Reference
- About This Guide
- I Advanced Administration
- II System
- 8 32-Bit and 64-Bit Applications in a 64-Bit System Environment
- 9 Booting a Linux System
- 10 The
systemdDaemon - 11
journalctl: Query thesystemdJournal - 12 The Boot Loader GRUB 2
- 13 Basic Networking
- 14 UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface)
- 15 Special System Features
- 16 Dynamic Kernel Device Management with
udev
- III Services
- IV Mobile Computers
- A An Example Network
- B GNU Licenses
25 Setting up an FTP Server with YaST
Abstract#
Using the YaST module, you can configure your machine to function as an FTP (File Transfer Protocol) server. Anonymous and/or authenticated users can connect to your machine and download files using the FTP protocol. Depending on the configuration, they can also upload files to the FTP server. YaST uses vsftpd (Very Secure FTP Daemon).
If the YaST FTP Server module is not available in your system,
install the yast2-ftp-server
package.
To configure the FTP server using YaST, follow these steps:
Open the YaST control center and choose › or run the
yast2 ftp-servercommand asroot.If there is not any FTP server installed in your system, you will be asked which server to install when the YaST FTP Server module starts. Choose the vsftpd server and confirm the dialog.
In the dialog, configure the options for starting of the FTP server. For more information, see Section 25.1, “Starting the FTP Server”.
In the dialog, configure FTP directories, welcome message, file creation masks and various other parameters. For more information, see Section 25.2, “FTP General Settings”.
In the dialog, set the parameters that affect the load on the FTP server. For more information, see Section 25.3, “FTP Performance Settings”.
In the dialog, set whether the FTP server should be available for anonymous and/or authenticated users. For more information, see Section 25.4, “Authentication”.
In the dialog, configure the operation mode of the FTP server, SSL connections and firewall settings. For more information, see Section 25.5, “Expert Settings”.
Press to save the configurations.
25.1 Starting the FTP Server #
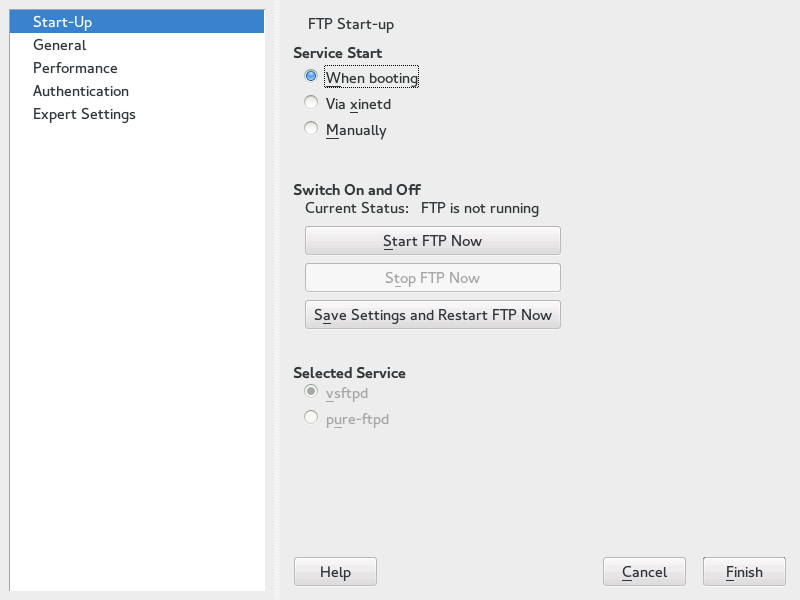
In the frame of the dialog set the way the FTP server is started up. You can choose between starting the server automatically during the system boot and starting it manually. If the FTP server should be started only after an FTP connection request, choose .
The current status of the FTP server is shown in the frame of the dialog. Start the FTP server by clicking . To stop the server, click . After having changed the settings of the server click . Your configurations will be saved by leaving the configuration module with .
The frame of the dialog shows which FTP server is used: either vsftpd or pure-ftpd. If both servers are installed, you can switch between them—the current configuration will automatically be converted.
Figure 25.1: FTP Server Configuration — Start-Up #
25.2 FTP General Settings #
In the frame of the dialog you can set the which is shown after connecting to the FTP server.
If you check the option, all local users will be placed in a chroot jail in their home directory after login. This option has security implications, especially if the users have upload permission or shell access, so be careful enabling this option.
If you check the option, all FTP requests and responses are logged.
You can limit permissions of files created by anonymous and/or
authenticated users with umask. Set the file creation mask for anonymous
users in and the file creation
mask for authenticated users in . The masks should be entered as octal numbers with a
leading zero. For more information about umask, see the umask man page
(man 1p umask).
In the frame set the directories used
for anonymous and authorized users. With , you
can select a directory to be used from the local file system. The default
FTP directory for anonymous users is /srv/ftp. Note
that vsftpd does not allow this directory to be writable for all users.
The subdirectory upload with write permissions for
anonymous users is created instead.
Note: Write Permissions in FTP Directory
The pure-ftpd server allows the FTP directory for anonymous users to be writable. When switching between servers, make sure you remove the write permissions in the directory that was used with pure-ftpd before switching back to the vsftpd server.
25.3 FTP Performance Settings #
In the dialog set the parameters which affect the load on the FTP server. is the maximum time (in minutes) the remote client may spend between FTP commands. In case of longer inactivity, the remote client is disconnected. determines the maximum number of clients which can be connected from a single IP address. determines the maximum number of clients which may be connected. Any additional clients will get an error message.
The maximum data transfer rate (in KB/s) is set in for local authenticated users, and in for anonymous clients respectively. The default value
for the rate settings is 0, which means unlimited data
transfer rate.
25.4 Authentication #
In the frame of the dialog, you can set which users are allowed to access your FTP server. You can choose between the following options: granting access to anonymous users only, to authenticated users only (with accounts on the system) or to both types of users.
If you want to allow users to upload files to the FTP server, check in the frame of the dialog. Here you are able to allow uploading or creating directories even for anonymous users by checking the respective box.
Note: vsftp—Allowing File Upload for Anonymous Users
If a vsftpd server is used and you want anonymous users to be able to upload files or create directories, a subdirectory with writing permissions for all users needs to be created in the anonymous FTP directory.
25.5 Expert Settings #
An FTP server can run in active or in passive mode. By default the server runs in passive mode. To switch into active mode, uncheck option in dialog. You can also change the range of ports on the server used for the data stream by tweaking the and options.
If you want encrypted communication between clients and the server, you can . Check the versions of the protocol to be supported and specify the DSA certificate to be used for SSL encrypted connections.
If your system is protected by a firewall, check to enable a connection to the FTP server.
25.6 For More Information #
For more information about the FTP server read the manual pages of
vsftpd and vsftpd.conf.