be helpful to check the current firewall rules.
The command
iptablesmay be used to check all the different firewall settings. To list all the rules of a chain, or even of the complete setup, you may use the commandsiptables-saveoriptables -S.
23.5 Providing Host Information for VM Guest Systems #
In a standard Xen environment, the VM Guest systems have only
very limited information about the VM Host Server system they are running
on. If a guest should know more about the VM Host Server it runs on,
vhostmd can provide more information to selected
guests. To set up your system to run vhostmd,
proceed as follows:
Install the package vhostmd on the VM Host Server.
To add or remove
metricsections from the configuration, edit the file/etc/vhostmd/vhostmd.conf. However, the default works well.Check the validity of the
vhostmd.confconfiguration file with the command:cd /etc/vhostmd xmllint --postvalid --noout vhostmd.conf
Start the vhostmd daemon with the command
sudo systemctl start vhostmd.If vhostmd should be started automatically during start-up of the system, run the command:
sudo systemctl enable vhostmd
Attach the image file
/dev/shm/vhostmd0to the VM Guest system named alice with the command:xl block-attach opensuse /dev/shm/vhostmd0,,xvdb,ro
Log on the VM Guest system.
Install the client package
vm-dump-metrics.Run the command
vm-dump-metrics. To save the result to a file, use the option-d <filename>.
The result of the vm-dump-metrics is an XML
output. The respective metric entries follow the DTD
/etc/vhostmd/metric.dtd.
For more information, see the manual pages man 8
vhostmd and /usr/share/doc/vhostmd/README
on the VM Host Server system. On the guest, see the manual page man
1 vm-dump-metrics.
24 XenStore: Configuration Database Shared between Domains #
This section introduces basic information about XenStore, its role in the Xen environment, the directory structure of files used by XenStore, and the description of XenStore's commands.
24.1 Introduction #
XenStore is a database of configuration and status information
shared between VM Guests and the management tools running in
Dom0. VM Guests and the management tools read and write to
XenStore to convey configuration information, status updates, and
state changes. The XenStore database is managed by Dom0 and
supports simple operations such as reading and writing a key.
VM Guests and management tools can be notified of any changes in
XenStore by watching entries of interest. Note that the
xenstored daemon is managed by the
xencommons service.
XenStore is located on Dom0 in a single database file
/var/lib/xenstored/tdb (tdb
represents tree database).
24.2 File System Interface #
XenStore database content is represented by a virtual file system
similar to /proc (for more information on
/proc, see Book “System Analysis and Tuning Guide”, Chapter 2 “System Monitoring Utilities”, Section 2.6 “The /proc File System”). The
tree has three main paths: /vm,
/local/domain, and /tool.
/vm- stores information about the VM Guest configuration./local/domain- stores information about VM Guest on the local node./tool- stores general information about various tools.
Tip
Each VM Guest has two different ID numbers. The universal unique identifier (UUID) remains the same even if the VM Guest is migrated to another machine. The domain identifier (DOMID) is an identification number that represents a particular running instance. It typically changes when the VM Guest is migrated to another machine.
24.2.1 XenStore Commands #
The file system structure of the XenStore database can be operated with the following commands:
xenstore-lsDisplays the full dump of the XenStore database.
xenstore-readpath_to_xenstore_entryDisplays the value of the specified XenStore entry.
xenstore-existsxenstore_pathReports whether the specified XenStore path exists.
xenstore-listxenstore_pathDisplays all the children entries of the specified XenStore path.
xenstore-writepath_to_xenstore_entryUpdates the value of the specified XenStore entry.
xenstore-rmxenstore_pathRemoves the specified XenStore entry or directory.
xenstore-chmodxenstore_pathmodeUpdates the read/write permission on the specified XenStore path.
xenstore-controlSends a command to the
xenstoredback-end, such as triggering an integrity check.
24.2.2 /vm #
The /vm path is indexed by the UUID of each
VM Guest, and stores configuration information such as the number of
virtual CPUs and the amount of allocated memory. There is a
/vm/<uuid> directory for each
VM Guest. To list the directory content, use
xenstore-list.
# xenstore-list /vm 00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000 9b30841b-43bc-2af9-2ed3-5a649f466d79-1
The first line of the output belongs to Dom0, and the second one to a running VM Guest. The following command lists all the entries related to the VM Guest:
# xenstore-list /vm/9b30841b-43bc-2af9-2ed3-5a649f466d79-1 image rtc device pool_name shadow_memory uuid on_reboot start_time on_poweroff bootloader_args on_crash vcpus vcpu_avail bootloader name
To read a value of an entry, for example the number of virtual CPUs
dedicated to the VM Guest, use xenstore-read:
# xenstore-read /vm/9b30841b-43bc-2af9-2ed3-5a649f466d79-1/vcpus 1
A list of selected /vm/<uuid> entries
follows:
uuidUUID of the VM Guest. It does not change during the migration process.
on_rebootSpecifies whether to destroy or restart the VM Guest in response to a reboot request.
on_poweroffSpecifies whether to destroy or restart the VM Guest in response to a halt request.
on_crashSpecifies whether to destroy or restart the VM Guest in response to a crash.
vcpusNumber of virtual CPUs allocated to the VM Guest.
vcpu_availBitmask of active virtual CPUs for the VM Guest. The bitmask has several bits equal to the value of
vcpus, with a bit set for each online virtual CPU.nameThe name of the VM Guest.
Regular VM Guests (not Dom0) use the
/vm/<uuid>/image path:
# xenstore-list /vm/9b30841b-43bc-2af9-2ed3-5a649f466d79-1/image ostype kernel cmdline ramdisk dmargs device-model display
An explanation of the used entries follows:
ostypeThe OS type of the VM Guest.
kernelThe path on Dom0 to the kernel for the VM Guest.
cmdlineThe kernel command line for the VM Guest used when booting.
ramdiskThe path on Dom0 to the RAM disk for the VM Guest.
dmargsShows arguments passed to the QEMU process. If you look at the QEMU process with
ps, you should see the same arguments as in/vm/<uuid>/image/dmargs.
24.2.3 /local/domain/<domid> #
This path is indexed by the running domain (VM Guest) ID, and contains information about the running VM Guest. Remember that the domain ID changes during VM Guest migration. The following entries are available:
vmThe path of the
/vmdirectory for this VM Guest.on_reboot, on_poweroff, on_crash, nameSee identical options in Section 24.2.2, “
/vm”domidDomain identifier for the VM Guest.
cpuThe current CPU to which the VM Guest is pinned.
cpu_weightThe weight assigned to the VM Guest for scheduling purposes. Higher weights use the physical CPUs more often.
Apart from the individual entries described above, there are also
several subdirectories under
/local/domain/<domid>, containing specific
entries. To see all entries available, refer to
XenStore
Reference.
/local/domain/<domid>/memoryContains memory information.
/local/domain/<domid>/memory/targetcontains target memory size for the VM Guest (in kilobytes)./local/domain/<domid>/consoleContains information about a console used by the VM Guest.
/local/domain/<domid>/backendContains information about all back-end devices used by the VM Guest. The path has subdirectories of its own.
/local/domain/<domid>/deviceContains information about the front-end devices for the VM Guest.
/local/domain/<domid>/device-miscContains miscellaneous information about devices.
/local/domain/<domid>/storeContains information about the VM Guest's store.
25 Xen as a High-Availability Virtualization Host #
Setting up two Xen hosts as a failover system has several advantages compared to a setup where every server runs on dedicated hardware.
Failure of a single server does not cause major interruption of the service.
A single big machine is normally way cheaper than multiple smaller machines.
Adding new servers as needed is a trivial task.
The utilization of the server is improved, which has positive effects on the power consumption of the system.
The setup of migration for Xen hosts is described in Section 23.3, “Migrating Xen VM Guest Systems”. In the following, several typical scenarios are described.
25.1 Xen HA with Remote Storage #
Xen can directly provide several remote block devices to the respective Xen guest systems. These include iSCSI, NPIV, and NBD. All of these may be used to do live migrations. When a storage system is already in place, first try to use the same device type you already used in the network.
If the storage system cannot be used directly but provides a possibility to offer the needed space over NFS, it is also possible to create image files on NFS. If the NFS file system is available on all Xen host systems, this method also allows live migrations of Xen guests.
When setting up a new system, one of the main considerations is whether a dedicated storage area network should be implemented. The following possibilities are available:
Table 25.1: Xen Remote Storage #
|
Method |
Complexity |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
Ethernet |
low |
Note that all block device traffic goes over the same Ethernet interface as the network traffic. This may be limiting the performance of the guest. |
|
Ethernet dedicated to storage. |
medium |
Running the storage traffic over a dedicated Ethernet interface may eliminate a bottleneck on the server side. However, planning your own network with your own IP address range and possibly a VLAN dedicated to storage requires numerous considerations. |
|
NPIV |
high |
NPIV is a method to virtualize Fibre channel connections. This is available with adapters that support a data rate of at least 4 Gbit/s and allows the setup of complex storage systems. |
Typically, a 1 Gbit/s Ethernet device can fully use a typical hard disk or storage system. When using very fast storage systems, such an Ethernet device will probably limit the speed of the system.
25.2 Xen HA with Local Storage #
For space or budget reasons, it may be necessary to rely on storage that is local to the Xen host systems. To still maintain the possibility of live migrations, it is necessary to build block devices that are mirrored to both Xen hosts. The software that allows this is called Distributed Replicated Block Device (DRBD).
If a system that uses DRBD to mirror the block devices or files between two Xen hosts should be set up, both hosts should use the identical hardware. If one of the hosts has slower hard disks, both hosts will suffer from this limitation.
During the setup, each of the required block devices should use its own DRBD device. The setup of such a system is quite a complex task.
25.3 Xen HA and Private Bridges #
When using several guest systems that need to communicate between each other, it is possible to do this over the regular interface. However, for security reasons it may be advisable to create a bridge that is only connected to guest systems.
In an HA environment that also should support live migrations, such a private bridge must be connected to the other Xen hosts. This is possible by using dedicated physical Ethernet devices and a dedicated network.
A different implementation method is using VLAN interfaces. In that case, all the traffic goes over the regular Ethernet interface. However, the VLAN interface does not get the regular traffic, because only the VLAN packets that are tagged for the correct VLAN are forwarded.
For more information about the setup of a VLAN interface see Section 13.2.3, “Using VLAN Interfaces”.
Part V Managing Virtual Machines with QEMU #
- 26 QEMU Overview
QEMU is a fast, cross-platform open source machine emulator which can emulate a huge number of hardware architectures for you. QEMU lets you run a complete unmodified operating system (VM Guest) on top of your existing system (VM Host Server).
- 27 Setting Up a KVM VM Host Server
This section documents how to set up and use openSUSE Leap 42.2 as a QEMU-KVM based virtual machine host.
- 28 Guest Installation
The
libvirt-based tools such asvirt-managerandvirt-installoffer convenient interfaces to set up and manage virtual machines. They act as a kind of wrapper for theqemu-system-ARCHcommand. However, it is also possible to useqemu-system-ARCHdirectly without usinglibvirt-based tools.- 29 Running Virtual Machines with qemu-system-ARCH
Once you have a virtual disk image ready (for more information on disk images, see Section 28.2, “Managing Disk Images with qemu-img”), it is time to start the related virtual machine. Section 28.1, “Basic Installation with qemu-system-ARCH” introduced simple commands to install and run a VM Guest. …
- 30 Virtual Machine Administration Using QEMU Monitor
When QEMU is running, a monitor console is provided for performing interaction with the user. Using the commands available in the monitor console, it is possible to inspect the running operating system, change removable media, take screenshots or audio grabs and control other aspects of the virtual …
26 QEMU Overview #
QEMU is a fast, cross-platform open source machine emulator which can emulate a huge number of hardware architectures for you. QEMU lets you run a complete unmodified operating system (VM Guest) on top of your existing system (VM Host Server).
You can also use QEMU for debugging purposes—you can easily stop your running virtual machine, inspect its state and save and restore it later.
QEMU consists of the following parts:
processor emulator (x86, s390x, PowerPC, Sparc)
emulated devices (graphic card, network card, hard disks, mice)
generic devices used to connect the emulated devices to the related host devices
descriptions of the emulated machines (PC, Power Mac)
debugger
user interface used to interact with the emulator
QEMU is central to KVM and Xen Virtualization, where it provides the general machine emulation. Xen's usage of QEMU is somewhat hidden from the user, while KVM's usage exposes most QEMU features transparently. If the VM Guest hardware architecture is the same as the VM Host Server's architecture, QEMU can take advantage of the KVM acceleration (SUSE only supports QEMU with the KVM acceleration loaded).
Apart from providing a core virtualization infrastructure and processor-specific drivers, QEMU also provides an architecture-specific user space program for managing VM Guests. Depending on the architecture this program is one of:
qemu-system-i386qemu-system-s390xqemu-system-x86_64
In the following this command is called qemu-system-ARCH; in
examples the qemu-system-x86_64 command is used.
27 Setting Up a KVM VM Host Server #
This section documents how to set up and use openSUSE Leap 42.2 as a QEMU-KVM based virtual machine host.
Tip: Resources
In general, the virtual guest system needs the same hardware resources as SUSE Linux Enterprise Server installed on a physical machine. The more guests you plan to run on the host system, the more hardware resources—CPU, disk, memory, and network—you need to add.
27.1 CPU Support for Virtualization #
To run KVM, your CPU must support virtualization, and
virtualization needs to be enabled in BIOS. The file
/proc/cpuinfo includes information about your CPU
features.
To find out whether your system supports virtualization, see Section 7.3, “KVM Hardware Requirements”.
27.2 Required Software #
The KVM host requires several packages to be installed. To install all necessary packages, do the following:
Run › › .
Figure 27.1: Installing the KVM Hypervisor and Tools #
Select and preferably also , and confirm with .
During the installation process, you can optionally let YaST create a for you automatically. If you do not plan to dedicate an additional physical network card to your virtual guests, network bridge is a standard way to connect the guest machines to the network.
Figure 27.2: Network Bridge #
After all the required packages are installed (and new network setup activated), try to load the KVM kernel module relevant for your CPU type—
kvm-intelorkvm-amd:root #modprobe kvm-intelCheck if the module is loaded into memory:
tux >lsmod | grep kvm kvm_intel 64835 6 kvm 411041 1 kvm_intelNow the KVM host is ready to serve KVM VM Guests. For more information, see Chapter 29, Running Virtual Machines with qemu-system-ARCH.
27.3 KVM Host-Specific Features #
You can improve the performance of KVM-based VM Guests by letting them fully use specific features of the VM Host Server's hardware (paravirtualization). This section introduces techniques to make the guests access the physical host's hardware directly—without the emulation layer—to make the most use of it.
Tip
Examples included in this section assume basic knowledge of the
qemu-system-ARCH command
line options. For more information, see
Chapter 29, Running Virtual Machines with qemu-system-ARCH.
27.3.1 Using the Host Storage with virtio-scsi #
virtio-scsi is an advanced storage stack for
KVM. It replaces the former virtio-blk stack
for SCSI devices pass-through. It has several advantages over
virtio-blk:
- Improved scalability
KVM guests have a limited number of PCI controllers, which results in a limited number of possibly attached devices.
virtio-scsisolves this limitation by grouping multiple storage devices on a single controller. Each device on avirtio-scsicontroller is represented as a logical unit, or LUN.- Standard command set
virtio-blkuses a small set of commands that need to be known to both thevirtio-blkdriver and the virtual machine monitor, and so introducing a new command requires updating both the driver and the monitor.By comparison,
virtio-scsidoes not define commands, but rather a transport protocol for these commands following the industry-standard SCSI specification. This approach is shared with other technologies, such as Fibre Channel, ATAPI, and USB devices.- Device naming
virtio-blkdevices are presented inside the guest as/dev/vdX, which is different from device names in physical systems and may cause migration problems.virtio-scsikeeps the device names identical to those on physical systems, making the virtual machines easily relocatable.- SCSI device pass-through
For virtual disks backed by a whole LUN on the host, it is preferable for the guest to send SCSI commands directly to the LUN (pass-through). This is limited in
virtio-blk, as guests need to use the virtio-blk protocol instead of SCSI command pass-through, and, moreover, it is not available for Windows guests.virtio-scsinatively removes these limitations.
27.3.1.1 virtio-scsi Usage #
KVM supports the SCSI pass-through feature with the
virtio-scsi-pci device:
qemu-system-x86_64 [...] \ -device virtio-scsi-pci,id=scsi
27.3.2 Accelerated Networking with vhost-net #
The vhost-net module is used to accelerate
KVM's paravirtualized network drivers. It provides better latency and
greater network throughput. Use the vhost-net
driver by starting the guest with the following example command line:
qemu-system-x86_64 [...] \ -netdev tap,id=guest0,vhost=on,script=no \ -net nic,model=virtio,netdev=guest0,macaddr=00:16:35:AF:94:4B
Note that guest0 is an identification string of the
vhost-driven device.
27.3.3 Scaling Network Performance with Multiqueue virtio-net #
As the number of virtual CPUs increases in VM Guests, QEMU offers a way of improving the network performance using multiqueue. Multiqueue virtio-net scales the network performance by allowing VM Guest virtual CPUs to transfer packets in parallel. Multiqueue support is required on both the VM Host Server and VM Guest sides.
Tip: Performance Benefit
The multiqueue virtio-net solution is most beneficial in the following cases:
Network traffic packets are large.
VM Guest has many connections active at the same time, mainly between the guest systems, or between the guest and the host, or between the guest and an external system.
The number of active queues is equal to the number of virtual CPUs in the VM Guest.
Note
While multiqueue virtio-net increases the total network throughput, it increases CPU consumption as it uses of the virtual CPU's power.
Procedure 27.1: How to Enable Multiqueue virtio-net #
The following procedure lists important steps to enable the multiqueue
feature with qemu-system-ARCH. It assumes that a tap
network device with multiqueue capability (supported since kernel
version 3.8) is set up on the VM Host Server.
In
qemu-system-ARCH, enable multiqueue for the tap device:-netdev tap,vhost=on,queues=N
where
Nstands for the number of queue pairs.In
qemu-system-ARCH, enable multiqueue and specify MSI-X (Message Signaled Interrupt) vectors for the virtio-net-pci device:-device virtio-net-pci,mq=on,vectors=2*N+2
where the formula for the number of MSI-X vectors results from: N vectors for TX (transmit) queues, N for RX (receive) queues, one for configuration purposes, and one for possible VQ (vector quantization) control.
In VM Guest, enable multiqueue on the relevant network interface (
eth0in this example):ethtool -L eth0 combined 2*N
The resulting qemu-system-ARCH command line will look
similar to the following example:
qemu-system-x86_64 [...] -netdev tap,id=guest0,queues=4,vhost=on \ -device virtio-net-pci,netdev=guest0,mq=on,vectors=10
Note that the id of the network device
(guest0 ) needs to be identical for both options.
Inside the running VM Guest, specify the following command as
root:
ethtool -L eth0 combined 8
Now the guest system networking uses the multiqueue support from the
qemu-system-ARCH hypervisor.
27.3.4 VFIO: Secure Direct Access to Devices #
Directly assigning a PCI device to a VM Guest (PCI pass-through) avoids performance issues caused by avoiding any emulation in performance-critical paths. VFIO replaces the traditional KVM PCI Pass-Through device assignment. A prerequisite for this feature is a VM Host Server configuration described in Important: Requirements for VFIO and SR-IOV.
To be able to assign a PCI device via VFIO to a VM Guest, you need to find out which IOMMU Group it belongs to. The IOMMU (input/output memory management unit that connects a direct memory access-capable I/O bus to the main memory) API supports the notion of groups. A group is a set of devices that can be isolated from all other devices in the system. Groups are therefore the unit of ownership used by VFIO.
Procedure 27.2: Assigning a PCI Device to a VM Guest via VFIO #
Identify the host PCI device to assign to the guest.
tux >sudo lspci -nn [...] 00:10.0 Ethernet controller [0200]: Intel Corporation 82576 \ Virtual Function [8086:10ca] (rev 01) [...]Note down the device ID (
00:10.0in this case) and the vendor ID (8086:10ca).Find the IOMMU group of this device:
tux >sudo readlink /sys/bus/pci/devices/0000\:00\:10.0/iommu_group ../../../kernel/iommu_groups/20The IOMMU group for this device is
20. Now you can check the devices belonging to the same IOMMU group:ls -l /sys/bus/pci/devices/0000:01:10.0/iommu_group/devices/0000:01:10.0 [...] 0000:00:1e.0 -> ../../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:1e.0 [...] 0000:01:10.0 -> ../../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:1e.0/0000:01:10.0 [...] 0000:01:10.1 -> ../../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:1e.0/0000:01:10.1
Unbind the device from the device driver:
sudo echo "0000:01:10.0" > /sys/bus/pci/devices/0000\:01\:10.0/driver/unbind
Bind the device to the vfio-pci driver using the vendor ID from step 1:
sudo echo "8086 153a" > /sys/bus/pci/drivers/vfio-pci/new_id
A new device
/dev/vfio/IOMMU_GROUPwill be created as a result,/dev/vfio/20in this case.Change the ownership of the newly created device:
chown qemu.qemu /dev/vfio/DEVICE
Now run the VM Guest with the PCI device assigned.
qemu-system-ARCH [...] -device vfio-pci,host=00:10.0,id=ID
Important: No Hotplugging
As of openSUSE Leap 42.2 hotplugging of PCI devices passed to a VM Guest via VFIO is not supported.
