Reference
- About This Guide
- I Advanced Administration
- II System
- 8 32-Bit and 64-Bit Applications in a 64-Bit System Environment
- 9 Booting a Linux System
- 10 The
systemdDaemon - 11
journalctl: Query thesystemdJournal - 12 The Boot Loader GRUB 2
- 13 Basic Networking
- 14 UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface)
- 15 Special System Features
- 16 Dynamic Kernel Device Management with
udev
- III Services
- IV Mobile Computers
- A An Example Network
- B GNU Licenses
5 Advanced Disk Setup
Sophisticated system configurations require specific disk setups. All common
partitioning tasks can be done with YaST. To get persistent device naming
with block devices, use the block devices below
/dev/disk/by-id or
/dev/disk/by-uuid. Logical Volume Management (LVM) is a
disk partitioning scheme that is designed to be much more flexible than the
physical partitioning used in standard setups. Its snapshot functionality
enables easy creation of data backups. Redundant Array of Independent Disks
(RAID) offers increased data integrity, performance, and fault tolerance.
openSUSE Leap also supports multipath I/O , and there is also the
option to use iSCSI as a networked disk.
5.1 Using the YaST Partitioner #
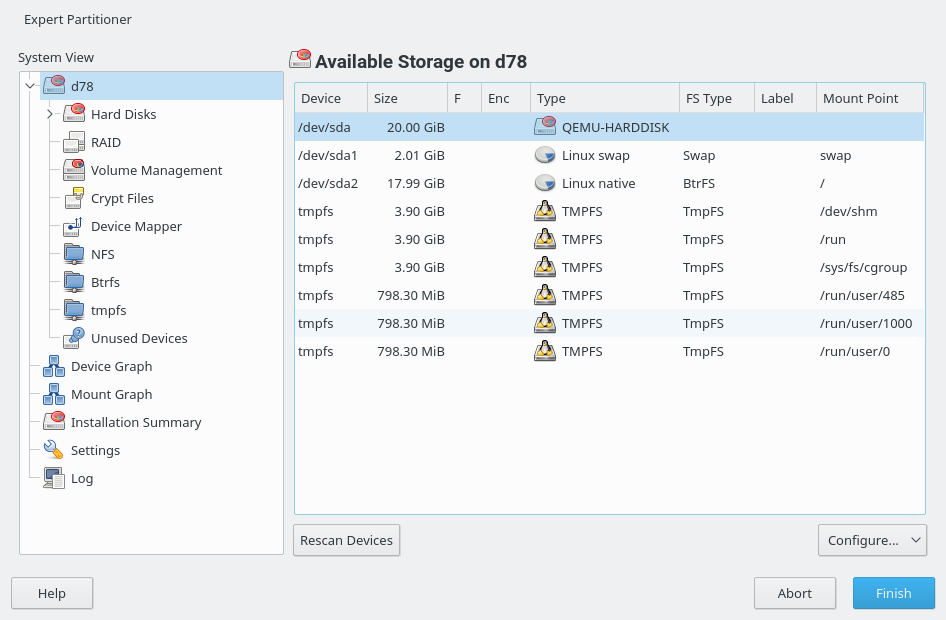
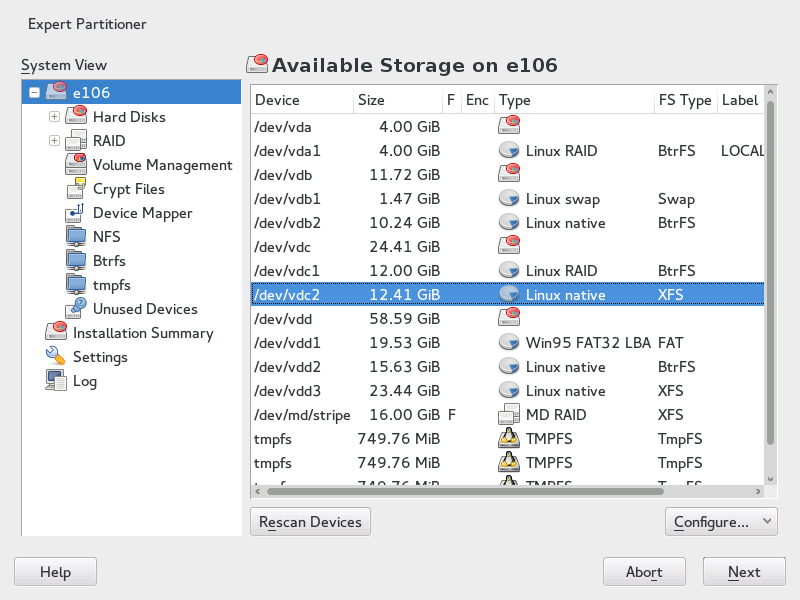
With the expert partitioner, shown in Figure 5.1, “The YaST Partitioner”, manually modify the partitioning of one or several hard disks. You can add, delete, resize, and edit partitions, or access the soft RAID, and LVM configuration.
