Virtualization Guide
- Preface
- I Introduction
- II Managing virtual machines with
libvirt- 7 Starting and stopping
libvirtd - 8 Preparing the VM Host Server
- 9 Guest installation
- 10 Basic VM Guest management
- 11 Connecting and authorizing
- 12 Advanced storage topics
- 13 Configuring virtual machines with Virtual Machine Manager
- 14 Configuring virtual machines with
virsh - 15 Managing virtual machines with Vagrant
- 16 Xen to KVM migration guide
- 7 Starting and stopping
- III Hypervisor-independent features
- IV Managing virtual machines with Xen
- 22 Setting up a virtual machine host
- 23 Virtual networking
- 24 Managing a virtualization environment
- 25 Block devices in Xen
- 26 Virtualization: configuration options and settings
- 27 Administrative tasks
- 28 XenStore: configuration database shared between domains
- 29 Xen as a high-availability virtualization host
- 30 Xen: converting a paravirtual (PV) guest into a fully virtual (FV/HVM) guest
- V Managing virtual machines with QEMU
- VI Troubleshooting
- Glossary
- A Configuring GPU Pass-Through for NVIDIA cards
- B GNU licenses
4 Introduction to KVM virtualization #Edit source
4.1 Basic components #Edit source
KVM is a full virtualization solution for hardware architectures that support hardware virtualization.
VM Guests (virtual machines), virtual storage, and virtual networks
can be managed with QEMU tools directly, or with the
libvirt-based stack. The QEMU tools include
qemu-system-ARCH, the QEMU monitor,
qemu-img, and qemu-ndb. A
libvirt-based stack includes libvirt itself, along with
libvirt-based applications such as virsh,
virt-manager, virt-install, and
virt-viewer.
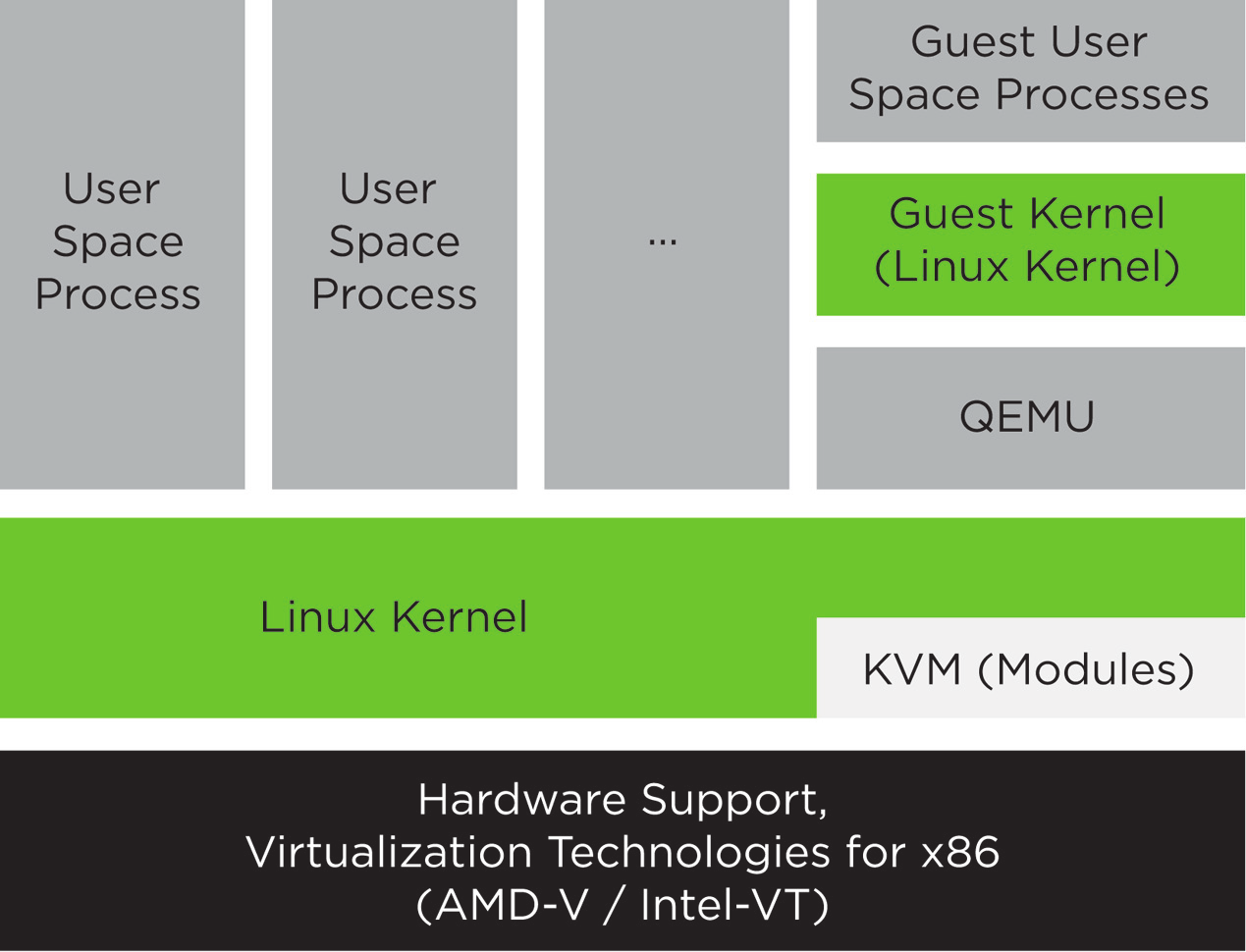
4.2 KVM virtualization architecture #Edit source
This full virtualization solution consists of two main components:
A set of kernel modules (
kvm.ko,kvm-intel.ko, andkvm-amd.ko) that provides the core virtualization infrastructure and processor-specific drivers.A user space program (
qemu-system-ARCH) that provides emulation for virtual devices and control mechanisms to manage VM Guests (virtual machines).
The term KVM more properly refers to the kernel level virtualization functionality, but is in practice more commonly used to refer to the user space component.