You can find more detailed information on the
VFIO driver in the
/usr/src/linux/Documentation/vfio.txt file (package
kernel-source needs to be installed).
27.3.5 VirtFS: Sharing Directories between Host and Guests #
VM Guests usually run in a separate computing space—they are provided their own memory range, dedicated CPUs, and file system space. The ability to share parts of the VM Host Server's file system makes the virtualization environment more flexible by simplifying mutual data exchange. Network file systems, such as CIFS and NFS, have been the traditional way of sharing directories. But as they are not specifically designed for virtualization purposes, they suffer from major performance and feature issues.
KVM introduces a new optimized method called VirtFS (sometimes called “file system pass-through”). VirtFS uses a paravirtual file system driver, which avoids converting the guest application file system operations into block device operations, and then again into host file system operations.
You typically use VirtFS for the following situations:
To access a shared directory from several guests, or to provide guest-to-guest file system access.
To replace the virtual disk as the root file system to which the guest's RAM disk connects during the guest boot process.
To provide storage services to different customers from a single host file system in a cloud environment.
27.3.5.1 Implementation #
In QEMU, the implementation of VirtFS is simplified by defining two types of devices:
virtio-9p-pcidevice which transports protocol messages and data between the host and the guest.fsdevdevice which defines the export file system properties, such as file system type and security model.
Example 27.1: Exporting Host's File System with VirtFS #
qemu-system-x86_64 [...] \ -fsdev local,id=exp11,path=/tmp/2,security_model=mapped3 \ -device virtio-9p-pci,fsdev=exp14,mount_tag=v_tmp5
Identification of the file system to be exported. | |
File system path on the host to be exported. | |
Security model to be used— | |
The exported file system ID defined before with | |
Mount tag used later on the guest to mount the exported file system. |
Such an exported file system can be mounted on the guest as follows:
sudo mount -t 9p -o trans=virtio v_tmp /mnt
where v_tmp is the mount tag defined earlier with
-device mount_tag= and /mnt is
the mount point where you want to mount the exported file system.
27.3.6 KSM: Sharing Memory Pages between Guests #
Kernel Same Page Merging (KSM) is a Linux Kernel feature that merges identical memory pages from multiple running processes into one memory region. Because KVM guests run as processes under Linux, KSM provides the memory overcommit feature to hypervisors for more efficient use of memory. Therefore, if you need to run multiple virtual machines on a host with limited memory, KSM may be helpful to you.
KSM stores its status information in
the files under the /sys/kernel/mm/ksm directory:
tux > ls -1 /sys/kernel/mm/ksm
full_scans
merge_across_nodes
pages_shared
pages_sharing
pages_to_scan
pages_unshared
pages_volatile
run
sleep_millisecs
For more information on the meaning of the
/sys/kernel/mm/ksm/* files, see
/usr/src/linux/Documentation/vm/ksm.txt (package
kernel-source).
To use KSM, do the following.
Although openSUSE Leap includes KSM support in the kernel, it is disabled by default. To enable it, run the following command:
root #echo 1 > /sys/kernel/mm/ksm/runNow run several VM Guests under KVM and inspect the content of files
pages_sharingandpages_shared, for example:while [ 1 ]; do cat /sys/kernel/mm/ksm/pages_shared; sleep 1; done 13522 13523 13519 13518 13520 13520 13528
28 Guest Installation #
The libvirt-based tools such as
virt-manager and virt-install
offer convenient interfaces to set up and
manage virtual machines. They act as a kind of wrapper for the
qemu-system-ARCHcommand. However, it is also possible to
use qemu-system-ARCH directly without using
libvirt-based tools.
Warning: qemu-system-ARCH and libvirt
Virtual Machines created with
qemu-system-ARCH are not "visible" for the
libvirt-based tools.
28.1 Basic Installation with qemu-system-ARCH #
In the following example, a virtual machine for a SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 installation is created. For detailed information on the commands, refer to the respective man pages.
If you do not already have an image of a system that you want to run in a virtualized environment, you need to create one from the installation media. In such case, you need to prepare a hard disk image, and obtain an image of the installation media or the media itself.
Create a hard disk with qemu-img.
qemu-img create1 -f raw2 /images/sles/hda3 8G4
The subcommand | |
Specify the disk's format with the | |
The full path to the image file. | |
The size of the image—8 GB in this case. The image is created as a Sparse image file file that grows when the disk is filled with data. The specified size defines the maximum size to which the image file can grow. |
After at least one hard disk image is created, you can set up a virtual
machine with qemu-system-ARCH that will boot into the
installation system:
qemu-system-x86_64 -name "sles"1-machine accel=kvm -M pc2 -m 7683 \ -smp 24 -boot d5 \ -drive file=/images/sles/hda,if=virtio,index=0,media=disk,format=raw6 \ -drive file=/isos/SLES-11-SP3-DVD-x86_64-GM-DVD1.iso,index=1,media=cdrom7 \ -net nic,model=virtio,macaddr=52:54:00:05:11:118 -net user \ -vga cirrus9 -balloon virtio10
Name of the virtual machine that will be displayed in the window caption and be used for the VNC server. This name must be unique. | |
Specifies the machine type. Use | |
Maximum amount of memory for the virtual machine. | |
Defines an SMP system with two processors. | |
Specifies the boot order. Valid values are | |
Defines the first ( | |
The second ( | |
Defines a paravirtualized ( | |
Specifies the graphic card. If you specify none, the graphic card will be disabled. | |
Defines the paravirtualized balloon device that allows to dynamically
change the amount of memory (up to the maximum value specified with the
parameter |
After the installation of the guest operating system finishes, you can start the related virtual machine without the need to specify the CD-ROM device:
qemu-system-x86_64 -name "sles" -machine type=pc,accel=kvm -m 768 \ -smp 2 -boot c \ -drive file=/images/sles/hda,if=virtio,index=0,media=disk,format=raw \ -net nic,model=virtio,macaddr=52:54:00:05:11:11 \ -vga cirrus -balloon virtio
28.2 Managing Disk Images with qemu-img #
In the previous section (see
Section 28.1, “Basic Installation with qemu-system-ARCH”), we used the
qemu-img command to create an image of a hard disk. You
can, however, use qemu-img for general disk image
manipulation. This section introduces qemu-img
subcommands to help manage the disk images flexibly.
28.2.1 General Information on qemu-img Invocation #
qemu-img uses subcommands (like
zypper does) to do specific tasks. Each subcommand
understands a different set of options. Some options are general and used
by more of these subcommands, while some are unique to the related
subcommand. See the qemu-img manual page (man 1
qemu-img) for a list of all supported options.
qemu-img uses the following general syntax:
qemu-img subcommand [options]
and supports the following subcommands:
createCreates a new disk image on the file system.
checkChecks an existing disk image for errors.
compareCheck if two images have the same content.
mapDumps the metadata of the image file name and its backing file chain.
amendAmends the image format specific options for the image file name.
convertConverts an existing disk image to a new one in a different format.
infoDisplays information about the relevant disk image.
snapshotManages snapshots of existing disk images.
commitApplies changes made to an existing disk image.
rebaseCreates a new base image based on an existing image.
resizeIncreases or decreases the size of an existing image.
28.2.2 Creating, Converting and Checking Disk Images #
This section describes how to create disk images, check their condition, convert a disk image from one format to another, and get detailed information about a particular disk image.
28.2.2.1 qemu-img create #
Use qemu-img create to create a new disk image for your
VM Guest operating system. The command uses the following syntax:
qemu-img create -f fmt1 -o options2 fname3 size4
The format of the target image. Supported formats are
| |
Some image formats support additional options to be passed on the
command line. You can specify them here with the | |
Path to the target disk image to be created. | |
Size of the target disk image (if not already specified with the
|
To create a new disk image sles.raw in the directory
/images growing up to a maximum size of 4 GB, run the
following command:
tux >qemu-img create -f raw -o size=4G /images/sles.raw Formatting '/images/sles.raw', fmt=raw size=4294967296tux >ls -l /images/sles.raw -rw-r--r-- 1 tux users 4294967296 Nov 15 15:56 /images/sles.rawtux >qemu-img info /images/sles.raw image: /images/sles11.raw file format: raw virtual size: 4.0G (4294967296 bytes) disk size: 0
As you can see, the virtual size of the newly created image is 4 GB, but the actual reported disk size is 0 as no data has been written to the image yet.
Tip: VM Guest Images on the Btrfs File System
If you need to create a disk image on the Btrfs file system, you can use
nocow=on to reduce the performance overhead created by
the copy-on-write feature of Btrfs:
qemu-img create -o nocow=on test.img 8G
If you, however, want to use copy-on-write (for example for creating
snapshots or sharing them across virtual machines), then leave the
command line without the nocow option.
28.2.2.2 qemu-img convert #
Use qemu-img convert to convert disk images to another
format. To get a complete list of image formats supported by QEMU, run
qemu-img -h and look at the last line
of the output. The command uses the following syntax:
qemu-img convert -c1 -f fmt2 -O out_fmt3 -o options4 fname5 out_fname6
Applies compression on the target disk image. Only
| |
The format of the source disk image. It is usually autodetected and can therefore be omitted. | |
The format of the target disk image. | |
Specify additional options relevant for the target image format. Use
| |
Path to the source disk image to be converted. | |
Path to the converted target disk image. |
tux >qemu-img convert -O vmdk /images/sles.raw \ /images/sles.vmdktux >ls -l /images/ -rw-r--r-- 1 tux users 4294967296 16. lis 10.50 sles.raw -rw-r--r-- 1 tux users 2574450688 16. lis 14.18 sles.vmdk
To see a list of options relevant for the selected target image format,
run the following command (replace vmdk with your image
format):
tux > qemu-img convert -O vmdk /images/sles.raw \
/images/sles.vmdk -o ?
Supported options:
size Virtual disk size
backing_file File name of a base image
compat6 VMDK version 6 image
subformat VMDK flat extent format, can be one of {monolithicSparse \
(default) | monolithicFlat | twoGbMaxExtentSparse | twoGbMaxExtentFlat}
scsi SCSI image28.2.2.3 qemu-img check #
Use qemu-img check to check the existing disk image for
errors. Not all disk image formats support this feature. The command uses
the following syntax:
qemu-img check -f fmt1 fname2
The format of the source disk image. It is usually autodetected and can therefore be omitted. | |
Path to the source disk image to be checked. |
If no error is found, the command returns no output. Otherwise, the type and number of errors found is shown.
tux > qemu-img check -f qcow2 /images/sles.qcow2
ERROR: invalid cluster offset=0x2af0000
[...]
ERROR: invalid cluster offset=0x34ab0000
378 errors were found on the image.28.2.2.4 Increasing the Size of an Existing Disk Image #
When creating a new image, you must specify its maximum size before the image is created (see Section 28.2.2.1, “qemu-img create”). After you have installed the VM Guest and have been using it for some time, the initial size of the image may no longer be sufficient and you may need to add more space to it.
To increase the size of an existing disk image by 2 gigabytes, use:
qemu-img resize /images/sles.raw +2GB
Note
You can resize the disk image using the formats raw,
qcow2 and qed. To resize an image
in another format, convert it to a supported format with
qemu-img convert first.
The image now contains an empty space of 2 GB after the final partition. You can resize the existing partitions or add new ones.
Figure 28.1: New 2 GB Partition in Guest YaST Partitioner #
28.2.2.5 Advanced Options for the qcow2 File Format #
qcow2 is the main disk image format used by QEMU. Its size grows on demand, and the disk space is only allocated when it is actually needed by the virtual machine.
A qcow2 formatted file is organized in units of constant size. These units are called clusters. Viewed from the guest side, the virtual disk is also divided into clusters of the same size. QEMU defaults to 64 kB clusters, but you can specify a different value when creating a new image:
qemu-img create -f qcow2 -o cluster_size=128K virt_disk.qcow2 4G
A qcow2 image contains a set of tables organized in two levels that are called the L1 and L2 tables. There is just one L1 table per disk image, while there can be many L2 tables depending on how big the image is.
To read or write data to the virtual disk, QEMU needs to read its corresponding L2 table to find out the relevant data location. Because reading the table for each I/O operation consumes system resources, QEMU keeps a cache of L2 tables in memory to speed up disk access.
28.2.2.5.1 Choosing the Right Cache Size #
The cache size relates to the amount of allocated space. L2 cache can map the following amount of virtual disk:
disk_size = l2_cache_size * cluster_size / 8
With the default 64 kB of cluster size, that is
disk_size = l2_cache_size * 8192
Therefore, to have a cache that maps
n gigabytes of disk space with the default cluster
size, you need
l2_cache_size = disk_size_GB * 131072
QEMU uses 1 MB (1048576 bytes) of L2 cache by default. Following the above formulas, 1 MB of L2 cache covers 8 GB (1048576 / 131072) of virtual disk. This means that the performance is fine with the default L2 cache size if your virtual disk size is up to 8 GB. For larger disks, you can speed up the disk access by increasing the L2 cache size.
28.2.2.5.2 Configuring the Cache Size #
You can use the -drive option on the QEMU command line
to specify the cache sizes. Alternatively when communicating via QMP, use
the blockdev-add command. For more information on QMP,
see Section 30.11, “QMP - QEMU Machine Protocol”.
The following options configure the cache size for the virtual guest:
- l2-cache-size
The maximum size of the L2 table cache.
- refcount-cache-size
The maximum size of the refcount block cache. For more information on refcount, see https://github.com/qemu/qemu/blob/master/docs/specs/qcow2.txt.
- cache-size
The maximum size of both caches combined.
When specifying values for the options above, be aware of the following:
The size of both the L2 and refcount block caches needs to be a multiple of the cluster size.
If you only set one of the options, QEMU will automatically adjust the other options so that the L2 cache is 4 times bigger than the refcount cache.
The refcount cache is used much less often than the L2 cache, therefore you can keep it relatively small:
qemu-system-ARCH [...] \ -drive file=disk_image.qcow2,l2-cache-size=4194304,refcount-cache-size=262144
28.2.2.5.3 Reducing the Memory Usage #
The larger the cache, the more memory it consumes. There is a separate L2 cache for each qcow2 file. When using a lot of big disk images, you will probably need a considerably large amount of memory. Memory consumption is even worse if you add backing files (Section 28.2.4, “Manipulate Disk Images Effectively”) and snapshots (see Section 28.2.3, “Managing Snapshots of Virtual Machines with qemu-img”) to the guest's setup chain.
That is why QEMU introduced the cache-clean-interval
setting. It defines an interval in seconds after which all cache entries
that have not been accessed are removed from memory.
The following example removes all unused cache entries every 10 minutes:
qemu-system-ARCH [...] -drive file=hd.qcow2,cache-clean-interval=600
If this option is not set, the default value is 0 and it disables this feature.
28.2.3 Managing Snapshots of Virtual Machines with qemu-img #
Virtual Machine snapshots are snapshots of the complete environment in which a VM Guest is running. The snapshot includes the state of the processor (CPU), memory (RAM), devices, and all writable disks.
Snapshots are helpful when you need to save your virtual machine in a particular state. For example, after you configured network services on a virtualized server and want to quickly start the virtual machine in the same state you last saved it. Or you can create a snapshot after the virtual machine has been powered off to create a backup state before you try something experimental and possibly make VM Guest unstable. This section introduces the latter case, while the former is described in Chapter 30, Virtual Machine Administration Using QEMU Monitor.
To use snapshots, your VM Guest must contain at least one writable hard
disk image in qcow2 format. This device is usually the
first virtual hard disk.
Virtual Machine snapshots are created with the
savevm command in the interactive QEMU monitor. To
make identifying a particular snapshot easier, you can assign it a
tag. For more information on QEMU monitor, see
Chapter 30, Virtual Machine Administration Using QEMU Monitor.
Once your qcow2 disk image contains saved snapshots, you
can inspect them with the qemu-img snapshot command.
Warning: Shut Down the VM Guest
Do not create or delete virtual machine snapshots with the
qemu-img snapshot command while the virtual machine is
running. Otherwise, you may damage the disk image with the state of the
virtual machine saved.
28.2.3.1 Listing Existing Snapshots #
Use qemu-img snapshot -l
disk_image to view a list of all existing
snapshots saved in the disk_image image. You can get
the list even while the VM Guest is running.
tux > qemu-img snapshot -l /images/sles.qcow2
Snapshot list:
ID1 TAG2 VM SIZE3 DATE4 VM CLOCK5
1 booting 4.4M 2013-11-22 10:51:10 00:00:20.476
2 booted 184M 2013-11-22 10:53:03 00:02:05.394
3 logged_in 273M 2013-11-22 11:00:25 00:04:34.843
4 ff_and_term_running 372M 2013-11-22 11:12:27 00:08:44.965Unique identification number of the snapshot. Usually auto-incremented. | |
Unique description string of the snapshot. It is meant as a human-readable version of the ID. | |
The disk space occupied by the snapshot. Note that the more memory is consumed by running applications, the bigger the snapshot is. | |
Time and date the snapshot was created. | |
The current state of the virtual machine's clock. |
28.2.3.2 Creating Snapshots of a Powered-Off Virtual Machine #
Use qemu-img snapshot -c
snapshot_title
disk_image to create a snapshot of the current
state of a virtual machine that was previously powered off.
tux > qemu-img snapshot -c backup_snapshot /images/sles.qcow2tux > qemu-img snapshot -l /images/sles.qcow2
Snapshot list:
ID TAG VM SIZE DATE VM CLOCK
1 booting 4.4M 2013-11-22 10:51:10 00:00:20.476
2 booted 184M 2013-11-22 10:53:03 00:02:05.394
3 logged_in 273M 2013-11-22 11:00:25 00:04:34.843
4 ff_and_term_running 372M 2013-11-22 11:12:27 00:08:44.965
5 backup_snapshot 0 2013-11-22 14:14:00 00:00:00.000If something breaks in your VM Guest and you need to restore the state of the saved snapshot (ID 5 in our example), power off your VM Guest and execute the following command:
tux > qemu-img snapshot -a 5 /images/sles.qcow2
The next time you run the virtual machine with
qemu-system-ARCH, it will be in the state of snapshot
number 5.
Note
The qemu-img snapshot -c command is not related to the
savevm command of QEMU monitor (see
Chapter 30, Virtual Machine Administration Using QEMU Monitor). For example, you cannot apply a
snapshot with qemu-img snapshot -a on a snapshot
created with savevm in QEMU's monitor.
28.2.3.3 Deleting Snapshots #
Use qemu-img snapshot -d
snapshot_id
disk_image to delete old or unneeded snapshots
of a virtual machine. This saves some disk space inside the
qcow2 disk image as the space occupied by the snapshot
data is restored:
tux > qemu-img snapshot -d 2 /images/sles.qcow228.2.4 Manipulate Disk Images Effectively #
Imagine the following real-life situation: you are a server administrator who runs and manages several virtualized operating systems. One group of these systems is based on one specific distribution, while another group (or groups) is based on different versions of the distribution or even on a different (and maybe non-Unix) platform. To make the case even more complex, individual virtual guest systems based on the same distribution usually differ according to the department and deployment. A file server typically uses a different setup and services than a Web server does, while both may still be based on SUSE® Linux Enterprise Server.
With QEMU it is possible to create “base” disk images. You can use them as template virtual machines. These base images will save you plenty of time because you will never need to install the same operating system more than once.
28.2.4.1 Base and Derived Images #
First, build a disk image as usual and install the target system on it.
For more information, see Section 28.1, “Basic Installation with qemu-system-ARCH”
and Section 28.2.2, “Creating, Converting and Checking Disk Images”. Then build a
new image while using the first one as a base image. The base image is
also called a backing file. After your new
derived image is built, never boot the base image
again, but boot the derived image instead. Several derived images may
depend on one base image at the same time. Therefore, changing the base
image can damage the dependencies. While using your derived image, QEMU
writes changes to it and uses the base image only for reading.