Warning: Repartitioning the Running System
Although it is possible to repartition your system while it is running, the risk of making a mistake that causes data loss is very high. Try to avoid repartitioning your installed system and always do a complete backup of your data before attempting to do so.
Figure 5.1: The YaST Partitioner #
All existing or suggested partitions on all connected hard disks are
displayed in the list of in the YaST
dialog. Entire hard disks are listed as
devices without numbers, such as
/dev/sda. Partitions are listed as parts of
these devices, such as
/dev/sda1. The size, type,
encryption status, file system, and mount point of the hard disks and their
partitions are also displayed. The mount point describes where the partition
appears in the Linux file system tree.
Several functional views are available on the left hand . Use these views to gather information about existing storage
configurations, or to configure functions like RAID,
Volume Management, Crypt Files, or view
file systems with additional features, such as Btrfs, NFS, or
TMPFS.
If you run the expert dialog during installation, any free hard disk space is also listed and automatically selected. To provide more disk space to openSUSE® Leap, free the needed space starting from the bottom toward the top of the list (starting from the last partition of a hard disk toward the first).
5.1.1 Partition Types #
Every hard disk has a partition table with space for four entries. Every entry in the partition table corresponds to a primary partition or an extended partition. Only one extended partition entry is allowed, however.
A primary partition simply consists of a continuous range of cylinders (physical disk areas) assigned to a particular operating system. With primary partitions you would be limited to four partitions per hard disk, because more do not fit in the partition table. This is why extended partitions are used. Extended partitions are also continuous ranges of disk cylinders, but an extended partition may be divided into logical partitions itself. Logical partitions do not require entries in the partition table. In other words, an extended partition is a container for logical partitions.
If you need more than four partitions, create an extended partition as the fourth partition (or earlier). This extended partition should occupy the entire remaining free cylinder range. Then create multiple logical partitions within the extended partition. The maximum number of logical partitions is 63, independent of the disk type. It does not matter which types of partitions are used for Linux. Primary and logical partitions both function normally.
Tip: GPT Partition Table
If you need to create more than 4 primary partitions on one hard disk, you need to use the GPT partition type. This type removes the primary partitions number restriction, and supports partitions bigger than 2 TB as well.
To use GPT, run the YaST Partitioner, click the relevant disk name in the and choose › › .
5.1.2 Creating a Partition #
To create a partition from scratch select and then a hard disk with free space. The actual modification can be done in the tab:
Select and specify the partition type (primary or extended). Create up to four primary partitions or up to three primary partitions and one extended partition. Within the extended partition, create several logical partitions (see Section 5.1.1, “Partition Types”).
Specify the size of the new partition. You can either choose to occupy all the free unpartitioned space, or enter a custom size.
Select the file system to use and a mount point. YaST suggests a mount point for each partition created. To use a different mount method, like mount by label, select . For more information on supported file systems, see
root.Specify additional file system options if your setup requires them. This is necessary, for example, if you need persistent device names. For details on the available options, refer to Section 5.1.3, “Editing a Partition”.
Click to apply your partitioning setup and leave the partitioning module.
If you created the partition during installation, you are returned to the installation overview screen.
5.1.2.1 Btrfs Partitioning #
The default file system for the root partition is Btrfs (see Chapter 3, System Recovery and Snapshot Management with Snapper for more information on Btrfs). The root file system is the default subvolume and it is not listed in the list of created subvolumes. As a default Btrfs subvolume, it can be mounted as a normal file system.
