Reference
- About This Guide
- I Advanced Administration
- II System
- 8 32-Bit and 64-Bit Applications in a 64-Bit System Environment
- 9 Booting a Linux System
- 10 The
systemdDaemon - 11
journalctl: Query thesystemdJournal - 12 The Boot Loader GRUB 2
- 13 Basic Networking
- 14 UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface)
- 15 Special System Features
- 16 Dynamic Kernel Device Management with
udev
- III Services
- IV Mobile Computers
- A An Example Network
- B GNU Licenses
6 Installing Multiple Kernel Versions
Abstract#
openSUSE Leap supports the parallel installation of multiple kernel versions. When installing a second kernel, a boot entry and an initrd are automatically created, so no further manual configuration is needed. When rebooting the machine, the newly added kernel is available as an additional boot option.
Using this functionality, you can safely test kernel updates while being able to always fall back to the proven former kernel. To do so, do not use the update tools (such as the YaST Online Update or the updater applet), but instead follow the process described in this chapter.
Tip: Check Your Boot Loader Configuration Kernel
It is recommended to check your boot loader configuration after having installed another kernel to set the default boot entry of your choice. See Section 12.3, “Configuring the Boot Loader with YaST” for more information.
6.1 Enabling and Configuring Multiversion Support #
Installing multiple versions of a software package (multiversion support) is enabled by default on SUSE Linux Enterprise 12. To verify this setting, proceed as follows:
Open
/etc/zypp/zypp.confwith the editor of your choice asroot.Search for the string
multiversion. If multiversion is enabled for all kernel packages capable of this feature, the following line appears uncommented:multiversion = provides:multiversion(kernel)
To restrict multiversion support to certain kernel flavors, add the package names as a comma-separated list to the
multiversionoption in/etc/zypp/zypp.conf—for examplemultiversion = kernel-default,kernel-default-base,kernel-source
Save your changes.
Warning: Kernel Module Packages (KMP)
Make sure that required vendor provided kernel modules (Kernel Module Packages) are also installed for the new updated kernel. The kernel update process will not warn about eventually missing kernel modules because package requirements are still fulfilled by the old kernel that is kept on the system.
6.1.1 Automatically Deleting Unused Kernels #
When frequently testing new kernels with multiversion support enabled, the
boot menu quickly becomes confusing. Since a /boot
partition usually has limited space you also might run into trouble with
/boot overflowing. While you may delete unused kernel
versions manually with YaST or Zypper (as described below), you can also
configure libzypp to automatically
delete kernels no longer used. By default no kernels are deleted.
Open
/etc/zypp/zypp.confwith the editor of your choice asroot.Search for the string
multiversion.kernelsand activate this option by uncommenting the line. This option takes a comma-separated list of the following values:3.12.24-7.1: keep the kernel with the specified version numberlatest: keep the kernel with the highest version numberlatest-N: keep the kernel with the Nth highest version numberrunning: keep the running kerneloldest: keep the kernel with the lowest version number (the one that was originally shipped with openSUSE Leap)oldest+N. keep the kernel with the Nth lowest version numberHere are some examples
multiversion.kernels = latest,runningKeep the latest kernel and the one currently running. This is similar to not enabling the multiversion feature, except that the old kernel is removed after the next reboot and not immediately after the installation.
multiversion.kernels = latest,latest-1,runningKeep the last two kernels and the one currently running.
multiversion.kernels = latest,running,3.12.25.rc7-testKeep the latest kernel, the one currently running, and 3.12.25.rc7-test.
Tip: Keep the
runningKernelUnless using special setups, you probably always want to keep the
runningKernel. If not keeping the running Kernel, it will be deleted in case of a Kernel update. This in turn makes it necessary to immediately reboot the system after the update, since modules for the Kernel that is currently running can no longer be loaded since they have been deleted.
6.2 Installing/Removing Multiple Kernel Versions with YaST #
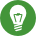
Start YaST and open the software manager via › .
List all packages capable of providing multiple versions by choosing › › .
Figure 6.1: The YaST Software Manager: Multiversion View #
Select a package and open its tab in the bottom pane on the left.
To install a package, click its check box. A green check mark indicates it is selected for installation.
To remove an already installed package (marked with a white check mark), click its check box until a red
Xindicates it is selected for removal.Click to start the installation.
6.3 Installing/Removing Multiple Kernel Versions with Zypper #
Use the command
zypper se -s 'kernel*'to display a list of all kernel packages available:S | Name | Type | Version | Arch | Repository --+----------------+------------+-----------------+--------+------------------- v | kernel-default | package | 2.6.32.10-0.4.1 | x86_64 | Alternative Kernel i | kernel-default | package | 2.6.32.9-0.5.1 | x86_64 | (System Packages) | kernel-default | srcpackage | 2.6.32.10-0.4.1 | noarch | Alternative Kernel i | kernel-default | package | 2.6.32.9-0.5.1 | x86_64 | (System Packages) ...
Specify the exact version when installing:
zypper in kernel-default-2.6.32.10-0.4.1
When uninstalling a kernel, use the commands
zypper se -si 'kernel*'to list all kernels installed andzypper rmPACKAGENAME-VERSION to remove the package.
6.4 Install the Latest Kernel Version from the Kernel:HEAD Repository #
Add the Kernel HEAD repository using the
sudo zypper ar http://download.opensuse.org/repositories/Kernel:/HEAD/standard/ kernel-repoRun the
sudo zypper refto refresh repositories.Execute the
sudo zypper dist-upgrade --from kernel-repoto upgrade the kernel to the latest version in the Kernel:HEAD repository.Reboot the machine.
Warning: Installing from Kernel HEAD may Break the System
Installing a Kernel from Kernel HEAD should never be necessary, because important fixes are backporten by SUSE and are made available as official updates. Installing the latest Kernel only makes sense for Kernel developers and Kernel testers. If installing from Kernel HEAD, be aware that it may break your system. Make sure to always have the original kernel available for booting as well.