It is a good practice to create a base image from a freshly installed (and, if needed, registered) operating system with no patches applied and no additional applications installed or removed. Later on, you can create another base image with the latest patches applied and based on the original base image.
28.2.4.2 Creating Derived Images #
Note
While you can use the raw format for base images, you
cannot use it for derived images because the raw
format does not support the backing_file option. Use
for example the qcow2 format for the derived images.
For example, /images/sles_base.raw is the base image
holding a freshly installed system.
tux > qemu-img info /images/sles_base.raw
image: /images/sles_base.raw
file format: raw
virtual size: 4.0G (4294967296 bytes)
disk size: 2.4G
The image's reserved size is 4 GB, the actual size is 2.4 GB, and its
format is raw. Create an image derived from the
/images/sles_base.raw base image with:
tux > qemu-img create -f qcow2 /images/sles_derived.qcow2 \
-o backing_file=/images/sles_base.raw
Formatting '/images/sles_derived.qcow2', fmt=qcow2 size=4294967296 \
backing_file='/images/sles_base.raw' encryption=off cluster_size=0Look at the derived image details:
tux > qemu-img info /images/sles_derived.qcow2
image: /images/sles_derived.qcow2
file format: qcow2
virtual size: 4.0G (4294967296 bytes)
disk size: 140K
cluster_size: 65536
backing file: /images/sles_base.raw \
(actual path: /images/sles_base.raw)Although the reserved size of the derived image is the same as the size of the base image (4 GB), the actual size is 140 KB only. The reason is that only changes made to the system inside the derived image are saved. Run the derived virtual machine, register it, if needed, and apply the latest patches. Do any other changes in the system such as removing unneeded or installing new software packages. Then shut the VM Guest down and examine its details once more:
tux > qemu-img info /images/sles_derived.qcow2
image: /images/sles_derived.qcow2
file format: qcow2
virtual size: 4.0G (4294967296 bytes)
disk size: 1.1G
cluster_size: 65536
backing file: /images/sles_base.raw \
(actual path: /images/sles_base.raw)
The disk size value has grown to 1.1 GB, which is the
disk space occupied by the changes on the file system compared to the base
image.
28.2.4.3 Rebasing Derived Images #
After you have modified the derived image (applied patches, installed specific applications, changed environment settings, etc.), it reaches the desired state. At that point, you can merge the original base image and the derived image to create a new base image.
Your original base image (/images/sles_base.raw)
holds a freshly installed system and can be a template for new modified
base images, while the new one can contain the same system as the first
one plus all security and update patches applied, for example. After you
have created this new base image, you can use it as a template for more
specialized derived images as well. The new base image becomes independent
of the original one. The process of creating base images from derived ones
is called rebasing:
tux > qemu-img convert /images/sles_derived.qcow2 \
-O raw /images/sles_base2.raw
This command created the new base image
/images/sles_base2.raw using the
raw format.
tux > qemu-img info /images/sles_base2.raw
image: /images/sles11_base2.raw
file format: raw
virtual size: 4.0G (4294967296 bytes)
disk size: 2.8GThe new image is 0.4 gigabytes bigger than the original base image. It uses no backing file, and you can easily create new derived images based upon it. This lets you create a sophisticated hierarchy of virtual disk images for your organization, saving a lot of time and work.
28.2.4.4 Mounting an Image on a VM Host Server #
It can be useful to mount a virtual disk image under the host system. It is strongly recommended to read Chapter 17, libguestfs and use dedicated tools to access a virtual machine image. However, if you need to do this manually, follow this guide.
Linux systems can mount an internal partition of a raw
disk image using a loopback device. The first example procedure is more
complex but more illustrative, while the second one is straightforward:
Procedure 28.1: Mounting Disk Image by Calculating Partition Offset #
Set a loop device on the disk image whose partition you want to mount.
tux >losetup /dev/loop0 /images/sles_base.rawFind the sector size and the starting sector number of the partition you want to mount.
tux >fdisk -lu /dev/loop0 Disk /dev/loop0: 4294 MB, 4294967296 bytes 255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 522 cylinders, total 8388608 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 5121 bytes Disk identifier: 0x000ceca8 Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System /dev/loop0p1 63 1542239 771088+ 82 Linux swap /dev/loop0p2 * 15422402 8385929 3421845 83 LinuxCalculate the partition start offset:
sector_size * sector_start = 512 * 1542240 = 789626880Delete the loop and mount the partition inside the disk image with the calculated offset on a prepared directory.
tux >losetup -d /dev/loop0tux >mount -o loop,offset=789626880 \ /images/sles_base.raw /mnt/sles/tux >ls -l /mnt/sles/ total 112 drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 16 10:02 bin drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Nov 16 10:27 boot drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 4096 Nov 16 09:11 dev [...] drwxrwxrwt 14 root root 4096 Nov 24 09:50 tmp drwxr-xr-x 12 root root 4096 Nov 16 09:16 usr drwxr-xr-x 15 root root 4096 Nov 16 09:22 varCopy one or more files onto the mounted partition and unmount it when finished.
tux >cp /etc/X11/xorg.conf /mnt/sles/root/tmptux >ls -l /mnt/sles/root/tmptux >umount /mnt/sles/
Warning: Do not Write to Images Currently in Use
Never mount a partition of an image of a running virtual machine in a
read-write mode. This could corrupt the partition and
break the whole VM Guest.
29 Running Virtual Machines with qemu-system-ARCH #
Once you have a virtual disk image ready (for more information on disk
images, see Section 28.2, “Managing Disk Images with qemu-img”), it is time to
start the related virtual machine.
Section 28.1, “Basic Installation with qemu-system-ARCH” introduced simple commands to
install and run a VM Guest. This chapter focuses on a more detailed
explanation of qemu-system-ARCH usage, and shows solutions
for more specific tasks. For a complete list of
qemu-system-ARCH's options, see its manual page
(man 1 qemu).
29.1 Basic qemu-system-ARCH Invocation #
The qemu-system-ARCH command uses the following syntax:
qemu-system-ARCH options1 disk_img2
| |
Path to the disk image holding the guest system you want to virtualize.
|
29.2 General qemu-system-ARCH Options #
This section introduces general qemu-system-ARCH options
and options related to the basic emulated hardware, such as the virtual
machine's processor, memory, model type, or time processing methods.
-name name_of_guestSpecifies the name of the running guest system. The name is displayed in the window caption and used for the VNC server.
-boot optionsSpecifies the order in which the defined drives will be booted. Drives are represented by letters, where
aandbstand for the floppy drives 1 and 2,cstands for the first hard disk,dstands for the first CD-ROM drive, andntopstand for Ether-boot network adapters.For example,
qemu-system-ARCH [...] -boot order=ndcfirst tries to boot from network, then from the first CD-ROM drive, and finally from the first hard disk.-pidfile fnameStores the QEMU's process identification number (PID) in a file. This is useful if you run QEMU from a script.
-nodefaultsBy default QEMU creates basic virtual devices even if you do not specify them on the command line. This option turns this feature off, and you must specify every single device manually, including graphical and network cards, parallel or serial ports, or virtual consoles. Even QEMU monitor is not attached by default.
-daemonize“Daemonizes” the QEMU process after it is started. QEMU will detach from the standard input and standard output after it is ready to receive connections on any of its devices.
Note: SeaBIOS BIOS Implementation
SeaBIOS is the default BIOS used. You can boot USB devices, any drive (CD-ROM, Floppy, or a hard disk). It has USB mouse and keyboard support and supports multiple VGA cards. For more information about SeaBIOS, refer to the SeaBIOS Website.
29.2.1 Basic Virtual Hardware #
29.2.1.1 Machine Type #
You can specifies the type of the emulated machine. Run
qemu-system-ARCH -M help to view a list of supported
machine types.
tux > qemu-system-x86_64 -M help
Supported machines are:
pc Standard PC (i440FX + PIIX, 1996) (alias of pc-i440fx-2.3)
pc-i440fx-2.3 Standard PC (i440FX + PIIX, 1996) (default)
pc-i440fx-2.2 Standard PC (i440FX + PIIX, 1996)
pc-i440fx-2.1 Standard PC (i440FX + PIIX, 1996)
pc-i440fx-2.0 Standard PC (i440FX + PIIX, 1996)
pc-i440fx-1.7 Standard PC (i440FX + PIIX, 1996)
pc-i440fx-1.6 Standard PC (i440FX + PIIX, 1996)
pc-i440fx-1.5 Standard PC (i440FX + PIIX, 1996)
pc-i440fx-1.4 Standard PC (i440FX + PIIX, 1996)
pc-1.3 Standard PC (i440FX + PIIX, 1996)
pc-1.2 Standard PC (i440FX + PIIX, 1996)
pc-1.1 Standard PC (i440FX + PIIX, 1996)
pc-1.0 Standard PC (i440FX + PIIX, 1996)
pc-0.15 Standard PC (i440FX + PIIX, 1996)
pc-0.14 Standard PC (i440FX + PIIX, 1996)
pc-0.13 Standard PC (i440FX + PIIX, 1996)
pc-0.12 Standard PC (i440FX + PIIX, 1996)
pc-0.11 Standard PC (i440FX + PIIX, 1996)
pc-0.10 Standard PC (i440FX + PIIX, 1996)
q35 Standard PC (Q35 + ICH9, 2009) (alias of pc-q35-2.3)
pc-q35-2.3 Standard PC (Q35 + ICH9, 2009)
pc-q35-2.2 Standard PC (Q35 + ICH9, 2009)
pc-q35-2.1 Standard PC (Q35 + ICH9, 2009)
pc-q35-2.0 Standard PC (Q35 + ICH9, 2009)
pc-q35-1.7 Standard PC (Q35 + ICH9, 2009)
pc-q35-1.6 Standard PC (Q35 + ICH9, 2009)
pc-q35-1.5 Standard PC (Q35 + ICH9, 2009)
pc-q35-1.4 Standard PC (Q35 + ICH9, 2009)
isapc ISA-only PC
none empty machine
xenfv Xen Fully-virtualized PC
xenpv Xen Para-virtualized PCNote: ISA-PC
The machine type isapc: ISA-only-PC is unsupported.
29.2.1.2 CPU Model #
To specify the type of the processor (CPU) model, run
qemu-system-ARCH -cpu MODEL.
Use qemu-system-ARCH -cpu help to view a list of
supported CPU models.
x86 qemu64 QEMU Virtual CPU version 2.3.1 x86 phenom AMD Phenom(tm) 9550 Quad-Core Processor x86 core2duo Intel(R) Core(TM)2 Duo CPU T7700 @ 2.40GHz x86 kvm64 Common KVM processor x86 qemu32 QEMU Virtual CPU version 2.3.1 x86 kvm32 Common 32-bit KVM processor x86 coreduo Genuine Intel(R) CPU T2600 @ 2.16GHz x86 486 x86 pentium x86 pentium2 x86 pentium3 x86 athlon QEMU Virtual CPU version 2.3.1 x86 n270 Intel(R) Atom(TM) CPU N270 @ 1.60GHz x86 Conroe Intel Celeron_4x0 (Conroe/Merom Class Core 2) x86 Penryn Intel Core 2 Duo P9xxx (Penryn Class Core 2) x86 Nehalem Intel Core i7 9xx (Nehalem Class Core i7) x86 Westmere Westmere E56xx/L56xx/X56xx (Nehalem-C) x86 SandyBridge Intel Xeon E312xx (Sandy Bridge) x86 IvyBridge Intel Xeon E3-12xx v2 (Ivy Bridge) x86 Haswell-noTSX Intel Core Processor (Haswell, no TSX) x86 Haswell Intel Core Processor (Haswell) x86 Broadwell-noTSX Intel Core Processor (Broadwell, no TSX) x86 Broadwell Intel Core Processor (Broadwell) x86 Opteron_G1 AMD Opteron 240 (Gen 1 Class Opteron) x86 Opteron_G2 AMD Opteron 22xx (Gen 2 Class Opteron) x86 Opteron_G3 AMD Opteron 23xx (Gen 3 Class Opteron) x86 Opteron_G4 AMD Opteron 62xx class CPU x86 Opteron_G5 AMD Opteron 63xx class CPU x86 host KVM processor with all supported host features (only available in KVM mode) Recognized CPUID flags: fpu vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 pn clflush ds acpi mmx fxsr sse sse2 ss ht tm ia64 pbe pni|sse3 pclmulqdq|pclmuldq dtes64 monitor ds_cpl vmx smx est tm2 ssse3 cid fma cx16 xtpr pdcm pcid dca sse4.1|sse4_1 sse4.2|sse4_2 x2apic movbe popcnt tsc-deadline aes xsave osxsave avx f16c rdrand hypervisor fsgsbase tsc_adjust bmi1 hle avx2 smep bmi2 erms invpcid rtm mpx avx512f rdseed adx smap avx512pf avx512er avx512cd syscall nx|xd mmxext fxsr_opt|ffxsr pdpe1gb rdtscp lm|i64 3dnowext 3dnow lahf_lm cmp_legacy svm extapic cr8legacy abm sse4a misalignsse 3dnowprefetch osvw ibs xop skinit wdt lwp fma4 tce nodeid_msr tbm topoext perfctr_core perfctr_nb invtsc xstore xstore-en xcrypt xcrypt-en ace2 ace2-en phe phe-en pmm pmm-en kvmclock kvm_nopiodelay kvm_mmu kvmclock kvm_asyncpf kvm_steal_time kvm_pv_eoi kvm_pv_unhalt kvmclock-stable-bit npt lbrv svm_lock nrip_save tsc_scale vmcb_clean flushbyasid decodeassists pause_filter pfthreshold xsaveopt xsavec xgetbv1 xsaves
CPU flags information can be found at CPUID Wikipedia.
29.2.1.3 Other Basics Options #
The following is a list of most commonly used options while launching qemu from command line. To see all options available refer to qemu-doc man page.
-m megabytesSpecifies how many megabytes are used for the virtual RAM size.
-balloon virtioSpecifies a paravirtualized device to dynamically change the amount of virtual RAM memory assigned to VM Guest. The top limit is the amount of memory specified with
-m.-smp number_of_cpusSpecifies how many CPUs will be emulated. QEMU supports up to 255 CPUs on the PC platform (up to 64 with KVM acceleration used). This option also takes other CPU-related parameters, such as number of sockets, number of cores per socket, or number of threads per core.
The following is an example of a working
qemu-system-ARCH command line:
tux > qemu-system-x86_64 -name "SLES 11 SP3" -M pc-i440fx-2.3 -m 512 \
-machine accel=kvm -cpu kvm64 -smp 2 /images/sles.rawFigure 29.1: QEMU Window with SLES 11 SP3 as VM Guest #
-no-acpiDisables ACPI support.
-SQEMU starts with CPU stopped. To start CPU, enter
cin QEMU monitor. For more information, see Chapter 30, Virtual Machine Administration Using QEMU Monitor.
29.2.2 Storing and Reading Configuration of Virtual Devices #
-readconfig cfg_fileInstead of entering the devices configuration options on the command line each time you want to run VM Guest,
qemu-system-ARCHcan read it from a file that was either previously saved with-writeconfigor edited manually.-writeconfig cfg_fileDumps the current virtual machine's devices configuration to a text file. It can be consequently re-used with the
-readconfigoption.tux >qemu-system-x86_64 -name "SLES 11 SP3" -machine accel=kvm -M pc-i440fx-2.3 -m 512 -cpu kvm64 \ -smp 2 /images/sles.raw -writeconfig /images/sles.cfg (exited)tux >cat /images/sles.cfg # qemu config file [drive] index = "0" media = "disk" file = "/images/sles_base.raw"This way you can effectively manage the configuration of your virtual machines' devices in a well-arranged way.
29.2.3 Guest Real-Time Clock #
-rtc optionsSpecifies the way the RTC is handled inside a VM Guest. By default, the clock of the guest is derived from that of the host system. Therefore, it is recommended that the host system clock is synchronized with an accurate external clock (for example, via NTP service).
If you need to isolate the VM Guest clock from the host one, specify
clock=vminstead of the defaultclock=host.You can also specify the initial time of the VM Guest's clock with the
baseoption:qemu-system-x86_64 [...] -rtc clock=vm,base=2010-12-03T01:02:00
Instead of a time stamp, you can specify
utcorlocaltime. The former instructs VM Guest to start at the current UTC value (Coordinated Universal Time, see http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/UTC), while the latter applies the local time setting.
29.3 Using Devices in QEMU #
QEMU virtual machines emulate all devices needed to run a VM Guest. QEMU supports, for example, several types of network cards, block devices (hard and removable drives), USB devices, character devices (serial and parallel ports), or multimedia devices (graphic and sound cards). This section introduces options to configure various types of supported devices.
Tip
If your device, such as -drive, needs a special driver
and driver properties to be set, specify them with the
-device option, and identify with
drive= suboption. For example:
qemu-system-x86_64 [...] -drive if=none,id=drive0,format=raw \ -device virtio-blk-pci,drive=drive0,scsi=off ...
To get help on available drivers and their properties, use -device
? and -device
driver,?.
29.3.1 Block Devices #
Block devices are vital for virtual machines. In general, these are fixed or removable storage media usually called drives. One of the connected hard disks typically holds the guest operating system to be virtualized.
Virtual Machine drives are defined with
-drive. This option has many sub-options, some of which
are described in this section. For the complete list, see the manual page
(man 1 qemu).
Sub-options for the -drive Option #
file=image_fnameSpecifies the path to the disk image that will be used with this drive. If not specified, an empty (removable) drive is assumed.
if=drive_interfaceSpecifies the type of interface to which the drive is connected. Currently only
floppy,scsi,ide, orvirtioare supported by SUSE.virtiodefines a paravirtualized disk driver. Default iside.index=index_of_connectorSpecifies the index number of a connector on the disk interface (see the
ifoption) where the drive is connected. If not specified, the index is automatically incremented.media=typeSpecifies the type of media. Can be
diskfor hard disks, orcdromfor removable CD-ROM drives.format=img_fmtSpecifies the format of the connected disk image. If not specified, the format is autodetected. Currently, SUSE supports
qcow2,qedandrawformats.cache=methodSpecifies the caching method for the drive. Possible values are
unsafe,writethrough,writeback,directsync, ornone. To improve performance when using theqcow2image format, choosewriteback.nonedisables the host page cache and, therefore, is the safest option. Default for image files iswriteback. For more information, see Chapter 15, Disk Cache Modes.
Tip
To simplify defining block devices, QEMU understands several shortcuts
which you may find handy when entering the
qemu-system-ARCH command line.
You can use
qemu-system-x86_64 -cdrom /images/cdrom.iso
instead of
qemu-system-x86_64 -drive file=/images/cdrom.iso,index=2,media=cdrom
and
qemu-system-x86_64 -hda /images/imagei1.raw -hdb /images/image2.raw -hdc \ /images/image3.raw -hdd /images/image4.raw
instead of
qemu-system-x86_64 -drive file=/images/image1.raw,index=0,media=disk \ -drive file=/images/image2.raw,index=1,media=disk \ -drive file=/images/image3.raw,index=2,media=disk \ -drive file=/images/image4.raw,index=3,media=disk
Tip: Using Host Drives Instead of Images
As an alternative to using disk images (see
Section 28.2, “Managing Disk Images with qemu-img”) you can also use existing
VM Host Server disks, connect them as drives, and access them from VM Guest.
Use the host disk device directly instead of disk image file names.
To access the host CD-ROM drive, use
qemu-system-x86_64 [...] -drive file=/dev/cdrom,media=cdrom
To access the host hard disk, use
qemu-system-x86_64 [...] -drive file=/dev/hdb,media=disk
A host drive used by a VM Guest must not be accessed concurrently by the VM Host Server or another VM Guest.
29.3.1.1 Freeing Unused Guest Disk Space #
A Sparse image file is a type of disk image file that grows in size as the user adds data to it, taking up only as much disk space as is stored in it. For example, if you copy 1 GB of data inside the sparse disk image, its size grows by 1 GB. If you then delete for example 500 MB of the data, the image size does not by default decrease as expected.
That is why the discard=on option is introduced on the
KVM command line. It tells the hypervisor to automatically free the
“holes” after deleting data from the sparse guest image. Note
that this option is valid only for the if=scsi drive
interface:
qemu-system-x86_64 [...] -drive file=/path/to/file.img,if=scsi,discard=on
Important: Support Status
if=scsi is not supported. This interface does not map to
virtio-scsi, but rather to the lsi SCSI
adapter.
29.3.1.2 virtio-blk-data-plane #
The virtio-blk-data-plane is a new feature for KVM. It enables a high-performance code path for I/O requests coming from VM Guests. More specifically, this feature introduces dedicated threads (one per virtual block device) to process I/O requests going through the virtio-blk driver. It uses the Linux AIO (asynchronous I/O) interface of the VM Host Server kernel directly—without the need to go through the QEMU block layer. Therefore, it can sustain very high I/O rates on storage setups.