Important: Btrfs on an Encrypted Root Partition
The default partitioning setup suggests the root partition as Btrfs with
/boot being a directory. If you need to have the root
partition encrypted in this setup, make sure to use the GPT partition
table type instead of the default MSDOS type. Otherwise the GRUB2 boot
loader may not have enough space for the second stage loader.
It is possible to create snapshots of Btrfs subvolumes—either
manually, or automatically based on system events. For example when making
changes to the file system, zypper invokes the
snapper command to create snapshots before and after the
change. This is useful if you are not satisfied with the change
zypper made and want to restore the previous state. As
snapper invoked by zypper snapshots
the root file system by default, it is reasonable to
exclude specific directories from being snapshot, depending on the nature
of data they hold. And that is why YaST suggests creating the following
separate subvolumes.
/boot/grub2/i386-pc,/boot/grub2/x86_64-efi,/boot/grub2/powerpc-ieee1275,/boot/grub2/s390x-emuA rollback of the boot loader configuration is not supported. The directories listed above are architecture-specific. The first two directories are present on AMD64/Intel 64 machines, the latter two on IBM POWER and on IBM z Systems, respectively.
/homeIf
/homedoes not reside on a separate partition, it is excluded to avoid data loss on rollbacks./opt,/var/optThird-party products usually get installed to
/opt. It is excluded to avoid uninstalling these applications on rollbacks./srvContains data for Web and FTP servers. It is excluded to avoid data loss on rollbacks.
/tmp,/var/tmp,/var/cache,/var/crashAll directories containing temporary files and caches are excluded from snapshots.
/usr/localThis directory is used when manually installing software. It is excluded to avoid uninstalling these installations on rollbacks.
/var/lib/libvirt/imagesThe default location for virtual machine images managed with libvirt. Excluded to ensure virtual machine images are not replaced with older versions during a rollback. By default, this subvolume is created with the option
no copy on write./var/lib/mailman,/var/spoolDirectories containing mails or mail queues are excluded to avoid a loss of mails after a rollback.
/var/lib/namedContains zone data for the DNS server. Excluded from snapshots to ensure a name server can operate after a rollback.
/var/lib/mariadb,/var/lib/mysql,/var/lib/pgqslThese directories contain database data. By default, these subvolumes are created with the option
no copy on write./var/logLog file location. Excluded from snapshots to allow log file analysis after the rollback of a broken system.
Tip: Size of Btrfs Partition
Because saved snapshots require more disk space, it is recommended to reserve more space for Btrfs partition than for a partition not capable of snapshotting (such as Ext3). Recommended size for a root Btrfs partition with suggested subvolumes is 20GB.
5.1.2.1.1 Managing Btrfs Subvolumes using YaST #
Subvolumes of a Btrfs partition can be now managed with the YaST module. You can add new or remove existing subvolumes.
Procedure 5.1: Btrfs Subvolumes with YaST #
Start the YaST with › .
Choose in the left pane.
Select the Btrfs partition whose subvolumes you need to manage and click .
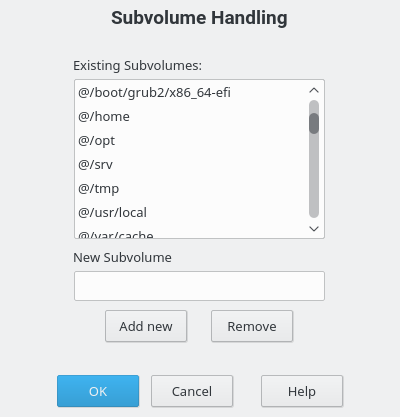
Click . You can see a list off all existing subvolumes of the selected Btrfs partition. You can notice several
@/.snapshots/xyz/snapshotentries—each of these subvolumes belongs to one existing snapshot.Depending on whether you want to add or remove subvolumes, do the following:
To remove a subvolume, select it from the list of and click .
To add a new subvolume, enter its name to the text box and click .
Figure 5.2: Btrfs Subvolumes in YaST Partitioner #
Confirm with and .
Leave the partitioner with .
5.1.3 Editing a Partition #
When you create a new partition or modify an existing partition, you can set various parameters. For new partitions, the default parameters set by YaST are usually sufficient and do not require any modification. To edit your partition setup manually, proceed as follows:
Select the partition.
Click to edit the partition and set the parameters:
- File System ID
Even if you do not want to format the partition at this stage, assign it a file system ID to ensure that the partition is registered correctly. Typical values are , , , and .
- File System
To change the partition file system, click and select file system type in the list.
openSUSE Leap supports several types of file systems. Btrfs is the Linux file system of choice for the root partition because of its advanced features. It supports copy-on-write functionality, creating snapshots, multi-device spanning, subvolumes, and other useful techniques. XFS, Ext3 and JFS are journaling file systems. These file systems can restore the system very quickly after a system crash, using write processes logged during the operation. Ext2 is not a journaling file system, but it is adequate for smaller partitions because it does not require much disk space for management.
The default file system for the root partition is Btrfs. The default file system for additional partitions is XFS.
Swap is a special format that allows the partition to be used as a virtual memory. Create a swap partition of at least 256 MB. However, if you use up your swap space, consider adding more memory to your system instead of adding more swap space.

Warning: Changing the File System
Changing the file system and reformatting partitions irreversibly deletes all data from the partition.
For details on the various file systems, refer to Storage Administration Guide.
- Encrypt Device
If you activate the encryption, all data is written to the hard disk in encrypted form. This increases the security of sensitive data, but reduces the system speed, as the encryption takes some time to process. More information about the encryption of file systems is provided in Book “Security Guide”, Chapter 11 “Encrypting Partitions and Files”.
- Mount Point
Specify the directory where the partition should be mounted in the file system tree. Select from YaST suggestions or enter any other name.
- Fstab Options
Specify various parameters contained in the global file system administration file (
/etc/fstab). The default settings should suffice for most setups. You can, for example, change the file system identification from the device name to a volume label. In the volume label, use all characters except/and space.To get persistent devices names, use the mount option , or . In openSUSE Leap, persistent device names are enabled by default.
If you prefer to mount the partition by its label, you need to define one in the text entry. For example, you could use the partition label
HOMEfor a partition intended to mount to/home.If you intend to use quotas on the file system, use the mount option . This must be done before you can define quotas for users in the YaST module. For further information on how to configure user quota, refer to Book “Start-Up”, Chapter 3 “Managing Users with YaST”, Section 3.3.4 “Managing Quotas”.
Select to save the changes.
Note: Resize File Systems
To resize an existing file system, select the partition and use . Note, that it is not possible to resize partitions while mounted. To resize partitions, unmount the relevant partition before running the partitioner.
5.1.4 Expert Options #
After you select a hard disk device (like ) in the pane, you can access the menu in the lower right part of the window. The menu contains the following commands:
- Create New Partition Table
This option helps you create a new partition table on the selected device.

Warning: Creating a New Partition Table
Creating a new partition table on a device irreversibly removes all the partitions and their data from that device.
- Clone This Disk
This option helps you clone the device partition layout (but not the data) to other available disk devices.
5.1.5 Advanced Options #
After you select the host name of the computer (the top-level of the tree in the pane), you can access the menu in the lower right part of the window. The menu contains the following commands:
- Configure iSCSI
To access SCSI over IP block devices, you first need to configure iSCSI. This results in additionally available devices in the main partition list.
- Configure Multipath
Selecting this option helps you configure the multipath enhancement to the supported mass storage devices.
5.1.6 More Partitioning Tips #
The following section includes a few hints and tips on partitioning that should help you make the right decisions when setting up your system.
Tip: Cylinder Numbers
Note, that different partitioning tools may start counting the cylinders of
a partition with 0 or with 1. When
calculating the number of cylinders, you should always use the difference
between the last and the first cylinder number and add one.
5.1.6.1 Using swap #
Swap is used to extend the available physical memory. It is then possible to use more memory than physical RAM available. The memory management system of kernels before 2.4.10 needed swap as a safety measure. Then, if you did not have twice the size of your RAM in swap, the performance of the system suffered. These limitations no longer exist.
Linux uses a page called “Least Recently Used” (LRU) to select pages that might be moved from memory to disk. Therefore, running applications have more memory available and caching works more smoothly.
If an application tries to allocate the maximum allowed memory, problems with swap can arise. There are three major scenarios to look at:
- System with no swap
The application gets the maximum allowed memory. All caches are freed, and thus all other running applications are slowed. After a few minutes, the kernel's out-of-memory kill mechanism activates and kills the process.