The virtio-blk-data-plane feature can be enabled or disabled by the
x-data-plane=on|off option on the qemu
command line when starting the VM Guest:
tux > qemu-system-x86_64 [...] -drive if=none,id=drive0,cache=none,aio=native,\
format=raw,file=filename -device virtio-blk-pci,drive=drive0,scsi=off,\
config-wce=off,x-data-plane=on [...]Currently, virtio-blk-data-plane has the following limitations:
Only the raw image format is supported.
No support for live migration.
Block jobs and hot unplug operations fail with
-EBUSY.I/O throttling limits are ignored.
Only Linux VM Host Servers are supported because of the Linux AIO usage, but non-Linux VM Guests are supported.
Important: Support Status
The virtio-blk-data-plane feature is not yet supported in openSUSE Leap. It is released as a technology preview only.
29.3.1.3 Bio-Based I/O Path for virtio-blk #
For better performance of I/O-intensive applications, a new I/O path was introduced for the virtio-blk interface in kernel version 3.7. This bio-based block device driver skips the I/O scheduler, and thus shortens the I/O path in guest and has lower latency. It is especially useful for high-speed storage devices, such as SSD disks.
The driver is disabled by default. To use it, do the following:
Append
virtio_blk.use_bio=1to the kernel command line on the guest. You can do so via › › .You can do it also by editing
/etc/default/grub, searching for the line that containsGRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT=, and adding the kernel parameter at the end. Then rungrub2-mkconfig >/boot/grub2/grub.cfgto update the grub2 boot menu.Reboot the guest with the new kernel command line active.
Tip: Bio-Based Driver on Slow Devices
The bio-based virtio-blk driver does not help on slow devices such as spin hard disks. The reason is that the benefit of scheduling is larger than what the shortened bio path offers. Do not use the bio-based driver on slow devices.
29.3.1.4 Accessing iSCSI Resources Directly #
QEMU now integrates with libiscsi. This allows
QEMU to access iSCSI resources directly and use them as virtual
machine block devices.
This feature does not require any host iSCSI initiator
configuration, as is needed for a libvirt iSCSI target based storage
pool setup. Instead it directly connects guest storage interfaces
to an iSCSI target LUN by means of the user space library libiscsi.
iSCSI-based disk devices can also be
specified in the libvirt XML configuration.
Note: RAW Image Format
This feature is only available using the RAW image format, as the iSCSI protocol has some technical limitations.
The following is the QEMU command line interface for iSCSI connectivity.
Note: virt-manager Limitation
The use of libiscsi based storage provisioning is not yet exposed by the virt-manager interface, but instead it would be configured by directly editing the guest xml. This new way of accessing iSCSI based storage is to be done at the command line.
qemu-system-x86_64 -machine accel=kvm \ -drive file=iscsi://192.168.100.1:3260/iqn.2016-08.com.example:314605ab-a88e-49af-b4eb-664808a3443b/0,\ format=raw,if=none,id=mydrive,cache=none \ -device ide-hd,bus=ide.0,unit=0,drive=mydrive ...
Here is an example snippet of guest domain xml which uses the protocol based iSCSI:
<devices>
...
<disk type='network' device='disk'>
<driver name='qemu' type='raw'/>
<source protocol='iscsi' name='iqn.2013-07.com.example:iscsi-nopool/2'>
<host name='example.com' port='3260'/>
</source>
<auth username='myuser'>
<secret type='iscsi' usage='libvirtiscsi'/>
</auth>
<target dev='vda' bus='virtio'/>
</disk>
</devices>Contrast that with an example which uses the host based iSCSI initiator which virt-manager sets up:
<devices>
...
<disk type='block' device='disk'>
<driver name='qemu' type='raw' cache='none' io='native'/>
<source dev='/dev/disk/by-path/scsi-0:0:0:0'/>
<target dev='hda' bus='ide'/>
<address type='drive' controller='0' bus='0' target='0' unit='0'/>
</disk>
<controller type='ide' index='0'>
<address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x00' slot='0x01'
function='0x1'/>
</controller>
</devices>29.3.2 Graphic Devices and Display Options #
This section describes QEMU options affecting the type of the emulated video card and the way VM Guest graphical output is displayed.
29.3.2.1 Defining Video Cards #
QEMU uses -vga to define a video card used to display
VM Guest graphical output. The -vga option understands
the following values:
noneDisables video cards on VM Guest (no video card is emulated). You can still access the running VM Guest via the serial console.
stdEmulates a standard VESA 2.0 VBE video card. Use it if you intend to use high display resolution on VM Guest.
cirrusEmulates Cirrus Logic GD5446 video card. Good choice if you insist on high compatibility of the emulated video hardware. Most operating systems (even Windows 95) recognize this type of card.

Tip
For best video performance with the
cirrustype, use 16-bit color depth both on VM Guest and VM Host Server.
29.3.2.2 Display Options #
The following options affect the way VM Guest graphical output is displayed.
-display gtkDisplay video output in a GTK window. This interface provides UI elements to configure and control the VM during runtime.
-display sdlDisplay video output via SDL, usually in a separate graphics window. For more information, see the SDL documentation.
-spice option[,option[,...]]Enables the spice remote desktop protocol.
-display vncRefer to Section 29.5, “Viewing a VM Guest with VNC” for more information.
-nographicDisables QEMU's graphical output. The emulated serial port is redirected to the console.
After starting the virtual machine with
-nographic, press Ctrl–A H in the virtual console to view the list of other useful shortcuts, for example, to toggle between the console and the QEMU monitor.tux >qemu-system-x86_64 -hda /images/sles_base.raw -nographic C-a h print this help C-a x exit emulator C-a s save disk data back to file (if -snapshot) C-a t toggle console timestamps C-a b send break (magic sysrq) C-a c switch between console and monitor C-a C-a sends C-a (pressed C-a c) QEMU 2.3.1 monitor - type 'help' for more information (qemu)-no-frameDisables decorations for the QEMU window. Convenient for dedicated desktop work space.
-full-screenStarts QEMU graphical output in full screen mode.
-no-quitDisables the close button of the QEMU window and prevents it from being closed by force.
-alt-grab,-ctrl-grabBy default, the QEMU window releases the “captured” mouse after pressing Ctrl–Alt. You can change the key combination to either Ctrl–Alt–Shift (
-alt-grab), or the right Ctrl key (-ctrl-grab).
29.3.3 USB Devices #
There are two ways to create USB devices usable by the VM Guest in KVM:
you can either emulate new USB devices inside a VM Guest, or assign an
existing host USB device to a VM Guest. To use USB devices in QEMU you
first need to enable the generic USB driver with the -usb
option. Then you can specify individual devices with the
-usbdevice option.
29.3.3.1 Emulating USB Devices in VM Guest #
SUSE currently supports the following types of USB devices:
disk, host,
serial, braille,
net, mouse, and
tablet.
Types of USB devices for the -usbdevice option #
diskEmulates a mass storage device based on file. The optional
formatoption is used rather than detecting the format.qemu-system-x86_64 [...] -usbdevice disk:format=raw:/virt/usb_disk.rawhostPass through the host device (identified by bus.addr).
serialSerial converter to a host character device.
brailleEmulates a braille device using BrlAPI to display the braille output.
netEmulates a network adapter that supports CDC Ethernet and RNDIS protocols.
mouseEmulates a virtual USB mouse. This option overrides the default PS/2 mouse emulation. The following example shows the hardware status of a mouse on VM Guest started with
qemu-system-ARCH [...] -usbdevice mouse:tux >sudo hwinfo --mouse 20: USB 00.0: 10503 USB Mouse [Created at usb.122] UDI: /org/freedesktop/Hal/devices/usb_device_627_1_1_if0 [...] Hardware Class: mouse Model: "Adomax QEMU USB Mouse" Hotplug: USB Vendor: usb 0x0627 "Adomax Technology Co., Ltd" Device: usb 0x0001 "QEMU USB Mouse" [...]tabletEmulates a pointer device that uses absolute coordinates (such as touchscreen). This option overrides the default PS/2 mouse emulation. The tablet device is useful if you are viewing VM Guest via the VNC protocol. See Section 29.5, “Viewing a VM Guest with VNC” for more information.
29.3.4 Character Devices #
Use -chardev to create a new character device. The
option uses the following general syntax:
qemu-system-x86_64 [...] -chardev backend_type,id=id_string
where backend_type can be one of
null, socket, udp,
msmouse, vc, file,
pipe, console,
serial, pty,
stdio, braille,
tty, or parport. All character
devices must have a unique identification string up to 127 characters long.
It is used to identify the device in other related directives. For the
complete description of all back-end's sub-options, see the manual page
(man 1 qemu). A brief description of the available
back-ends follows:
nullCreates an empty device that outputs no data and drops any data it receives.
stdioConnects to QEMU's process standard input and standard output.
socketCreates a two-way stream socket. If path is specified, a Unix socket is created:
qemu-system-x86_64 [...] -chardev \ socket,id=unix_socket1,path=/tmp/unix_socket1,server
The server suboption specifies that the socket is a listening socket.
If port is specified, a TCP socket is created:
qemu-system-x86_64 [...] -chardev \ socket,id=tcp_socket1,host=localhost,port=7777,server,nowait
The command creates a local listening (
server) TCP socket on port 7777. QEMU will not block waiting for a client to connect to the listening port (nowait).udpSends all network traffic from VM Guest to a remote host over the UDP protocol.
qemu-system-x86_64 [...] \ -chardev udp,id=udp_fwd,host=mercury.example.com,port=7777
The command binds port 7777 on the remote host mercury.example.com and sends VM Guest network traffic there.
vcCreates a new QEMU text console. You can optionally specify the dimensions of the virtual console:
qemu-system-x86_64 [...] -chardev vc,id=vc1,width=640,height=480 \ -mon chardev=vc1
The command creates a new virtual console called
vc1of the specified size, and connects the QEMU monitor to it.fileLogs all traffic from VM Guest to a file on VM Host Server. The
pathis required and will be created if it does not exist.qemu-system-x86_64 [...] \ -chardev file,id=qemu_log1,path=/var/log/qemu/guest1.log
By default QEMU creates a set of character devices for serial and parallel ports, and a special console for QEMU monitor. However, you can create your own character devices and use them for the mentioned purposes. The following options will help you:
-serial char_devRedirects the VM Guest's virtual serial port to a character device char_dev on VM Host Server. By default, it is a virtual console (
vc) in graphical mode, andstdioin non-graphical mode. The-serialunderstands many sub-options. See the manual pageman 1 qemufor a complete list of them.You can emulate up to 4 serial ports. Use
-serial noneto disable all serial ports.-parallel deviceRedirects the VM Guest's parallel port to a device. This option supports the same devices as
-serial.
Tip
With SUSE Linux Enterprise Server as a VM Host Server, you can directly use the hardware parallel port devices
/dev/parportNwhereNis the number of the port.You can emulate up to 3 parallel ports. Use
-parallel noneto disable all parallel ports.-monitor char_devRedirects the QEMU monitor to a character device char_dev on VM Host Server. This option supports the same devices as
-serial. By default, it is a virtual console (vc) in a graphical mode, andstdioin non-graphical mode.
For a complete list of available character devices back-ends, see the man
page (man 1 qemu).
29.4 Networking in QEMU #
Use the -netdev option in combination with
-device to define a specific type of networking and a
network interface card for your VM Guest. The syntax for the
-netdev option is
-netdev type[,prop[=value][,...]]
Currently, SUSE supports the following network types:
user, bridge, and
tap. For a complete list of -netdev
sub-options, see the manual page (man 1 qemu).
Supported -netdev Sub-options #
bridgeUses a specified network helper to configure the TAP interface and attach it to a specified bridge. For more information, see Section 29.4.3, “Bridged Networking”.
userSpecifies user-mode networking. For more information, see Section 29.4.2, “User-Mode Networking”.
tapSpecifies bridged or routed networking. For more information, see Section 29.4.3, “Bridged Networking”.
29.4.1 Defining a Network Interface Card #
Use -netdev together with the related
-device option to add a new emulated network card:
qemu-system-x86_64 [...] \ -netdev tap1,id=hostnet0 \ -device virtio-net-pci2,netdev=hostnet0,vlan=13,\ macaddr=00:16:35:AF:94:4B4,name=ncard1
Specifies the network device type. | |
Specifies the model of the network card. Use qemu-system-x86_64 -device help [...] Network devices: name "e1000", bus PCI, desc "Intel Gigabit Ethernet" name "e1000-82540em", bus PCI, desc "Intel Gigabit Ethernet" name "e1000-82544gc", bus PCI, desc "Intel Gigabit Ethernet" name "e1000-82545em", bus PCI, desc "Intel Gigabit Ethernet" name "i82550", bus PCI, desc "Intel i82550 Ethernet" name "i82551", bus PCI, desc "Intel i82551 Ethernet" name "i82557a", bus PCI, desc "Intel i82557A Ethernet" [...]
Currently, SUSE supports the models qemu-system-x86_64 -device e1000,help e1000.mac=macaddr e1000.vlan=vlan e1000.netdev=netdev e1000.bootindex=int32 e1000.autonegotiation=on/off e1000.mitigation=on/off e1000.addr=pci-devfn e1000.romfile=str e1000.rombar=uint32 e1000.multifunction=on/off e1000.command_serr_enable=on/off | |
Connects the network interface to VLAN number 1. You can specify your own number—it is mainly useful for identification purpose. If you omit this suboption, QEMU uses the default 0. | |
Specifies the Media Access Control (MAC) address for the network card. It is a unique identifier and you are advised to always specify it. If not, QEMU supplies its own default MAC address and creates a possible MAC address conflict within the related VLAN. |
29.4.2 User-Mode Networking #
The -netdev user option instructs QEMU to use
user-mode networking. This is the default if no networking mode is
selected. Therefore, these command lines are equivalent:
qemu-system-x86_64 -hda /images/sles_base.raw
qemu-system-x86_64 -hda /images/sles_base.raw -netdev user,id=hostnet0
This mode is useful if you want to allow the VM Guest to access the external network resources, such as the Internet. By default, no incoming traffic is permitted and therefore, the VM Guest is not visible to other machines on the network. No administrator privileges are required in this networking mode. The user-mode is also useful for doing a network boot on your VM Guest from a local directory on VM Host Server.
The VM Guest allocates an IP address from a virtual DHCP server. VM Host Server
(the DHCP server) is reachable at 10.0.2.2, while the IP address range for
allocation starts from 10.0.2.15. You can use ssh to
connect to VM Host Server at 10.0.2.2, and scp to copy files
back and forth.
29.4.2.1 Command Line Examples #
This section shows several examples on how to set up user-mode networking with QEMU.
Example 29.1: Restricted User-mode Networking #
qemu-system-x86_64 [...] \ -netdev user1,id=hostnet0 \ -device virtio-net-pci,netdev=hostnet0,vlan=12,name=user_net13,restrict=yes4
Specifies user-mode networking. | |
Connects to VLAN number 1. If omitted, defaults to 0. | |
Specifies a human-readable name of the network stack. Useful when identifying it in the QEMU monitor. | |
Isolates VM Guest. It then cannot communicate with VM Host Server and no network packets will be routed to the external network. |
Example 29.2: User-mode Networking with Custom IP Range #
qemu-system-x86_64 [...] \ -netdev user,id=hostnet0 \ -device virtio-net-pci,netdev=hostnet0,net=10.2.0.0/81,host=10.2.0.62,\ dhcpstart=10.2.0.203,hostname=tux_kvm_guest4
Specifies the IP address of the network that VM Guest sees and optionally the netmask. Default is 10.0.2.0/8. | |
Specifies the VM Host Server IP address that VM Guest sees. Default is 10.0.2.2. | |
Specifies the first of the 16 IP addresses that the built-in DHCP server can assign to VM Guest. Default is 10.0.2.15. | |
Specifies the host name that the built-in DHCP server will assign to VM Guest. |
Example 29.3: User-mode Networking with Network-boot and TFTP #
qemu-system-x86_64 [...] \ -netdev user,id=hostnet0 \ -device virtio-net-pci,netdev=hostnet0,tftp=/images/tftp_dir1,\ bootfile=/images/boot/pxelinux.02
Activates a built-in TFTP (a file transfer protocol with the functionality of a very basic FTP) server. The files in the specified directory will be visible to a VM Guest as the root of a TFTP server. | |
Broadcasts the specified file as a BOOTP (a network protocol that
offers an IP address and a network location of a boot image, often used
in diskless workstations) file. When used together with
|
Example 29.4: User-mode Networking with Host Port Forwarding #
qemu-system-x86_64 [...] \ -netdev user,id=hostnet0 \ -device virtio-net-pci,netdev=hostnet0,hostfwd=tcp::2222-:22
Forwards incoming TCP connections to the port 2222 on the host to the
port 22 (SSH) on VM Guest. If
sshd is running on VM Guest,
enter
ssh qemu_host -p 2222
where qemu_host is the host name or IP address of the
host system, to get a SSH prompt
from VM Guest.
29.4.3 Bridged Networking #
With the -netdev tap option, QEMU creates a network
bridge by connecting the host TAP network device to a specified VLAN of
VM Guest. Its network interface is then visible to the rest of the
network. This method does not work by default and needs to be explicitly
specified.
First, create a network bridge and add a VM Host Server physical network
interface (usually eth0) to it:
Start and select › .
Click and select from the drop-down box in the window. Click .
Choose whether you need a dynamically or statically assigned IP address, and fill the related network settings if applicable.
In the pane, select the Ethernet device to add to the bridge.
Figure 29.2: Configuring Network Bridge with YaST #
Click . When asked about adapting an already configured device, click .
Click to apply the changes. Check if the bridge is created:
tux >brctl show bridge name bridge id STP enabled interfaces br0 8000.001676d670e4 no eth0
29.4.3.1 Connecting to a Bridge Manually #
Use the following example script to connect VM Guest to the newly created
bridge interface br0. Several commands in the script
are run via the sudo mechanism because they require
root privileges.
Note: Required Packages
Make sure the tunctl and
bridge-utils packages are installed on the
VM Host Server. If not, install them with zypper in tunctl
bridge-utils.
#!/bin/bash bridge=br01 tap=$(sudo tunctl -u $(whoami) -b)2 sudo ip link set $tap up3 sleep 1s4 sudo brctl addif $bridge $tap5 qemu-system-x86_64 -machine accel=kvm -m 512 -hda /images/sles_base.raw \ -netdev tap,id=hostnet0 \ -device virtio-net-pci,netdev=hostnet0,vlan=0,macaddr=00:16:35:AF:94:4B,\ ifname=$tap6,script=no7,downscript=no sudo brctl delif $bridge $tap8 sudo ip link set $tap down9 sudo tunctl -d $tap10
Name of the bridge device. | |
Prepare a new TAP device and assign it to the user who runs the script. TAP devices are virtual network devices often used for virtualization and emulation setups. | |
Bring up the newly created TAP network interface. | |
Make a 1-second pause to make sure the new TAP network interface is really up. | |
Add the new | |
The | |
Before | |
Deletes the TAP interface from a network bridge | |
Sets the state of the TAP device to | |
Deconfigures the TAP device. |
29.4.3.2 Connecting to a Bridge with qemu-bridge-helper #
Another way to connect VM Guest to a network through a network bridge is
by means of the qemu-bridge-helper helper program. It
configures the TAP interface for you, and attaches it to the specified
bridge. The default helper executable is
/usr/lib/qemu-bridge-helper. The helper executable is
setuid root, which is only executable by the members of the virtualization
group (kvm). Therefore the
qemu-system-ARCH command itself does not need to be run
under root privileges.
The helper is automatically called when you specify a network bridge:
qemu-system-x86_64 [...] \ -netdev bridge,id=hostnet0,vlan=0,br=br0 \ -device virtio-net-pci,netdev=hostnet0
You can specify your own custom helper script that will take care of the
TAP device (de)configuration, with the
helper=/path/to/your/helper option:
qemu-system-x86_64 [...] \ -netdev bridge,id=hostnet0,vlan=0,br=br0,helper=/path/to/bridge-helper \ -device virtio-net-pci,netdev=hostnet0
Tip
To define access privileges to qemu-bridge-helper,
inspect the /etc/qemu/bridge.conf file. For example
the following directive
allow br0
allows the qemu-system-ARCH command to connect its
VM Guest to the network bridge br0.
29.5 Viewing a VM Guest with VNC #
By default QEMU uses a GTK (a cross-platform toolkit library) window to
display the graphical output of a VM Guest.
With the -vnc option specified, you can make QEMU
listen on a specified VNC display and redirect its graphical output to the
VNC session.
Tip
When working with QEMU's virtual machine via VNC session, it is useful to
work with the -usbdevice tablet option.
Moreover, if you need to use another keyboard layout than the default
en-us, specify it with the -k option.
The first suboption of -vnc must be a
display value. The -vnc option
understands the following display specifications:
host:displayOnly connections from
hoston the display numberdisplaywill be accepted. The TCP port on which the VNC session is then running is normally a 5900 +displaynumber. If you do not specifyhost, connections will be accepted from any host.unix:pathThe VNC server listens for connections on Unix domain sockets. The
pathoption specifies the location of the related Unix socket.noneThe VNC server functionality is initialized, but the server itself is not started. You can start the VNC server later with the QEMU monitor. For more information, see Chapter 30, Virtual Machine Administration Using QEMU Monitor.
Following the display value there may be one or more option flags separated by commas. Valid options are:
reverseConnect to a listening VNC client via a reverse connection.
websocketOpens an additional TCP listening port dedicated to VNC Websocket connections. By definition the Websocket port is 5700+display.
passwordRequire that password-based authentication is used for client connections.
tlsRequire that clients use TLS when communicating with the VNC server.
x509=/path/to/certificate/dirValid if TLS is specified. Require that x509 credentials are used for negotiating the TLS session.
x509verify=/path/to/certificate/dirValid if TLS is specified. Require that x509 credentials are used for negotiating the TLS session.
saslRequire that the client uses SASL to authenticate with the VNC server.
aclTurn on access control lists for checking of the x509 client certificate and SASL party.
lossyEnable lossy compression methods (gradient, JPEG, ...).
non-adaptiveDisable adaptive encodings. Adaptive encodings are enabled by default.
share=[allow-exclusive|force-shared|ignore]Set display sharing policy.
Note
For more details about the display options, see the qemu-doc man page.
An example VNC usage:
tux >qemu-system-x86_64 [...] -vnc :5 (on the client:)wilber >:~>vinagre venus:5905 &
Figure 29.3: QEMU VNC Session #
29.5.1 Secure VNC Connections #
The default VNC server setup does not use any form of authentication. In the previous example, any user can connect and view the QEMU VNC session from any host on the network.
There are several levels of security that you can apply to your VNC client/server connection. You can either protect your connection with a password, use x509 certificates, use SASL authentication, or even combine some authentication methods in one QEMU command.
See Section B.1, “Generating x509 Client/Server Certificates” for more information about the
x509 certificates generation. For more information about configuring x509
certificates on a VM Host Server and the client, see
Section 11.3.2, “Remote TLS/SSL Connection with x509 Certificate (qemu+tls or xen+tls)” and
Section 11.3.2.3, “Configuring the Client and Testing the Setup”.
The Vinagre VNC viewer supports advanced authentication mechanisms.
Therefore, it will be used to view the graphical output of VM Guest in the
following examples. For this example, let us assume that the server x509
certificates ca-cert.pem,
server-cert.pem, and
server-key.pem are located in the
/etc/pki/qemu directory on the host, while the
client's certificates are distributed in the following locations on the
client:
/etc/pki/CA/cacert.pem
|
/etc/pki/libvirt-vnc/clientcert.pem
|
/etc/pki/libvirt-vnc/private/clientkey.pem
|
Example 29.5: Password Authentication #
qemu-system-x86_64 [...] -vnc :5,password -monitor stdio
Starts the VM Guest graphical output on VNC display number 5 (usually
port 5905). The password suboption initializes a simple
password-based authentication method. There is no password set by default
and you need to set one with the change vnc password
command in QEMU monitor:
QEMU 2.3.1 monitor - type 'help' for more information (qemu) change vnc password Password: ****
You need the -monitor stdio option here, because you
would not be able to manage the QEMU monitor without redirecting its
input/output.
Figure 29.4: Authentication Dialog in Vinagre #
Example 29.6: x509 Certificate Authentication #
The QEMU VNC server can use TLS encryption for the session and x509 certificates for authentication. The server asks the client for a certificate and validates it against the CA certificate. Use this authentication type if your company provides an internal certificate authority.
qemu-system-x86_64 [...] -vnc :5,tls,x509verify=/etc/pki/qemu
Example 29.7: x509 Certificate and Password Authentication #
You can combine the password authentication with TLS encryption and x509 certificate authentication to create a two-layer authentication model for clients. Remember to set the password in the QEMU monitor after you run the following command:
qemu-system-x86_64 [...] -vnc :5,password,tls,x509verify=/etc/pki/qemu \ -monitor stdio
Example 29.8: SASL Authentication #
Simple Authentication and Security Layer (SASL) is a framework for authentication and data security in Internet protocols. It integrates several authentication mechanisms, like PAM, Kerberos, LDAP and more. SASL keeps its own user database, so the connecting user accounts do not need to exist on VM Host Server.
For security reasons, you are advised to combine SASL authentication with TLS encryption and x509 certificates:
qemu-system-x86_64 [...] -vnc :5,tls,x509,sasl -monitor stdio
30 Virtual Machine Administration Using QEMU Monitor #
- 30.1 Accessing Monitor Console
- 30.2 Getting Information about the Guest System
- 30.3 Changing VNC Password
- 30.4 Managing Devices
- 30.5 Controlling Keyboard and Mouse
- 30.6 Changing Available Memory
- 30.7 Dumping Virtual Machine Memory
- 30.8 Managing Virtual Machine Snapshots
- 30.9 Suspending and Resuming Virtual Machine Execution
- 30.10 Live Migration
- 30.11 QMP - QEMU Machine Protocol
When QEMU is running, a monitor console is provided for performing interaction with the user. Using the commands available in the monitor console, it is possible to inspect the running operating system, change removable media, take screenshots or audio grabs and control other aspects of the virtual machine.
Note
The following sections list selected useful QEMU monitor commands
and their purpose. To get the full list, enter help in
the QEMU monitor command line.
30.1 Accessing Monitor Console #
You can access the monitor console from QEMU window either by a keyboard shortcut—press Ctrl–Alt–2 (to return to QEMU, press Ctrl–Alt–1)—or alternatively by clicking in the QEMU GUI window, then . The most convenient way is to show the QEMU window tabs with › . Then you can easily switch between the guest screen, monitor screen, and the output of the serial and parallel console.
To get help while using the console, use help or
?. To get help for a specific command, use
help command.
30.2 Getting Information about the Guest System #
To get information about the guest system, use
info. If used without any option, the list of possible
options is printed. Options determine which part of the system will be
analyzed:
info versionShows the version of QEMU.
info commandsLists available QMP commands.
info networkShows the network state.
info chardevShows the character devices.
info blockInformation about block devices, such as hard disks, floppy drives, or CD-ROMs.
info blockstatsRead and write statistics on block devices.
info registersShows the CPU registers.
info cpusShows information about available CPUs.
info historyShows the command line history.
info irqShows the interrupt statistics.
info picShows the i8259 (PIC) state.
info pciShows the PCI information.
info tlbShows virtual to physical memory mappings.
info memShows the active virtual memory mappings.
info jitShows dynamic compiler information.
info kvmShows the KVM information.
info numaShows the NUMA information.
info usbShows the guest USB devices.
info usbhostShows the host USB devices.
info profileShows the profiling information.
info captureShows the capture (audio grab) information.
info snapshotsShows the currently saved virtual machine snapshots.
info statusShows the current virtual machine status.
info pcmciaShows the guest PCMCIA status.
info miceShows which guest mice are receiving events.
info vncShows the VNC server status.
info nameShows the current virtual machine name.
info uuidShows the current virtual machine UUID.
info usernetShows the user network stack connection states.
info migrateShows the migration status.
info balloonShows the balloon device information.
info qtreeShows the device tree.
info qdmShows the qdev device model list.
info romsShows the ROMs.
info migrate_cache_sizeShows the current migration xbzrle (“Xor Based Zero Run Length Encoding”) cache size.
info migrate_capabilitiesShows the status of the various migration capabilities, such as xbzrle compression.
info mtreeShows the VM Guest memory hierarchy.
info trace-eventsShows available trace-events and their status.
30.3 Changing VNC Password #
To change the VNC password, use the change vnc
password command and enter the new password:
(qemu) change vnc password Password: ******** (qemu)
30.4 Managing Devices #
To add a new disk while the guest is running (hotplug), use the
drive_add and device_add commands.
First define a new drive to be added as a device to bus 0:
(qemu) drive_add 0 if=none,file=/tmp/test.img,format=raw,if=disk1 OK
You can confirm your new device by querying the block subsystem:
(qemu) info block [...] disk1: removable=1 locked=0 tray-open=0 file=/tmp/test.img ro=0 drv=raw \ encrypted=0 bps=0 bps_rd=0 bps_wr=0 iops=0 iops_rd=0 iops_wr=0
After the new drive is defined, it needs to be connected to a device so
that the guest can see it. The typical device would be a
virtio-blk-pci or scsi-disk. To get
the full list of available driver values, run:
(qemu) device_add ? name "VGA", bus PCI name "usb-storage", bus usb-bus [...] name "virtio-blk-pci", bus virtio-bus
Now add the device
(qemu) device_add virtio-blk-pci,drive=disk1,id=myvirtio1
and confirm with
(qemu) info pci
[...]
Bus 0, device 4, function 0:
SCSI controller: PCI device 1af4:1001
IRQ 0.
BAR0: I/O at 0xffffffffffffffff [0x003e].
BAR1: 32 bit memory at 0xffffffffffffffff [0x00000ffe].
id "myvirtio1"Tip
Devices added with the device_add command can be
removed from the guest with device_del. Enter
help device_del on the QEMU monitor command line
for more information.
To release the device or file connected to the removable media device,
use the eject device
command. Use the optional -f to force ejection.
To change removable media (like CD-ROMs), use the
change device command. The
name of the removable media can be determined using the info
block command:
(qemu) info block ide1-cd0: type=cdrom removable=1 locked=0 file=/dev/sr0 ro=1 drv=host_device (qemu) change ide1-cd0 /path/to/image
30.5 Controlling Keyboard and Mouse #
It is possible to use the monitor console to emulate keyboard and mouse
input if necessary. For example, if your graphical user interface
intercepts some key combinations at low level (such as Ctrl–Alt–F1
in X Window), you can still enter them using the sendkey
keys:
sendkey ctrl-alt-f1
To list the key names used in the keys option,
enter sendkey and press →|.
To control the mouse, the following commands can be used:
mouse_movedxdy [dz]Move the active mouse pointer to the specified coordinates dx, dy with the optional scroll axis dz.
mouse_buttonvalChange the state of the mouse buttons (1=left, 2=middle, 4=right).
mouse_setindexSet which mouse device receives events. Device index numbers can be obtained with the
info micecommand.
30.6 Changing Available Memory #
If the virtual machine was started with the -balloon
virtio option and the paravirtualized balloon device that allows
to dynamically change the amount of memory available is therefore
enabled, it is possible to change the available memory dynamically. For
more information about enabling the balloon device, see
Section 28.1, “Basic Installation with qemu-system-ARCH”.
To get information about the balloon device in the monitor console and to
determine whether the device is enabled, use the info
balloon command:
(qemu) info balloon
If the balloon device is enabled, use the balloon
memory_in_MB command to set the requested
amount of memory:
(qemu) balloon 400
30.7 Dumping Virtual Machine Memory #
To save the content of the virtual machine memory to a disk or console output, use the following commands:
memsaveaddrsizefilenameSaves virtual memory dump starting at addr of size size to file filename
pmemsaveaddrsizefilenameSaves physical memory dump starting at addr of size size to file filename-
- x /fmtaddr
Makes a virtual memory dump starting at address addr and formatted according to the fmt string. The fmt string consists of three parameters
countformatsize:The count parameter is the number of items to be dumped.
The format can be
x(hex),d(signed decimal),u(unsigned decimal),o(octal),c(char) ori(assembly instruction).The size parameter can be
b(8 bits),h(16 bits),w(32 bits) org(64 bits). On x86,horwcan be specified with theiformat to respectively select 16 or 32-bit code instruction size.- xp /fmtaddr
Makes a physical memory dump starting at address addr and formatted according to the fmt string. The fmt string consists of three parameters
countformatsize:The count parameter is the number of the items to be dumped.
The format can be
x(hex),d(signed decimal),u(unsigned decimal),o(octal),c(char) ori(asm instruction).The size parameter can be
b(8 bits),h(16 bits),w(32 bits) org(64 bits). On x86,horwcan be specified with theiformat to respectively select 16 or 32-bit code instruction size.
30.8 Managing Virtual Machine Snapshots #
Managing snapshots in QEMU monitor is not officially supported by SUSE yet. The information found in this section may be helpful in specific cases.
Virtual Machine snapshots are snapshots of the complete
virtual machine including the state of CPU, RAM, and the content of all
writable disks. To use virtual machine snapshots, you must have at least
one non-removable and writable block device using the
qcow2 disk image format.
Snapshots are helpful when you need to save your virtual machine in a particular state. For example, after you have configured network services on a virtualized server and want to quickly start the virtual machine in the same state that was saved last. You can also create a snapshot after the virtual machine has been powered off to create a backup state before you try something experimental and possibly make VM Guest unstable. This section introduces the former case, while the latter is described in Section 28.2.3, “Managing Snapshots of Virtual Machines with qemu-img”.
The following commands are available for managing snapshots in QEMU monitor:
savevmnameCreates a new virtual machine snapshot under the tag name or replaces an existing snapshot.
loadvmnameLoads a virtual machine snapshot tagged name.
delvmDeletes a virtual machine snapshot.
info snapshotsPrints information about available snapshots.
(qemu) info snapshots Snapshot list: ID1 TAG2 VM SIZE3 DATE4 VM CLOCK5 1 booting 4.4M 2013-11-22 10:51:10 00:00:20.476 2 booted 184M 2013-11-22 10:53:03 00:02:05.394 3 logged_in 273M 2013-11-22 11:00:25 00:04:34.843 4 ff_and_term_running 372M 2013-11-22 11:12:27 00:08:44.965
Unique identification number of the snapshot. Usually auto-incremented.
Unique description string of the snapshot. It is meant as a human readable version of the ID.
The disk space occupied by the snapshot. Note that the more memory is consumed by running applications, the bigger the snapshot is.
Time and date the snapshot was created.
The current state of the virtual machine's clock.
30.9 Suspending and Resuming Virtual Machine Execution #
The following commands are available for suspending and resuming virtual machines:
stopSuspends the execution of the virtual machine.
contResumes the execution of the virtual machine.
system_resetResets the virtual machine. The effect is similar to the reset button on a physical machine. This may leave the file system in an unclean state.
system_powerdownSends an ACPI shutdown request to the machine. The effect is similar to the power button on a physical machine.
qorquitTerminates QEMU immediately.
30.10 Live Migration #
The live migration process allows to transmit any virtual machine from one host system to another host system without any interruption in availability. It is possible to change hosts permanently or only during maintenance.
The requirements for live migration:
All requirements from Section 10.7.1, “Migration Requirements” are applicable.
Live migration is only possible between VM Host Servers with the same CPU features.
AHCI interface, VirtFS feature, and the
-mem-pathcommand line option are not compatible with migration.The guest on the source and destination hosts must be started in the same way.
-snapshotqemu command line option should not be used for migration (and thisqemucommand line option is not supported).
Important: Support Status
The postcopy mode is not yet supported in
openSUSE Leap. It is released as a technology preview only. For
more information about postcopy, see http://wiki.qemu.org/Features/PostCopyLiveMigration.
More recommendations can be found at the following Web site: http://www.linux-kvm.org/page/Migration
The live migration process has the following steps:
The virtual machine instance is running on the source host.
The virtual machine is started on the destination host in the frozen listening mode. The parameters used are the same as on the source host plus the
-incoming tcp:ip:portparameter, where ip specifies the IP address and port specifies the port for listening to the incoming migration. If 0 is set as IP address, the virtual machine listens on all interfaces.On the source host, switch to the monitor console and use the
migrate -d tcp:destination_ip:port command to initiate the migration.To determine the state of the migration, use the
info migratecommand in the monitor console on the source host.To cancel the migration, use the
migrate_cancelcommand in the monitor console on the source host.To set the maximum tolerable downtime for migration in seconds, use the
migrate_set_downtimenumber_of_seconds command.To set the maximum speed for migration in bytes per second, use the
migrate_set_speedbytes_per_second command.
30.11 QMP - QEMU Machine Protocol #
QMP is a JSON-based protocol that allows applications—such as
libvirt—to communicate with a running QEMU instance.
There are several ways you can access the QEMU monitor using QMP
commands.
30.11.1 Access QMP via Standard Input/Output #
The most flexible way to use QMP is by specifying the
-mon option. The following example creates a QMP
instance using standard input/output. Note that in the following
examples, -> marks lines with commands sent
from client to the running QEMU instance, while
<- marks lines with the output returned from
QEMU.
# qemu-system-x86_64 [...] \
-chardev stdio,id=mon0 \
-mon chardev=mon0,mode=control,pretty=on
<- {
"QMP": {
"version": {
"qemu": {
"micro": 0,
"minor": 0,
"major": 2
},
"package": ""
},
"capabilities": [
]
}
}
When a new QMP connection is established, QMP sends its greeting message
and enters capabilities negotiation mode. In this mode, only the
qmp_capabilities command works. To exit capabilities
negotiation mode and enter command mode, the
qmp_capabilities command must be issued first:
-> { "execute": "qmp_capabilities" }
<- {
"return": {
}
}
Note that "return": {} is a QMP's success response.
QMP's commands can have arguments. For example to eject a CD-ROM drive, enter the following:
->{ "execute": "eject", "arguments": { "device": "ide1-cd0" } }
<- {
"timestamp": {
"seconds": 1410353381,
"microseconds": 763480
},
"event": "DEVICE_TRAY_MOVED",
"data": {
"device": "ide1-cd0",
"tray-open": true
}
}
{
"return": {
}
}30.11.2 Access QMP via Telnet #
Instead of the standard input/output, you can connect the QMP interface to a network socket and communicate with it via a specified port:
# qemu-system-x86_64 [...] \ -chardev socket,id=mon0,host=localhost,port=4444,server,nowait \ -mon chardev=mon0,mode=control,pretty=on
And then run telnet to connect to port 4444:
# telnet localhost 4444
Trying ::1...
Connected to localhost.
Escape character is '^]'.
<- {
"QMP": {
"version": {
"qemu": {
"micro": 0,
"minor": 0,
"major": 2
},
"package": ""
},
"capabilities": [
]
}
}You can create several monitor interfaces at the same time. The following example creates one HMP instance—human monitor which understands 'normal' QEMU monitor's commands—on the standard input/output, and one QMP instance on localhost port 4444:
# qemu-system-x86_64 [...] \ -chardev stdio,id=mon0 -mon chardev=mon0,mode=readline \ -chardev socket,id=mon1,host=localhost,port=4444,server,nowait \ -mon chardev=mon1,mode=control,pretty=on
30.11.3 Access QMP via Unix Socket #
Invoke QEMU using the -qmp option, and create a
unix socket:
# qemu-system-x86_64 [...] \ -qmp unix:/tmp/qmp-sock,server --monitor stdio QEMU waiting for connection on: unix:./qmp-sock,server
To communicate with the QEMU instance via the
/tmp/qmp-sock socket, use nc (see
man 1 nc for more information) from another terminal
on the same host:
# nc -U /tmp/qmp-sock
<- {"QMP": {"version": {"qemu": {"micro": 0, "minor": 0, "major": 2} [...]30.11.4 Access QMP via libvirt's virsh Command #
If you run your virtual machines under libvirt (see
Part II, “Managing Virtual Machines with libvirt”), you can communicate with its
running guests by running the virsh
qemu-monitor-command:
# virsh qemu-monitor-command vm_guest1 \
--pretty '{"execute":"query-kvm"}'
<- {
"return": {
"enabled": true,
"present": true
},
"id": "libvirt-8"
}
In the above example, we ran the simple command
query-kvm which checks if the host is capable of
running KVM and if KVM is enabled.
Tip: Generating Human-Readable Output
To use the standard human-readable output format of QEMU
instead of the JSON format, use the --hmp
option:
# virsh qemu-monitor-command vm_guest1 --hmp "query-kvm"
Part VI Managing Virtual Machines with LXC #
- 31 Linux Containers
- 32 Migration from LXC to
libvirt-lxc Since SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12, LXC is integrated into libvirt library. This decision has several advantages over using LXC as a separate solution—such as a unified approach with other virtualization solutions or independence on the kernel used. This chapter describes steps needed to migrate …
31 Linux Containers #
31.1 Setting Up LXC Distribution Containers #
A container is a kind of “virtual machine” that can be started, stopped, frozen, or cloned (to name but a few tasks). To set up an LXC container, you first need to create a root file system containing the guest distribution:
Procedure 31.1: Creating a Root File System #
There is currently no GUI to create a root file system. You will thus
need to open a terminal and use virt-create-rootfs as
root to populate the new root file system. In the following steps, the
new root file system will be created in
/path/to/rootfs.