- System with medium sized swap (128 MB–512 MB)
At first, the system slows like a system without swap. After all physical RAM has been allocated, swap space is used as well. At this point, the system becomes very slow and it becomes impossible to run commands from remote. Depending on the speed of the hard disks that run the swap space, the system stays in this condition for about 10 to 15 minutes until the out-of-memory kill mechanism resolves the issue. Note that you will need a certain amount of swap if the computer needs to perform a “suspend to disk”. In that case, the swap size should be large enough to contain the necessary data from memory (512 MB–1GB).
- System with lots of swap (several GB)
It is better to not have an application that is out of control and swapping excessively in this case. If you use such application, the system will need many hours to recover. In the process, it is likely that other processes get timeouts and faults, leaving the system in an undefined state, even after terminating the faulty process. In this case, do a hard machine reboot and try to get it running again. Lots of swap is only useful if you have an application that relies on this feature. Such applications (like databases or graphics manipulation programs) often have an option to directly use hard disk space for their needs. It is advisable to use this option instead of using lots of swap space.
If your system is not out of control, but needs more swap after some time, it is possible to extend the swap space online. If you prepared a partition for swap space, add this partition with YaST. If you do not have a partition available, you can also use a swap file to extend the swap. Swap files are generally slower than partitions, but compared to physical RAM, both are extremely slow so the actual difference is negligible.
Procedure 5.2: Adding a Swap File Manually #
To add a swap file in the running system, proceed as follows:
Create an empty file in your system. For example, if you want to add a swap file with 128 MB swap at
/var/lib/swap/swapfile, use the commands:mkdir -p /var/lib/swap dd if=/dev/zero of=/var/lib/swap/swapfile bs=1M count=128
Initialize this swap file with the command
mkswap /var/lib/swap/swapfile

Note: Changed UUID for Swap Partitions when Formatting via
mkswapDo not reformat existing swap partitions with
mkswapif possible. Reformatting withmkswapwill change the UUID value of the swap partition. Either reformat via YaST (will update/etc/fstab) or adjust/etc/fstabmanually.Activate the swap with the command
swapon /var/lib/swap/swapfile
To disable this swap file, use the command
swapoff /var/lib/swap/swapfile
Check the current available swap spaces with the command
cat /proc/swaps
Note that at this point, it is only temporary swap space. After the next reboot, it is no longer used.
To enable this swap file permanently, add the following line to
/etc/fstab:/var/lib/swap/swapfile swap swap defaults 0 0
5.1.7 Partitioning and LVM #
From the , access the LVM configuration by clicking the item in the pane. However, if a working LVM configuration already exists on your system, it is automatically activated upon entering the initial LVM configuration of a session. In this case, all disks containing a partition (belonging to an activated volume group) cannot be repartitioned. The Linux kernel cannot reread the modified partition table of a hard disk when any partition on this disk is in use. If you already have a working LVM configuration on your system, physical repartitioning should not be necessary. Instead, change the configuration of the logical volumes.
At the beginning of the physical volumes (PVs), information about the volume
is written to the partition. To reuse such a partition for other non-LVM
purposes, it is advisable to delete the beginning of this volume. For
example, in the VG system and PV
/dev/sda2, do this with the command
dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sda2 bs=512
count=1.
Warning: File System for Booting
The file system used for booting (the root file system or
/boot) must not be stored on an LVM logical volume.
Instead, store it on a normal physical partition.
In case you want to change your /usr or
swap, refer to
Procedure 9.1, “Updating Init RAM Disk When Switching to Logical Volumes”.
5.2 LVM Configuration #
This section explains specific steps to take when configuring LVM.
Warning: Back up Your Data
Using LVM is sometimes associated with increased risk such as data loss. Risks also include application crashes, power failures, and faulty commands. Save your data before implementing LVM or reconfiguring volumes. Never work without a backup.
5.2.1 LVM Configuration with YaST #
The YaST LVM configuration can be reached from the YaST Expert Partitioner (see Section 5.1, “Using the YaST Partitioner”) within the item in the pane. The Expert Partitioner allows you to edit and delete existing partitions and create new ones that need to be used with LVM. The first task is to create PVs that provide space to a volume group:
Select a hard disk from .