Run the
virt-create-rootfscommand:virt-create-rootfs --root /path/to/rootfs --distro SLES-12.0 -c registration code
Change the root path to the root file system with the
chrootcommand:chroot /path/to/rootfs
Change the password for user
rootwithpasswd.Create an
operatoruser withoutrootprivileges:useradd -m operator
Change the operator's password:
passwd operator
Leave the chroot environment with
exit.
Procedure 31.2: Defining the Container #
Start Virtual Machine Manager.
(Optional) If not already present, add a local LXC connection by clicking › .
Select as the hypervisor and click .
Select the connection and click menu.
Activate and click .
Type the path to the root file system from Procedure 31.1, “Creating a Root File System” and click the button.
Choose the maximum amount of memory and CPUs to allocate to the container. Then click the button.
Type in a name for the container. This name will be used for all
virshcommands on the container.Click . Select the network to connect the container to and click the button: the container will then be created and started. A console will also be automatically opened.
Warning: Container Network
To configure the container network, edit the
/etc/sysconfig/network/ifcfg-* files. Make sure not
to change the IPv6 setting: this would lead to errors while starting the
network.
31.2 Setting Up LXC Application Containers #
Libvirt also allows to run single applications instead of full blown
Linux distributions in containers. In this example,
bash will be started in its own container.
Procedure 31.3: Defining an Application Container Using YaST #
Start Virtual Machine Manager.
(Optional) If not already present, add a local LXC connection by clicking › .
Select as the hypervisor and click .
Select the connection and click menu.
Activate and click .
Set the path to the application to be launched. As an example, the field is filled with
/bin/sh, which is fine to create a first container. Click .Choose the maximum amount of memory and CPUs to allocate to the container. Click .
Type in a name for the container. This name will be used for all
virshcommands on the container.Click . Select the network to connect the container to and click . The container will be created and started. A console will be opened automatically.
Note that the container will be destroyed after the application has finished running.
31.3 Securing a Container Using AppArmor #
By default, containers are not secured using AppArmor or SELinux. There
is no graphical user interface to change the security model for a libvirt
domain, but virsh will help.
Edit the container XML configuration using virsh:
virsh -c lxc:/// edit mycontainer
Add the following to the XML configuration, save it and exit the editor.
<domain> ... <seclabel type="dynamic" model="apparmor"/> ... </domain>With this configuration, an AppArmor profile for the container will be created in the
/etc/apparmor.d/libvirtdirectory. The default profile only allows the minimum applications to run in the container. This can be changed by modifying thelibvirt-container-uuidfile: this file is not overwritten by libvirt.
31.4 Differences Between the libvirt LXC Driver and LXC #
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 SP3 was shipping LXC, while SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 comes with the libvirt LXC driver, sometimes named libvirt-lxc to avoid confusion. The containers are not managed or configured in the same way in these tools. Here is a non-exhaustive list of differences.
The main difference is that domain configuration in libvirt is an XML file, while LXC configuration is a properties file. Most of the LXC properties can be mapped to the domain XML. The properties that cannot be migrated are:
lxc.network.script.up: this script can be implemented using the
/etc/libvirt/hooks/networklibvirt hook, though the script will need to be adapted.lxc.network.ipv*: libvirt cannot set the container network configuration from the domain configuration.
lxc.network.name: libvirt cannot set the container network card name.
lxc.devttydir: libvirt does not allow changing the location of the console devices.
lxc.console: there is currently no way to log the output of the console into a file on the host for libvirt LXC containers.
lxc.pivotdir: libvirt does not allow to fine-tune the directory used for the
pivot_root./.olrootis used.lxc.rootfs.mount: libvirt does not allow to fine-tune this.
LXC VLAN networks automatically create the VLAN interface on the host and then move it into the guest namespace. libvirt-lxc configuration can mention a VLAN tag ID only for Open vSwitch tap devices or PCI pass-through of SR-IOV VF. The conversion tool actually needs the user to manually create the VLAN interface on the host side.
LXC rootfs can also be an image file, but LXC brute-forces the mount to try to detect the proper file system format. libvirt-lxc can mount image files of several formats, but the 'auto' value for the format parameter is explicitly not supported. This means that the generated configuration will need to be tweaked by the user to get a proper match in that case.
LXC can support any cgroup configuration, even future ones, while libvirt domain configuration, needs to map each of them.
LXC can mount block devices in the rootfs, but it cannot mount raw partition files: the file needs to be manually attached to a loop device. On the other hand libvirt-lxc can mount block devices, but also partition files of any format.
31.5 For More Information #
- LXC Container Driver
32 Migration from LXC to libvirt-lxc #
Since SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12, LXC is integrated into libvirt library. This
decision has several advantages over using LXC as a separate
solution—such as a unified approach with other virtualization
solutions or independence on the kernel used. This chapter describes steps
needed to migrate an existing LXC environment for use with the
libvirt library.
32.1 Host Migration #
The migration itself has two phases. You first need to migrate the host,
then the LXC containers. After that, you can run the original containers
as VM Guests in the libvirt environment.
Procedure 32.1: Host Migration #
Upgrade the host to SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 using the official DVD media.
After the upgrade, install the
libvirt-daemon-lxcandlibvirt-daemon-config-networkpackages.Create a
libvirtXML configurationlxc_container.xmlfrom the existing containerlxc_container:# virt-lxc-convert /etc/lxc/lxc_container/config > lxc_container.xml
Check if the network configuration on the host is the same as in the container configuration file, and fix it if needed.
Check the
lxc_container.xmlfile for any weird or missing configuration. Note that some LXC configuration options cannot be mapped tolibvirtconfiguration. Although the conversion should usually be fine, check Section 31.4, “Differences Between the libvirt LXC Driver and LXC” for more details.Define the container in
libvirtbased on the created XML definition:# virsh -c lxc:/// define lxc_container.xml
32.2 Container Migration #
After the host is migrated, the LXC container in libvirt will
not boot. It needs to be migrated to SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 as well to get
everything working.
Procedure 32.2: Container Migration #
The
baseproductfile is missing (andzypperkeeps complaining about it). Create the relevant symbolic link:# ROOTFS=/var/lib/lxc/lxc_container/rootfs # ln -s $ROOTFS/etc/products.d/SUSE_SLES.prod $ROOTFS/etc/products.d/baseproduct
Add the DVD repository. Note that you need to replace the DVD device with the one attached to your container:
# zypper --root $ROOTFS ar \ cd:///?devices=/dev/dvd SLES12-12
Disable or remove previous repositories:
# zypper --root $ROOTFS lr | Alias | Name | Enabled | Refresh --+-----------------------------+------------------------------+---------+-------- 1 | SLES12-12 | SLES12-12 | Yes | No 2 | SUSE-[...]-Server-11-SP3 38 | SUSE-[...]-Server-11-SP3 138 | Yes | No # zypper --root $ROOTFS rr 2
Upgrade the container:
# zypper --root $ROOTFS dup
Install the Minimal pattern to make sure everything required is installed:
# zypper --root $ROOTFS in -t pattern Minimal
32.3 Starting the Container #
After the host and container migration is complete, the container can be started:
# virsh -c lxc:/// start lxc_container
If you need to get a console to view the logging messages produced by the container, run:
# virsh -c lxc:/// console lxc_container
Glossary #
General
- Create Virtual Machine Wizard #
A software program available in YaST and Virtual Machine Manager that provides a graphical interface to guide you through the steps to create virtual machines. It can also be run in text mode by entering
virt-installat a command prompt in the host environment.- Dom0 #
The term is used in Xen environments, and refers to a virtual machine. The host operating system is actually a virtual machine running in a privileged domain and can be called Dom0. All other virtual machines on the host run in unprivileged domains and can be called domain U's.
- hardware-assisted #
Intel* and AMD* provide virtualization hardware-assisted technology. This reduces frequency of VM IN/OUT (fewer VM traps), because software is a major source of overhead, and increases the efficiency (the execution is done by the hardware). Moreover this reduces the memory footprint, provides better resource control, and allows secure assignment of specific I/O devices.
- Host Environment #
The desktop or command line environment that allows interaction with the host computer's environment. It provides a command line environment and can also include a graphical desktop, such as GNOME or IceWM. The host environment runs as a special type of virtual machine that has privileges to control and manage other virtual machines. Other commonly used terms include Dom0, privileged domain, and host operating system.
- Hypervisor #
The software that coordinates the low-level interaction between virtual machines and the underlying physical computer hardware.
- KVM #
- Paravirtualized Frame Buffer #
The video output device that drives a video display from a memory buffer containing a complete frame of data for virtual machine displays running in paravirtual mode.
- VHS #
Virtualization Host Server
The physical computer running a SUSE virtualization platform software. The virtualization environment consists of the hypervisor, the host environment, virtual machines, and associated tools, commands, and configuration files. Other commonly used terms include host, Host Computer, Host Machine (HM), Virtual Server (VS), Virtual Machine Host (VMH), and VM Host Server (VHS).
- VirtFS #
VirtFS is a new paravirtualized file system interface designed for improving pass-through technologies in the KVM environment. It is based on the VirtIO framework.
- Virtual Machine #
A virtualized PC environment (VM) capable of hosting a guest operating system and associated applications. Could be also called a VM Guest.
- Virtual Machine Manager #
A software program that provides a graphical user interface for creating and managing virtual machines.
- Virtualized #
A guest operating system or application running on a virtual machine.
- Xen #
- xl #
A set of commands for Xen that lets administrators manage virtual machines from a command prompt on the host computer. It replaced the deprecated
xmtool stack.
CPU
- CPU capping #
Virtual CPU capping allows you to set vCPU capacity to 1–100 percent of the physical CPU capacity.
- CPU hotplugging #
CPU hotplugging is used to describe the functions of replacing/adding/removing a CPU without shutting down the system.
- CPU over-commitment #
Virtual CPU over-commitment is the ability to assign more virtual CPUs to VMs than the actual number of physical CPUs present in the physical system. This procedure does not increase the overall performance of the system, but might be useful for testing purposes.
- CPU pinning #
Processor affinity, or CPU pinning enables the binding and unbinding of a process or a thread to a central processing unit (CPU) or a range of CPUs.
Network
- Bridged Networking #
A type of network connection that lets a virtual machine be identified on an external network as a unique identity that is separate from and unrelated to its host computer.
- Empty Bridge #
A type of network bridge that has no physical network device or virtual network device provided by the host. This lets virtual machines communicate with other virtual machines on the same host but not with the host or on an external network.
- External Network #
The network outside a host's internal network environment.
- Internal Network #
A type of network configuration that restricts virtual machines to their host environment.
- Local Bridge #
A type of network bridge that has a virtual network device but no physical network device provided by the host. This lets virtual machines communicate with the host and other virtual machines on the host. Virtual machines can communicate on an external network through the host.
- Network Address Translation (NAT) #
A type of network connection that lets a virtual machine use the IP address and MAC address of the host.
- No Host Bridge #
A type of network bridge that has a physical network device but no virtual network device provided by the host. This lets virtual machines communicate on an external network but not with the host. This lets you separate virtual machine network communications from the host environment.
- Traditional Bridge #
A type of network bridge that has both a physical network device and a virtual network device provided by the host.
Storage
- AHCI #
The Advanced Host Controller Interface (AHCI) is a technical standard defined by Intel* that specifies the operation of Serial ATA (SATA) host bus adapters in a non-implementation-specific manner.
- Block Device #
Data storage devices, such as CD-ROM drives or disk drives, that move data in the form of blocks. Partitions and volumes are also considered block devices.
- File-Backed Virtual Disk #
A virtual disk based on a file, also called a disk image file.
- Raw Disk #
A method of accessing data on a disk at the individual byte level instead of through its file system.
- Sparse image file #
A disk image file that does not reserve its entire amount of disk space but expands as data is written to it.
- xvda #
The drive designation given to the first virtual disk on a paravirtual machine.
Linux Containers
- cgroups #
Kernel Control Groups (commonly called “cgroups”) are a Kernel feature that allows aggregating or partitioning tasks (processes) and all their children into hierarchical organized groups to isolate resources.
See also Book “System Analysis and Tuning Guide”, Chapter 9 “Kernel Control Groups”.
- chroot #
A change root (chroot, or change root jail) is a section in the file system that is isolated from the rest of the file system. For this purpose, the
chrootorpivot_rootcommand is used to change the root of the file system. A program that is executed in such a “chroot jail” cannot access files outside the designated directory tree.- container #
Can be seen as a kind of “virtual machine” on the host server that can run any Linux system, for example openSUSE, SUSE Linux Enterprise Desktop, or SUSE Linux Enterprise Server. The main difference with a normal virtual machine is that the container shares its kernel with the host it runs on.
- Kernel namespaces #
A Kernel feature to isolate some resources like network, users, and others for a group of processes.
Acronyms
- ACPI #
Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) specification provides an open standard for device configuration and power management by the operating system.
- AER #
Advanced Error Reporting
AER is a capability provided by the PCI Express specification which allows for reporting of PCI errors and recovery from some of them.
- APIC #
Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller (APIC) is a family of interrupt controllers.
- BDF #
Bus:Device:Function
Notation used to succinctly describe PCI and PCIe devices.
- CG #
Control Groups
Feature to limit, account and isolate resource usage (CPU, memory, disk I/O, etc.).
- EDF #
Earliest Deadline First
This scheduler provides weighted CPU sharing in an intuitive way and uses real-time algorithms to ensure time guarantees.
- EPT #
Extended Page Tables
Performance in a virtualized environment is close to that in a native environment. Virtualization does create some overheads, however. These come from the virtualization of the CPU, the MMU, and the I/O devices. In some recent x86 processors AMD and Intel have begun to provide hardware extensions to help bridge this performance gap. In 2006, both vendors introduced their first generation hardware support for x86 virtualization with AMD-Virtualization (AMD-V) and Intel® VT-x technologies. Recently Intel introduced its second generation of hardware support that incorporates MMU-virtualization, called Extended Page Tables (EPT). EPT-enabled systems can improve performance compared to using shadow paging for MMU virtualization. EPT increases memory access latencies for a few workloads. This cost can be reduced by effectively using large pages in the guest and the hypervisor.
- FLASK #
Flux Advanced Security Kernel
Xen implements a type of mandatory access control via a security architecture called FLASK using a module of the same name.
- HAP #
High Assurance Platform
HAP combines hardware and software technologies to improve workstation and network security.
- HVM #
Hardware Virtual Machine (commonly called like this by Xen).
- IOMMU #
Input/Output Memory Management Unit
IOMMU (AMD* technology) is a memory management unit (MMU) that connects a direct memory access-capable (DMA-capable) I/O bus to the main memory.
- KSM #
Kernel Same Page Merging
KSM allows for automatic sharing of identical memory pages between guests to save host memory. KVM is optimized to use KSM if enabled on the VM Host Server.
- MMU #
Memory Management Unit
is a computer hardware component responsible for handling accesses to memory requested by the CPU. Its functions include translation of virtual addresses to physical addresses (that is, virtual memory management), memory protection, cache control, bus arbitration and in simpler computer architectures (especially 8-bit systems) bank switching.
- PAE #
Physical Address Extension
32-bit x86 operating systems use Physical Address Extension (PAE) mode to enable addressing of more than 4 GB of physical memory. In PAE mode, page table entries (PTEs) are 64 bits in size.
- PCID #
Process-context identifiers
These are a facility by which a logical processor may cache information for multiple linear-address spaces so that the processor may retain cached information when software switches to a different linear address space. INVPCID instruction is used for fine-grained TLB flush, which is benefit for kernel.
- PCIe #
Peripheral Component Interconnect Express
PCIe was designed to replace older PCI, PCI-X and AGP bus standards. PCIe has numerous improvements including a higher maximum system bus throughput, a lower I/O pin count and smaller physical footprint. Moreover it also has a more detailed error detection and reporting mechanism (AER), and a native hotplug functionality. It is also backward compatible with PCI.
- PSE and PSE36 #
Page Size Extended
PSE refers to a feature of x86 processors that allows for pages larger than the traditional 4 KiB size. PSE-36 capability offers 4 more bits, in addition to the normal 10 bits, which are used inside a page directory entry pointing to a large page. This allows a large page to be located in 36-bit address space.
- PT #
Page Table
A page table is the data structure used by a virtual memory system in a computer operating system to store the mapping between virtual addresses and physical addresses. Virtual addresses are those unique to the accessing process. Physical addresses are those unique to the hardware (RAM).
- QXL #
QXL is a cirrus VGA framebuffer (8M) driver for virtualized environment.
- RVI or NPT #
Rapid Virtualization Indexing, Nested Page Tables
An AMD second generation hardware-assisted virtualization technology for the processor memory management unit (MMU).
- SATA #
Serial ATA
SATA is a computer bus interface that connects host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disks and optical drives.
- Seccomp2-based sandboxing #
Sandboxed environment where only predetermined system calls are permitted for added protection against malicious behavior.
- SMEP #
Supervisor Mode Execution Protection
This prevents the execution of user-mode pages by the Xen hypervisor, making many application-to-hypervisor exploits much harder.
- SPICE #
Simple Protocol for Independent Computing Environments
- SXP #
An SXP file is a Xen Configuration File.
- TCG #
Tiny Code Generator
Instructions are emulated rather than executed by the CPU.
- THP #
Transparent Huge Pages
This allows CPUs to address memory using pages larger than the default 4 KB. This helps reduce memory consumption and CPU cache usage. KVM is optimized to use THP (via madvise and opportunistic methods) if enabled on the VM Host Server.
- TLB #
Translation Lookaside Buffer
TLB is a cache that memory management hardware uses to improve virtual address translation speed. All current desktop, notebook, and server processors use a TLB to map virtual and physical address spaces, and it is nearly always present in any hardware that uses virtual memory.
- VCPU #
A scheduling entity, containing each state for virtualized CPU.
- VDI #
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure
- VFIO #
Since kernel v3.6; a new method of accessing PCI devices from user space called VFIO.
- VHS #
Virtualization Host Server
- VM root #
VMM will run in VMX root operation and guest software will run in VMX non-root operation. Transitions between VMX root operation and VMX non-root operation are called VMX transitions.
- VMCS #
Virtual Machine Control Structure
VMX non-root operation and VMX transitions are controlled by a data structure called a virtual-machine control structure (VMCS). Access to the VMCS is managed through a component of processor state called the VMCS pointer (one per logical processor). The value of the VMCS pointer is the 64-bit address of the VMCS. The VMCS pointer is read and written using the instructions VMPTRST and VMPTRLD. The VMM configures a VMCS using the VMREAD, VMWRITE, and VMCLEAR instructions. A VMM could use a different VMCS for each virtual machine that it supports. For a virtual machine with multiple logical processors (virtual processors), the VMM could use a different VMCS for each virtual processor.
- VMDq #
Virtual Machine Device Queue
Multi-queue network adapters exist which support multiple VMs at the hardware level, having separate packet queues associated to the different hosted VMs (by means of the IP addresses of the VMs).
- VMM #
Virtual Machine Monitor (Hypervisor)
When the processor encounters an instruction or event of interest to the Hypervisor (VMM), it exits from guest mode back to the VMM. The VMM emulates the instruction or other event, at a fraction of native speed, and then returns to guest mode. The transitions from guest mode to the VMM and back again are high-latency operations, during which guest execution is completely stalled.
- VMX #
Virtual Machine eXtensions
- VPID #
New support for software control of TLB (VPID improves TLB performance with small VMM development effort).
- VT-d #
Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O
- vTPM #
Component to establish end-to-end integrity for guests via Trusted Computing.
A Virtual Machine Drivers #
Virtualization allows the consolidation of workloads on newer, more powerful, energy-efficient hardware. Paravirtualized operating systems such as openSUSE® Leap and other Linux distributions are aware of the underlying virtualization platform, and can therefore interact efficiently with it. Unmodified operating systems such as Microsoft Windows* are unaware of the virtualization platform and expect to interact directly with the hardware. Because this is not possible when consolidating servers, the hardware must be emulated for the operating system. Emulation can be slow, but it is especially troubling for high-throughput disk and network subsystems. Most performance loss occurs in this area.
The SUSE Linux Enterprise Virtual Machine Driver Pack (VMDP) contains 32-bit and 64-bit paravirtualized network, bus and block drivers for several Microsoft Windows operating systems. These drivers bring many of the performance advantages of paravirtualized operating systems to unmodified operating systems because only the paravirtualized device driver (not the rest of the operating system) is aware of the virtualization platform. For example, a paravirtualized disk device driver appears as a normal, physical disk to the operating system. However, the device driver interacts directly with the virtualization platform (with no emulation) to efficiently deliver disk access, allowing the disk and network subsystems to operate at near native speeds in a virtualized environment, without requiring changes to existing operating systems.
The SUSE® Linux Enterprise Virtual Machine Driver Pack is available as an add-on product for openSUSE Leap. For detailed information refer to http://www.suse.com/products/vmdriverpack/.
Refer to the Official VMDP Installation Guide at https://www.suse.com/documentation/sle-vmdp-22/ for more information.
B Appendix #
B.1 Generating x509 Client/Server Certificates #
To be able to create x509 client and server certificates you
need to issue them by a Certificate Authority (CA). It is recommended to
set up an independent CA that only issues certificates for
libvirt.
Set up a CA as described in Book “Security Guide”, Chapter 17 “Managing X.509 Certification”, Section 17.2.1 “Creating a Root CA”.
Create a server and a client certificate as described in Book “Security Guide”, Chapter 17 “Managing X.509 Certification”, Section 17.2.4 “Creating or Revoking User Certificates”. The Common Name (CN) for the server certificate must be the fully qualified host name, while the Common Name for the client certificate can be freely chosen. For all other fields stick with the defaults suggested by YaST.
Export the client and server certificates to a temporary location (for example,
/tmp/x509/) by performing the following steps:Select the certificate on the tab.
Choose › › , provide the and the full path and the file name under , for example,
/tmp/x509/server.pemor/tmp/x509/client.pem.Open a terminal and change to the directory where you have saved the certificate and issue the following commands to split it into certificate and key (this example splits the server key):
csplit -z -f s_ server.pem '/-----BEGIN/' '{1}' mv s_00 servercert.pem mv s_01 serverkey.pemRepeat the procedure for each client and server certificate you want to export.
Finally export the CA certificate by performing the following steps:
Switch to the tab.
Choose › › and enter the full path and the file name under , for example,
/tmp/x509/cacert.pem.
C XM, XL Toolstacks and Libvirt framework #
C.1 Xen Toolstacks #
Since the early Xen 2.x releases, xend has been
the de facto toolstack for managing Xen installations. In Xen
4.1, a new toolstack called libxenlight (also known as libxl) was
introduced with technology preview status. libxl is a small, low-level
library written in C. It has been designed to provide a simple API for
all client toolstacks
(XAPI,
libvirt, xl). In Xen 4.2, libxl was promoted to officially
supported status and xend was marked deprecated.
xend has been included in the Xen 4.3 and 4.4
series to give users ample time to convert their tooling to libxl, but it
has been removed from the upstream Xen project and will no longer be
provided starting with the Xen 4.5 series and openSUSE Leap
42.1.
Although SLES 11 SP3 contains Xen 4.2, SUSE retained the
xend toolstack since making such an invasive change in
a service pack would be too disruptive for SUSE Linux Enterprise customers. However,
SLES 12 provides a suitable opportunity to move to the new libxl toolstack
and remove the deprecated, unmaintained xend
stack. Starting with openSUSE Leap 42.1, xend is no longer
supported.
One of the major differences between xend and libxl is
that the former is stateful, while the latter is stateless. With
xend, all client applications such as
xm and libvirt see the same system state.
xend is responsible for maintaining state for the
entire Xen host. In libxl, client applications such as
xl or libvirt must maintain state. Thus domains
created with xl or not visible or known to other libxl
applications such as libvirt. Generally, it is discouraged to mix
and match libxl applications and is preferred that a single libxl
application be used to manage a Xen host. In SUSE Linux Enterprise 12 , it is
recommended to use libvirt to manage Xen hosts, allowing
management of the Xen system through libvirt applications such
as virt-manager, virt-install,
virt-viewer,
libguestfs, etc. If xl is used to manage the Xen
host, any virtual machines under its management will not be accessible
to libvirt, and hence not accessible to any of the libvirt
applications.
C.1.1 Upgrading from xend/xm to xl/libxl #
The xl application, along with its configuration
format (see man xl.cfg), was designed to be
backward-compatible with the xm application and its
configuration format (see man xm.cfg). Existing
xm configuration should be usable with
xl. Since libxl is stateless, and
xl does not support the notion of managed domains,
SUSE recommends using libvirt to manage SLES 12 Xen hosts.
SUSE has provided a tool called xen2libvirt, which
provides a simple mechanism to import domains previously managed by
xend into libvirt. See
Section C.2, “Import Xen Domain Configuration into libvirt” for more information on
xen2libvirt.
C.1.2 XL design #
The basic structure of every xl command is:
xl subcommandOPTIONSDOMAIN
DOMAIN is the numeric domain id, or the domain name (which will be internally translated to domain id), and OPTIONS are subcommand specific options.
Although xl/libxl was designed to be backward-compatible with xm/xend, there are a few differences that should be noted:
Managed or persistent domains.
libvirtnow provides this functionality.xl/libxl does not support Python code in the domain configuration files.
xl/libxl does not support creating domains from SXP format configuration files (
xmcreate-F).xl/libxl does not support sharing storage across DomU's via
w!in domain configuration files.
xl/libxl is relatively new and under heavy development, hence a few features are still missing with regard to the xm/xend toolstack:
SCSI LUN/Host pass-through (PVSCSI)
USB pass-through (PVUSB)
Support Direct Kernel Boot for fully virtualized Linux guests for Xen does not work anymore.
C.1.3 Checklist before Upgrade #
Before upgrading a SLES 11 SP3 Xen host to SLES 12:
You must remove any Python code from your xm domain configuration files.
It is recommended to capture the libvirt domain XML from all existing virtual machines using
virshdumpxmlDOMAIN_NAME DOMAIN_NAME.xml.It is recommended to do a backup of
/etc/xen/xend-config.sxpand/boot/grub/menu.lstfiles to keep references of previous parameters used for Xen.
Note
Currently, live migrating virtual machines running on a SLES 11 SP3
Xen host to a SLES 12 Xen host is not supported. The
xend and libxl toolstacks are not
runtime-compatible. Virtual machine downtime will be required to move
the virtual machines from SLES 11 SP3 to a SLES 12 host.
C.2 Import Xen Domain Configuration into libvirt #
xen2libvirt is a command line tool to import legacy
Xen domain configuration into the libvirt virtualization library
(see The Virtualization book for more information on libvirt).
xen2libvirt provides an easy way to import domains managed by the
deprecated xm/xend tool stack into the new
libvirt/libxl tool stack. Several domains can be imported at once
using its --recursive mode
xen2libvirt is included in the
xen-tools package. If needed, install it with
zypper install xen-tools
xen2libvirt general syntax is
xen2libvirt <options> /path/to/domain/config
where options can be:
-h,--helpPrints short information about
xen2libvirtusage.-c,--convert-onlyConverts the domain configuration to the
libvirtXML format, but does not do the import tolibvirt.-r,--recursiveConverts and/or imports all domains configuration recursively, starting at the specified path.
-f,--formatSpecifies the format of the source domain configuration. Can be either
xm, orsexpr(S-expression format).-v,--verbosePrints more detailed information about the import process.
Example C.1: Converting Xen Domain Configuration to libvirt #
Suppose you have a Xen domain managed with xm
with the following configuration saved in
/etc/xen/sle12.xm:
kernel = "/boot/vmlinuz-2.6-xenU" memory = 128 name = "SLE12" root = "/dev/hda1 ro" disk = [ "file:/var/xen/sle12.img,hda1,w" ]
Convert it to libvirt XML without importing it, and look at its
content:
# xen2libvirt -f xm -c /etc/xen/sle12.xm > /etc/libvirt/qemu/sles12.xml # cat /etc/libvirt/qemu/sles12.xml <domain type='xen'> <name>SLE12</name> <uuid>43e1863c-8116-469c-a253-83d8be09aa1d</uuid> <memory unit='KiB'>131072</memory> <currentMemory unit='KiB'>131072</currentMemory> <vcpu placement='static'>1</vcpu> <os> <type arch='x86_64' machine='xenpv'>linux</type> <kernel>/boot/vmlinuz-2.6-xenU</kernel> </os> <clock offset='utc' adjustment='reset'/> <on_poweroff>destroy</on_poweroff> <on_reboot>restart</on_reboot> <on_crash>restart</on_crash> <devices> <disk type='file' device='disk'> <driver name='file'/> <source file='/var/xen/sle12.img'/> <target dev='hda1' bus='xen'/> </disk> <console type='pty'> <target type='xen' port='0'/> </console> </devices> </domain>
To import the domain into libvirt, you can either run the same
xen2libvirt command without the -c
option, or use the exported file
/etc/libvirt/qemu/sles12.xml and define a new
Xen domain using virsh:
# sudo virsh define /etc/libvirt/qemu/sles12.xml
C.3 Differences Between the xm and xl Applications #
The purpose of this chapter is to list all differences between
xm and xl applications. Generally,
xl is designed to be compatible with
xm. Replacing xm with
xl in custom scripts or tools is usually sufficient.
You can also use the libvirt framework using the
virsh command. In this documentation only the first
OPTION for virsh will be
shown. To get more help on this option do a:
virshhelpOPTION
C.3.1 Notation Conventions #
To easily understand the difference between xl and
xm commands, the following notation is used in this
section:
Table C.1: Notation Conventions #
|
Notation |
Meaning |
|---|---|
|
(-) minus |
Option exists in |
|
(+) plus |
Option exists in |
C.3.2 New Global Options #
Table C.2: New Global Options #
|
Options |
Task |
|---|---|
|
(+) |
Verbose, increase the verbosity of the output |
|
(+) |
Dry run, do not actually execute the command |
|
(+) |
Force execution. |
C.3.3 Unchanged Options #
List of common options of xl and
xm, and their libvirt equivalents.
Table C.3: Common Options #
|
Options |
Task |
|
|---|---|---|
|
destroy DOMAIN |
Immediately terminate the domain. |
|
|
domid DOMAIN_NAME |
Convert a domain name to a DOMAIN_ID. |
|
|
domname DOMAIN_ID |
Convert a DOMAIN_ID to a DOMAIN_NAME. |
|
|
help |
Display the short help message (that is, common commands). |
|
|
pause DOMAIN_ID |
Pause a domain. When in a paused state, the domain will still consume allocated resources such as memory, but will not be eligible for scheduling by the Xen hypervisor. |
|
|
unpause DOMAIN_ID |
Move a domain out of the paused state. This will allow a previously paused domain to be eligible for scheduling by the Xen hypervisor. |
|
|
rename DOMAIN_ID NEW_DOMAIN_NAME |
Change the domain name of DOMAIN_ID to NEW_DOMAIN_NAME. |
|
|
sysrq DOMAIN <letter> |
Send a Magic System Request to the domain, each type of request is
represented by a different letter. It can be used to send SysRq
requests to Linux guests, see |
|
|
vncviewer OPTIONS DOMAIN |
Attach to domain's VNC server, forking a vncviewer process. |
|
|
vcpu-set DOMAIN_ID <vCPUs> |
Enable the vcpu-count virtual CPUs for the domain in question. Like
|
|
|
vcpu-list DOMAIN_ID |
List VCPU information for a specific domain. If no domain is specified, VCPU information for all domains will be provided. |
|
|
vcpu-pin DOMAIN_ID <VCPU|all> <CPUs|all> |
Pin the VCPU to only run on the specific CPUs. The keyword all can be used to apply the CPU list to all VCPUs in the domain. |
|
|
dmesg [-c] |
Read the Xen message buffer, similar to dmesg on a Linux system. The buffer contains informational, warning, and error messages created during Xen's boot process. | |
|
top |
Execute the |
|
|
uptime [-s] DOMAIN |
Print the current uptime of the domains running. With the
| |
|
debug-keys KEYS |
Send debug keys to Xen. It is the same as pressing the Xen conswitch (Ctrl-A by default) three times and then pressing "keys". | |
|
cpupool-migrate DOMAIN CPU_POOL |
Move a domain specified by DOMAIN_ID or DOMAIN into a CPU_POOL. | |
|
cpupool-destroy CPU_POOL |
Deactivate a cpu pool. This is possible only if no domain is active in the cpu-pool. | |
|
block-detach DOMAIN_ID DevId |
Detach a domain's virtual block device. devid
may be the symbolic name or the numeric device id given to the
device by Dom0. You will need to run |
|
|
network-attach DOMAIN_ID NETWORK_DEVICE |
Create a new network device in the domain specified by DOMAIN_ID. network-device describes the device to attach, using the same format as the vif string in the domain configuration file |
|
|
pci-attach DOMAIN <BDF> [Virtual Slot] |
Hotplug a new pass-through PCI device to the specified domain. BDF is the PCI Bus/Device/Function of the physical device to be passed through. |
|
|
pci-list DOMAIN_ID |
List pass-through PCI devices for a domain | |
|
getenforce |
Determine if the FLASK security module is loaded and enforcing its policy. | |
|
setenforce |
Enable or disable enforcing of the FLASK access controls. The default is permissive and can be changed using the flask_enforcing option on the hypervisor's command line. |
C.3.4 Removed Options #
List of xm options which are no more
available with the XL tool stack and a replacement solution if available.
C.3.4.1 Domain Management #
The list of Domain management removed command and their replacement.
Table C.4: Domain Management Removed Options #
|
Domain Management Removed Options | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Options |
Task |
Equivalent |
|
(-) |
Print out the Xend log. |
This log file can be found in
|
|
(-) |
Remove a domain from Xend domain management. The
|
|
|
(-) |
Adds a domain to Xend domain management |
|
|
(-) |
Start a Xend managed domain that was added using the
|
|
|
(-) |
Dry run - prints the resulting configuration in SXP but does not create the domain |
|
|
(-) |
Reset a domain |
|
|
(-) |
Show domain state |
|
|
(-) |
Proxy Xend XMLRPC over stdio | |
|
(-) |
Moves a domain out of the suspended state and back into memory |
|
|
(-) |
Suspend a domain to a state file so that it can be later resumed
using the |
|
C.3.4.2 USB Devices #
USB options are not available with xl/libxl tool stack.
virsh has the attach-device and
detach-device options but it does not work yet with
USB.
Table C.5: USB Devices Management Removed Options #
|
USB Devices Management Removed Options | |
|---|---|
|
Options |
Task |
|
(-) |
Add a new USB physical bus to a domain |
|
(-) |
Delete a USB physical bus from a domain |
|
(-) |
Attach a new USB physical bus to domain's virtual port |
|
(-) |
Detach a USB physical bus from domain's virtual port |
|
(-) |
List domain's attachment state of all virtual port |
|
(-) |
List all the assignable USB devices |
|
(-) |
Create a domain's new virtual USB host controller |
|
(-) |
Destroy a domain's virtual USB host controller |
C.3.4.3 CPU Management #
CPU management options has changed. New options are available, see:
Section C.3.5.10, “xl cpupool-*”
Table C.6: CPU Management Removed options #
|
CPU Management Removed Options | |
|---|---|
|
Options |
Task |
|
(-) |
Adds a CPU pool to Xend CPU pool management |
|
(-) |
Starts a Xend CPU pool |
|
(-) |
Removes a CPU pool from Xend management |
C.3.5 Changed Options #
C.3.5.1 create #
xl create
CONFIG_FILE OPTIONS
VARS
Note: libvirt Equivalent:
virsh create
Table C.8: xl create Changed Options #
|
| |
|---|---|
|
Options |
Task |
|
(*) -f=FILE, --defconfig=FILE |
Use the given configuration file |
Table C.9: xm create Removed Options #
|
| |
|---|---|
|
Options |
Task |
|
(-) |
Skip DTD checking - skips checks on XML before creating |
|
(-) |
XML dry run |
|
(-) |
Use the given SXP formatted configuration script |
|
(-) |
Search path for configuration scripts |
|
(-) |
Print the available configuration variables (vars) for the configuration script |
|
(-) |
Dry run — prints the configuration in SXP but does not create the domain |
|
(-) |
Connect to the console after the domain is created |
|
(-) |
Quiet mode |
|
(-) |
Leave the domain paused after it is created |
Table C.10: xl create Added Options #
|
| |
|---|---|
|
Options |
Task |
|
(+) |
Attach to domain's VNC server, forking a vncviewer process |
|
(+) |
Pass VNC password to vncviewer via stdin |
C.3.5.2 console #
xl console
OPTIONS DOMAIN
Note: libvirt Equivalent
virsh console
Table C.11: xl console Added Options #
|
| |
|---|---|
|
Option |
Task |
|
(+) |
Connect to a PV console or connect to an emulated serial console. PV consoles are the only consoles available for PV domains while HVM domains can have both |
C.3.5.3 info #
xl info
Table C.12: xm info Removed Options #
|
| |
|---|---|
|
Options |
Task |
|
(-) |
Numa info |
|
(-) |
List Xend configuration parameters |
C.3.5.4 dump-core #
xl dump-core
DOMAIN FILENAME
Note: libvirt Equivalent
virsh dump
Table C.13: xm dump-core Removed Options #
|
| |
|---|---|
|
Options |
Task |
|
(-) |
Dump core without pausing the domain |
|
(-) |
Crash domain after dumping core |
|
(-) |
Reset domain after dumping core |
C.3.5.5 list #
xl list options
DOMAIN
Note: libvirt Equivalent
virsh list --all
Table C.14: xm list Removed Options #
|
| |
|---|---|
|
Options |
Task |
|
(-) |
The output for |
|
(-) |
Output information for VMs in the specified state |
Table C.15: xl list Added Options #
|
| |
|---|---|
|
Options |
Task |
|
(+) |
Also prints the security labels |
|
(+) |
Also prints the domain UUIDs, the shutdown reason and security labels |
C.3.5.6 mem-* #
Note: libvirt Equivalent
virsh setmem
virsh setmaxmem
Table C.16: xl mem-* Changed Options #
|
| |
|---|---|
|
Options |
Task |
|
|
Appending |
|
|
Set the domain's used memory using the balloon driver |
C.3.5.7 migrate #
xl migrate
OPTIONS DOMAIN
HOST
Note: libvirt Equivalent
virsh migrate --live hvm-sles11-qcow2 xen+
CONNECTOR://USER@IP_ADDRESS/
Table C.17: xm migrate Removed Options #
|
| |
|---|---|
|
Options |
Task |
|
(-) |
Use live migration. This will migrate the domain between hosts without shutting down the domain |
|
(-) |
Set maximum Mbs allowed for migrating the domain |
|
(-) |
Change home server for managed domains |
|
(-)
|
Number of iterations before final suspend (default:30) |
|
(-)
|
Max amount of memory to transfer before final suspend (default: 3*RAM). |
|
(-)
|
Number of dirty pages before final suspend (default:50) |
|
(-) |
Abort migration instead of doing final suspend |
|
(-) |
Log progress of migration to |
|
(-) |
Use ssl connection for migration |
Table C.18: xl migrate Added Options #
|
| |
|---|---|
|
Options |
Task |
|
(+) |
Use <sshcommand> instead of |
|
(+) |
On the new host, do not wait in the background (on <host>) for the death of the domain |
|
(+) |
Send <config> instead of a configuration file from creation |
C.3.5.8 Domain Management #
xl reboot
OPTIONS DOMAIN
Note: libvirt Equivalent
virsh reboot
Table C.19: xm reboot Removed Options #
|
| |
|---|---|
|
Options |
Task |
|
(-) |
Reboot all domains |
|
(-) |
Wait for reboot to complete before returning. This may take a while, as all services in the domain need to be shut down cleanly |
Table C.20: xl reboot Added Options #
|
| |
|---|---|
|
Option |
Task |
|
(+) |
Fallback to ACPI reset event for HVM guests with no PV drivers |
xl save
OPTIONS DOMAIN
CHECK_POINT_FILE
CONFIG_FILE
Note: libvirt Equivalent
virsh save
Table C.21: xl save Added Options #
|
| |
|---|---|
|
Option |
Task |
|
(+) |
Leave domain running after creating the snapshot |
xl restore
OPTIONS
CONFIG_FILE
CHECK_POINT_FILE
Note: libvirt Equivalent
virsh restore
Table C.22: xl restore Added Options #
|
| |
|---|---|
|
Options |
Task |
|
(+) |
Do not unpause domain after restoring it |
|
(+) |
Do not wait in the background for the death of the domain on the new host |
|
(+) |
Enable debug messages |
|
(+) |
Attach to domain's VNC server, forking a vncviewer process |
|
(+) |
Pass VNC password to vncviewer via stdin |
xl shutdown
OPTIONS DOMAIN
Note: libvirt Equivalent
virsh shutdown
Table C.23: xm shutdown Removed Options #
|
| |
|---|---|
|
Options |
Task |
|
(-) |
Wait for the domain to complete shutdown before returning |
|
(-) |
Shutdown all guest domains |
|
(-) | |
|
(-) | |
Table C.24: xl shutdown Added Options #
|
| |
|---|---|
|
Option |
Task |
|
(+) |
If the guest does not support PV shutdown control then fallback to sending an ACPI power event |
Table C.25: xl trigger Changed Options #
|
| |
|---|---|
|
Option |
Task |
|
|
Send a trigger to a domain. Only available for HVM domains |
C.3.5.9 xl sched-* #
xl sched-credit
OPTIONS
Note: libvirt Equivalent
virsh schedinfo
Table C.26: xm sched-credit Removed Options #
|
| |
|---|---|
|
Options |
Task |
|
|
Domain |
|
|
A domain with a weight of 512 will get twice as much CPU as a domain with a weight of 256 on a contended host. Legal weights range from 1 to 65535 and the default is 256 |
|
|
The CAP optionally fixes the maximum amount of CPU a domain can consume |
Table C.27: xl sched-credit Added Options #
|
| |
|---|---|
|
Options |
Task |
|
(+) |
Restrict output to domains in the specified cpupool |
|
(+) |
Specify to list or set pool-wide scheduler parameters |
|
(+) |
Timeslice tells the scheduler how long to allow VMs to run before pre-empting |
|
(+) |
Ratelimit attempts to limit the number of schedules per second |
xl sched-credit2
OPTIONS
Note: libvirt Status
virsh only supports credit scheduler, not credit2
scheduler
Table C.28: xm sched-credit2 Removed Options #
|
| |
|---|---|
|
Options |
Task |
|
|
Domain |
|
|
Legal weights range from 1 to 65535 and the default is 256 |
Table C.29: xl sched-credit2 Added Options #
|
| |
|---|---|
|
Option |
Task |
|
(+) |
Restrict output to domains in the specified cpupool |
xl sched-sedf
OPTIONS
Table C.30: xm sched-sedf Removed Options #
|
| |
|---|---|
|
Options |
Task |
|
|
The normal EDF scheduling usage in milliseconds |
|
|
The normal EDF scheduling usage in milliseconds |
|
|
Scaled period if domain is doing heavy I/O |
|
|
Flag for allowing domain to run in extra time (0 or 1) |
|
|
Another way of setting CPU slice |
Table C.31: xl sched-sedf Added Options #
|
| |
|---|---|
|
Options |
Task |
|
(+) |
Restrict output to domains in the specified cpupool |
|
(+) |
Domain |
C.3.5.10 xl cpupool-* #
xl cpupool-cpu-remove
CPU_POOL <CPU
nr>|node:<node nr>
xl cpupool-list [-c|--cpus]
CPU_POOL
Table C.32: xm cpupool-list Removed Options #
|
| |
|---|---|
|
Option |
Task |
|
(-) |
Output all CPU pool details in SXP format |
xl cpupool-cpu-add
CPU_POOL cpu-nr|node:node-nr
xl cpupool-create
OPTIONS
CONFIG_FILE [Variable=Value ...]