Change to the tab.
Click and enter the desired size of the PV on this disk.
Use and change the to . Do not mount this partition.
Repeat this procedure until you have defined all the desired physical volumes on the available disks.
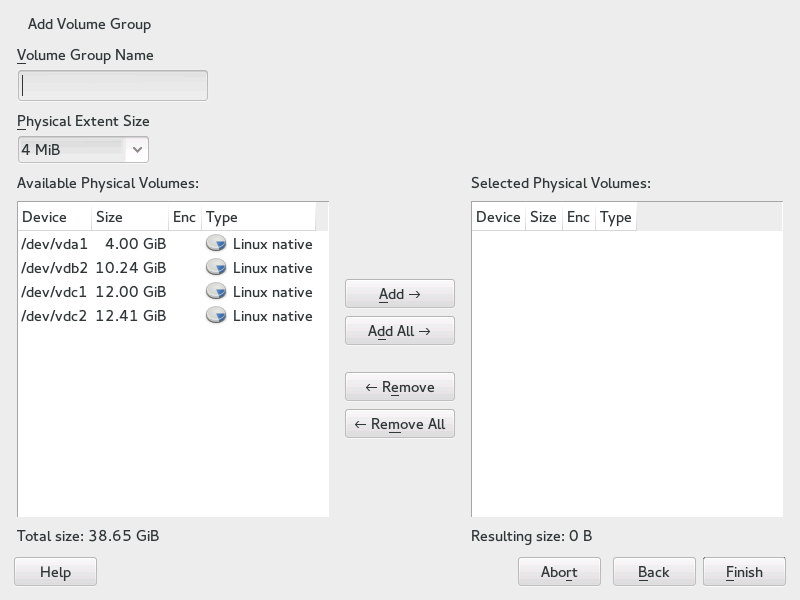
5.2.1.1 Creating Volume Groups #
If no volume group exists on your system, you must add one (see Figure 5.3, “Creating a Volume Group”). It is possible to create additional groups by clicking in the pane, and then on . One single volume group is usually sufficient.
Enter a name for the VG, for example,
system.Select the desired . This value defines the size of a physical block in the volume group. All the disk space in a volume group is handled in blocks of this size.
Add the prepared PVs to the VG by selecting the device and clicking . Selecting several devices is possible by holding Ctrl while selecting the devices.
Select to make the VG available to further configuration steps.
Figure 5.3: Creating a Volume Group #
If you have multiple volume groups defined and want to add or remove PVs, select the volume group in the list and click . In the following window, you can add or remove PVs to the selected volume group.
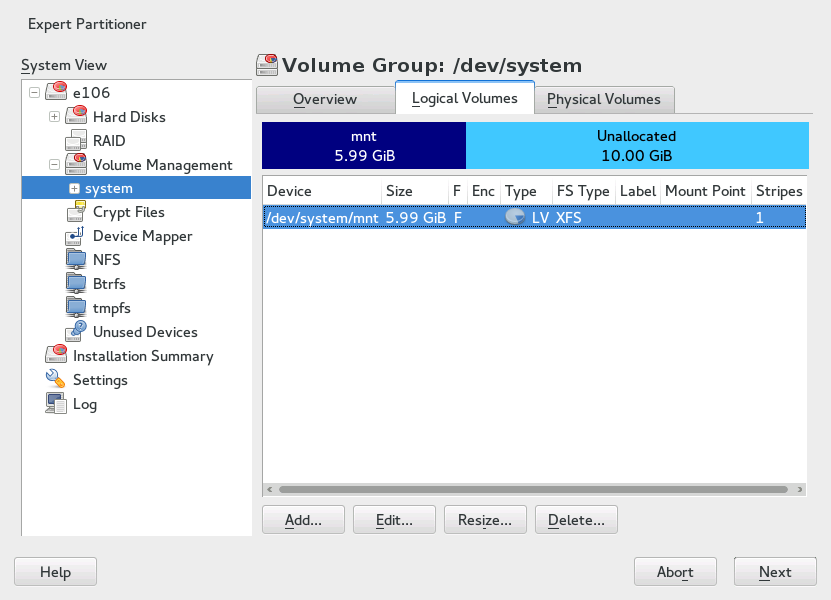
5.2.1.2 Configuring Logical Volumes #
After the volume group has been filled with PVs, define the LVs which the operating system should use in the next dialog. Choose the current volume group and change to the tab. , , , and LVs as needed until all space in the volume group has been occupied. Assign at least one LV to each volume group.