Table C.33: xm cpupool-create Removed Options #
|
| |
|---|---|
|
Options |
Task |
|
(-) |
Use the given Python configuration script. The configuration script is loaded after arguments have been processed |
|
(-) |
Dry run - prints the resulting configuration in SXP but does not create the CPU pool |
|
(-) |
Print the available configuration variables (vars) for the configuration script |
|
(-) |
Search path for configuration scripts. The value of PATH is a colon-separated directory list |
|
(-) |
CPU pool configuration to use (SXP) |
C.3.5.11 PCI and Block Devices #
xl pci-detach [-f]
DOMAIN_ID <BDF>
Note: libvirt Equivalent
virsh detach-device
Table C.34: xl pci-detach Added Options #
|
| |
|---|---|
|
Option |
Task |
|
(+) |
If |
Table C.35: xm block-list Removed Options #
|
| |
|---|---|
|
Option |
Task |
|
(-) |
List virtual block devices for a domain |
Table C.36: Other Options #
|
Option |
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C.3.5.12 Network #
Table C.37: Network Options #
|
Option |
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table C.38: xl network-attach Removed Options #
|
Removed Options | |
|---|---|
|
Option |
Task |
|
(-) | |
C.3.6 New Options #
Table C.39: New Options #
|
Options |
Task |
|---|---|
|
|
Update the saved configuration for a running domain. This has no immediate effect but will be applied when the guest is next restarted. This command is useful to ensure that runtime modifications made to the guest will be preserved when the guest is restarted |
|
| |
|
|
List count of shared pages.List specifically for that domain. Otherwise, list for all domains |
|
|
Prints information about guests. This list excludes information about service or auxiliary domains such as Dom0 and stubdoms |
|
|
Renames a cpu-pool to newname |
|
|
Splits up the machine into one cpu-pool per numa node |
|
cd-insert DOMAIN <VirtualDevice> <type:path> |
Insert a CD-ROM into a guest domain's existing virtual CD drive. The virtual drive must already exist but can be current empty |
|
|
Eject a CD-ROM from a guest's virtual CD drive. Only works with HVM domains |
|
|
List all the assignable PCI devices. These are devices in the system which are configured to be available for pass-through and are bound to a suitable PCI back-end driver in Dom0 rather than a real driver |
|
|
Make the device at PCI Bus/Device/Function BDF assignable to guests.This will bind the device to the pciback driver |
|
|
Make the device at PCI Bus/Device/Function BDF assignable to guests. This will at least unbind the device from pciback |
|
|
Load FLASK policy from the given policy file. The initial policy is provided to the hypervisor as a multiboot module; this command allows runtime updates to the policy. Loading new security policy will reset runtime changes to device labels |
C.4 External links #
For more information on Xen tool stacks refer to the following online resources:
- XL in Xen
xlcommandXL command line.
- xl.cfg
xl.cfg domain configuration file syntax.
- xl disk
xl disk configuration option.
- XL vs Xend
XL vs Xend feature comparison.
- BDF doc
- libvirt
virsh command.
C.5 Saving a Xen Guest Configuration in an xm Compatible Format #
Although xl is now the current toolkit for managing
Xen guests (apart from the preferred libvirt), you may need to
export the guest configuration to the previously used
xm format. To do this, follow these steps:
First export the guest configuration to a file:
virsh dumpxml guest_id > guest_cfg.xml
Then convert the configuration to the
xmformat:virsh domxml-to-native xen-xm guest_cfg.xml > guest_xm_cfg
D GNU Licenses #
This appendix contains the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.2.
GNU Free Documentation License #
Copyright (C) 2000, 2001, 2002 Free Software Foundation, Inc. 51 Franklin St, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA. Everyone is permitted to copy and distribute verbatim copies of this license document, but changing it is not allowed.
0. PREAMBLE #
The purpose of this License is to make a manual, textbook, or other functional and useful document "free" in the sense of freedom: to assure everyone the effective freedom to copy and redistribute it, with or without modifying it, either commercially or non-commercially. Secondarily, this License preserves for the author and publisher a way to get credit for their work, while not being considered responsible for modifications made by others.
This License is a kind of "copyleft", which means that derivative works of the document must themselves be free in the same sense. It complements the GNU General Public License, which is a copyleft license designed for free software.
We have designed this License to use it for manuals for free software, because free software needs free documentation: a free program should come with manuals providing the same freedoms that the software does. But this License is not limited to software manuals; it can be used for any textual work, regardless of subject matter or whether it is published as a printed book. We recommend this License principally for works whose purpose is instruction or reference.
1. APPLICABILITY AND DEFINITIONS #
This License applies to any manual or other work, in any medium, that contains a notice placed by the copyright holder saying it can be distributed under the terms of this License. Such a notice grants a world-wide, royalty-free license, unlimited in duration, to use that work under the conditions stated herein. The "Document", below, refers to any such manual or work. Any member of the public is a licensee, and is addressed as "you". You accept the license if you copy, modify or distribute the work in a way requiring permission under copyright law.
A "Modified Version" of the Document means any work containing the Document or a portion of it, either copied verbatim, or with modifications and/or translated into another language.
A "Secondary Section" is a named appendix or a front-matter section of the Document that deals exclusively with the relationship of the publishers or authors of the Document to the Document's overall subject (or to related matters) and contains nothing that could fall directly within that overall subject. (Thus, if the Document is in part a textbook of mathematics, a Secondary Section may not explain any mathematics.) The relationship could be a matter of historical connection with the subject or with related matters, or of legal, commercial, philosophical, ethical or political position regarding them.
The "Invariant Sections" are certain Secondary Sections whose titles are designated, as being those of Invariant Sections, in the notice that says that the Document is released under this License. If a section does not fit the above definition of Secondary then it is not allowed to be designated as Invariant. The Document may contain zero Invariant Sections. If the Document does not identify any Invariant Sections then there are none.
The "Cover Texts" are certain short passages of text that are listed, as Front-Cover Texts or Back-Cover Texts, in the notice that says that the Document is released under this License. A Front-Cover Text may be at most 5 words, and a Back-Cover Text may be at most 25 words.
A "Transparent" copy of the Document means a machine-readable copy, represented in a format whose specification is available to the general public, that is suitable for revising the document straightforwardly with generic text editors or (for images composed of pixels) generic paint programs or (for drawings) some widely available drawing editor, and that is suitable for input to text formatters or for automatic translation to a variety of formats suitable for input to text formatters. A copy made in an otherwise Transparent file format whose markup, or absence of markup, has been arranged to thwart or discourage subsequent modification by readers is not Transparent. An image format is not Transparent if used for any substantial amount of text. A copy that is not "Transparent" is called "Opaque".
Examples of suitable formats for Transparent copies include plain ASCII without markup, Texinfo input format, LaTeX input format, SGML or XML using a publicly available DTD, and standard-conforming simple HTML, PostScript or PDF designed for human modification. Examples of transparent image formats include PNG, XCF and JPG. Opaque formats include proprietary formats that can be read and edited only by proprietary word processors, SGML or XML for which the DTD and/or processing tools are not generally available, and the machine-generated HTML, PostScript or PDF produced by some word processors for output purposes only.
The "Title Page" means, for a printed book, the title page itself, plus such following pages as are needed to hold, legibly, the material this License requires to appear in the title page. For works in formats which do not have any title page as such, "Title Page" means the text near the most prominent appearance of the work's title, preceding the beginning of the body of the text.
A section "Entitled XYZ" means a named subunit of the Document whose title either is precisely XYZ or contains XYZ in parentheses following text that translates XYZ in another language. (Here XYZ stands for a specific section name mentioned below, such as "Acknowledgements", "Dedications", "Endorsements", or "History".) To "Preserve the Title" of such a section when you modify the Document means that it remains a section "Entitled XYZ" according to this definition.
The Document may include Warranty Disclaimers next to the notice which states that this License applies to the Document. These Warranty Disclaimers are considered to be included by reference in this License, but only as regards disclaiming warranties: any other implication that these Warranty Disclaimers may have is void and has no effect on the meaning of this License.
2. VERBATIM COPYING #
You may copy and distribute the Document in any medium, either commercially or non-commercially, provided that this License, the copyright notices, and the license notice saying this License applies to the Document are reproduced in all copies, and that you add no other conditions whatsoever to those of this License. You may not use technical measures to obstruct or control the reading or further copying of the copies you make or distribute. However, you may accept compensation in exchange for copies. If you distribute a large enough number of copies you must also follow the conditions in section 3.
You may also lend copies, under the same conditions stated above, and you may publicly display copies.
3. COPYING IN QUANTITY #
If you publish printed copies (or copies in media that commonly have printed covers) of the Document, numbering more than 100, and the Document's license notice requires Cover Texts, you must enclose the copies in covers that carry, clearly and legibly, all these Cover Texts: Front-Cover Texts on the front cover, and Back-Cover Texts on the back cover. Both covers must also clearly and legibly identify you as the publisher of these copies. The front cover must present the full title with all words of the title equally prominent and visible. You may add other material on the covers in addition. Copying with changes limited to the covers, as long as they preserve the title of the Document and satisfy these conditions, can be treated as verbatim copying in other respects.
If the required texts for either cover are too voluminous to fit legibly, you should put the first ones listed (as many as fit reasonably) on the actual cover, and continue the rest onto adjacent pages.
If you publish or distribute Opaque copies of the Document numbering more than 100, you must either include a machine-readable Transparent copy along with each Opaque copy, or state in or with each Opaque copy a computer-network location from which the general network-using public has access to download using public-standard network protocols a complete Transparent copy of the Document, free of added material. If you use the latter option, you must take reasonably prudent steps, when you begin distribution of Opaque copies in quantity, to ensure that this Transparent copy will remain thus accessible at the stated location until at least one year after the last time you distribute an Opaque copy (directly or through your agents or retailers) of that edition to the public.
It is requested, but not required, that you contact the authors of the Document well before redistributing any large number of copies, to give them a chance to provide you with an updated version of the Document.
4. MODIFICATIONS #
You may copy and distribute a Modified Version of the Document under the conditions of sections 2 and 3 above, provided that you release the Modified Version under precisely this License, with the Modified Version filling the role of the Document, thus licensing distribution and modification of the Modified Version to whoever possesses a copy of it. In addition, you must do these things in the Modified Version:
Use in the Title Page (and on the covers, if any) a title distinct from that of the Document, and from those of previous versions (which should, if there were any, be listed in the History section of the Document). You may use the same title as a previous version if the original publisher of that version gives permission.
List on the Title Page, as authors, one or more persons or entities responsible for authorship of the modifications in the Modified Version, together with at least five of the principal authors of the Document (all of its principal authors, if it has fewer than five), unless they release you from this requirement.
State on the Title page the name of the publisher of the Modified Version, as the publisher.
Preserve all the copyright notices of the Document.
Add an appropriate copyright notice for your modifications adjacent to the other copyright notices.
Include, immediately after the copyright notices, a license notice giving the public permission to use the Modified Version under the terms of this License, in the form shown in the Addendum below.
Preserve in that license notice the full lists of Invariant Sections and required Cover Texts given in the Document's license notice.
Include an unaltered copy of this License.
Preserve the section Entitled "History", Preserve its Title, and add to it an item stating at least the title, year, new authors, and publisher of the Modified Version as given on the Title Page. If there is no section Entitled "History" in the Document, create one stating the title, year, authors, and publisher of the Document as given on its Title Page, then add an item describing the Modified Version as stated in the previous sentence.
Preserve the network location, if any, given in the Document for public access to a Transparent copy of the Document, and likewise the network locations given in the Document for previous versions it was based on. These may be placed in the "History" section. You may omit a network location for a work that was published at least four years before the Document itself, or if the original publisher of the version it refers to gives permission.
For any section Entitled "Acknowledgements" or "Dedications", Preserve the Title of the section, and preserve in the section all the substance and tone of each of the contributor acknowledgements and/or dedications given therein.
Preserve all the Invariant Sections of the Document, unaltered in their text and in their titles. Section numbers or the equivalent are not considered part of the section titles.
Delete any section Entitled "Endorsements". Such a section may not be included in the Modified Version.
Do not retitle any existing section to be Entitled "Endorsements" or to conflict in title with any Invariant Section.
Preserve any Warranty Disclaimers.
If the Modified Version includes new front-matter sections or appendices that qualify as Secondary Sections and contain no material copied from the Document, you may at your option designate some or all of these sections as invariant. To do this, add their titles to the list of Invariant Sections in the Modified Version's license notice. These titles must be distinct from any other section titles.
You may add a section Entitled "Endorsements", provided it contains nothing but endorsements of your Modified Version by various parties--for example, statements of peer review or that the text has been approved by an organization as the authoritative definition of a standard.
You may add a passage of up to five words as a Front-Cover Text, and a passage of up to 25 words as a Back-Cover Text, to the end of the list of Cover Texts in the Modified Version. Only one passage of Front-Cover Text and one of Back-Cover Text may be added by (or through arrangements made by) any one entity. If the Document already includes a cover text for the same cover, previously added by you or by arrangement made by the same entity you are acting on behalf of, you may not add another; but you may replace the old one, on explicit permission from the previous publisher that added the old one.
The author(s) and publisher(s) of the Document do not by this License give permission to use their names for publicity for or to assert or imply endorsement of any Modified Version.
5. COMBINING DOCUMENTS #
You may combine the Document with other documents released under this License, under the terms defined in section 4 above for modified versions, provided that you include in the combination all of the Invariant Sections of all of the original documents, unmodified, and list them all as Invariant Sections of your combined work in its license notice, and that you preserve all their Warranty Disclaimers.
The combined work need only contain one copy of this License, and multiple identical Invariant Sections may be replaced with a single copy. If there are multiple Invariant Sections with the same name but different contents, make the title of each such section unique by adding at the end of it, in parentheses, the name of the original author or publisher of that section if known, or else a unique number. Make the same adjustment to the section titles in the list of Invariant Sections in the license notice of the combined work.
In the combination, you must combine any sections Entitled "History" in the various original documents, forming one section Entitled "History"; likewise combine any sections Entitled "Acknowledgements", and any sections Entitled "Dedications". You must delete all sections Entitled "Endorsements".
6. COLLECTIONS OF DOCUMENTS #
You may make a collection consisting of the Document and other documents released under this License, and replace the individual copies of this License in the various documents with a single copy that is included in the collection, provided that you follow the rules of this License for verbatim copying of each of the documents in all other respects.
You may extract a single document from such a collection, and distribute it individually under this License, provided you insert a copy of this License into the extracted document, and follow this License in all other respects regarding verbatim copying of that document.
7. AGGREGATION WITH INDEPENDENT WORKS #
A compilation of the Document or its derivatives with other separate and independent documents or works, in or on a volume of a storage or distribution medium, is called an "aggregate" if the copyright resulting from the compilation is not used to limit the legal rights of the compilation's users beyond what the individual works permit. When the Document is included in an aggregate, this License does not apply to the other works in the aggregate which are not themselves derivative works of the Document.
If the Cover Text requirement of section 3 is applicable to these copies of the Document, then if the Document is less than one half of the entire aggregate, the Document's Cover Texts may be placed on covers that bracket the Document within the aggregate, or the electronic equivalent of covers if the Document is in electronic form. Otherwise they must appear on printed covers that bracket the whole aggregate.
8. TRANSLATION #
Translation is considered a kind of modification, so you may distribute translations of the Document under the terms of section 4. Replacing Invariant Sections with translations requires special permission from their copyright holders, but you may include translations of some or all Invariant Sections in addition to the original versions of these Invariant Sections. You may include a translation of this License, and all the license notices in the Document, and any Warranty Disclaimers, provided that you also include the original English version of this License and the original versions of those notices and disclaimers. In case of a disagreement between the translation and the original version of this License or a notice or disclaimer, the original version will prevail.
If a section in the Document is Entitled "Acknowledgements", "Dedications", or "History", the requirement (section 4) to Preserve its Title (section 1) will typically require changing the actual title.
9. TERMINATION #
You may not copy, modify, sublicense, or distribute the Document except as expressly provided for under this License. Any other attempt to copy, modify, sublicense or distribute the Document is void, and will automatically terminate your rights under this License. However, parties who have received copies, or rights, from you under this License will not have their licenses terminated so long as such parties remain in full compliance.
10. FUTURE REVISIONS OF THIS LICENSE #
The Free Software Foundation may publish new, revised versions of the GNU Free Documentation License from time to time. Such new versions will be similar in spirit to the present version, but may differ in detail to address new problems or concerns. See http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/.
Each version of the License is given a distinguishing version number. If the Document specifies that a particular numbered version of this License "or any later version" applies to it, you have the option of following the terms and conditions either of that specified version or of any later version that has been published (not as a draft) by the Free Software Foundation. If the Document does not specify a version number of this License, you may choose any version ever published (not as a draft) by the Free Software Foundation.
ADDENDUM: How to use this License for your documents #
Copyright (c) YEAR YOUR NAME. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later version published by the Free Software Foundation; with no Invariant Sections, no Front-Cover Texts, and no Back-Cover Texts. A copy of the license is included in the section entitled “GNU Free Documentation License”.
If you have Invariant Sections, Front-Cover Texts and Back-Cover Texts, replace the “with...Texts.” line with this:
with the Invariant Sections being LIST THEIR TITLES, with the Front-Cover Texts being LIST, and with the Back-Cover Texts being LIST.
If you have Invariant Sections without Cover Texts, or some other combination of the three, merge those two alternatives to suit the situation.
If your document contains nontrivial examples of program code, we recommend releasing these examples in parallel under your choice of free software license, such as the GNU General Public License, to permit their use in free software.