Figure 5.4: Logical Volume Management #
Click and go through the wizard-like pop-up that opens:
Enter the name of the LV. For a partition that should be mounted to
/home, a name likeHOMEcould be used.Select the type of the LV. It can be either , , or . Note that you need to create a thin pool first, which can store individual thin volumes. The big advantage of thin provisioning is that the total sum of all thin volumes stored in a thin pool can exceed the size of the pool itself.
Select the size and the number of stripes of the LV. If you have only one PV, selecting more than one stripe is not useful.
Choose the file system to use on the LV and the mount point.
By using stripes it is possible to distribute the data stream in the LV among several PVs (striping). However, striping a volume can only be done over different PVs, each providing at least the amount of space of the volume. The maximum number of stripes equals to the number of PVs, where Stripe "1" means "no striping". Striping only makes sense with PVs on different hard disks, otherwise performance will decrease.
Warning: Striping
YaST cannot, at this point, verify the correctness of your entries concerning striping. Any mistake made here is apparent only later when the LVM is implemented on disk.
If you have already configured LVM on your system, the existing logical volumes can also be used. Before continuing, assign appropriate mount points to these LVs. With , return to the YaST Expert Partitioner and finish your work there.
5.3 Soft RAID Configuration with YaST #
This section describes actions required to create and configure various types of RAID. .
5.3.1 Soft RAID Configuration with YaST #
The YaST configuration can be reached from the YaST Expert Partitioner, described in Section 5.1, “Using the YaST Partitioner”. This partitioning tool enables you to edit and delete existing partitions and create new ones to be used with soft RAID:
Select a hard disk from .
Change to the tab.
Click and enter the desired size of the raid partition on this disk.
Use and change the to . Do not mount this partition.
Repeat this procedure until you have defined all the desired physical volumes on the available disks.
For RAID 0 and RAID 1, at least two partitions are needed—for RAID 1, usually exactly two and no more. If RAID 5 is used, at least three partitions are required, RAID 6 and RAID 10 require at least four partitions. It is recommended to use partitions of the same size only. The RAID partitions should be located on different hard disks to decrease the risk of losing data if one is defective (RAID 1 and 5) and to optimize the performance of RAID 0. After creating all the partitions to use with RAID, click › to start the RAID configuration.
In the next dialog, choose between RAID levels 0, 1, 5, 6 and 10. Then, select all partitions with either the “Linux RAID” or “Linux native” type that should be used by the RAID system. No swap or DOS partitions are shown.
Tip: Classify Disks
For RAID types where the order of added disks matters, you can mark individual disks with one of the letters A to E. Click the button, select the disk and click of the buttons, where X is the letter you want to assign to the disk. Assign all available RAID disks this way, and confirm with . You can easily sort the classified disks with the or buttons, or add a sort pattern from a text file with .
Figure 5.5: RAID Partitions #
To add a previously unassigned partition to the selected RAID volume, first click the partition then . Assign all partitions reserved for RAID. Otherwise, the space on the partition remains unused. After assigning all partitions, click to select the available .
In this last step, set the file system to use, encryption and the mount
point for the RAID volume. After completing the configuration with
, see the /dev/md0 device and
others indicated with RAID in the expert partitioner.
5.3.2 Troubleshooting #
Check the file /proc/mdstat to find out whether a RAID
partition has been damaged. If Th system fails, shut down your Linux system
and replace the defective hard disk with a new one partitioned the same way.
Then restart your system and enter the command mdadm /dev/mdX --add
/dev/sdX. Replace 'X' with your particular device identifiers.
This integrates the hard disk automatically into the RAID system and fully
reconstructs it.
Note that although you can access all data during the rebuild, you may encounter some performance issues until the RAID has been fully rebuilt.
5.3.3 For More Information #
Configuration instructions and more details for soft RAID can be found in the HOWTOs at:
/usr/share/doc/packages/mdadm/Software-RAID.HOWTO.html
Linux RAID mailing lists are available, such as http://marc.info/?l=linux-raid.