Virtualization Guide
- Preface
- I Introduction
- II Managing virtual machines with
libvirt - III Hypervisor-independent features
- IV Managing virtual machines with Xen
- 22 Setting up a virtual machine host
- 23 Virtual networking
- 24 Managing a virtualization environment
- 25 Block devices in Xen
- 26 Virtualization: configuration options and settings
- 27 Administrative tasks
- 28 XenStore: configuration database shared between domains
- 29 Xen as a high-availability virtualization host
- 30 Xen: converting a paravirtual (PV) guest into a fully virtual (FV/HVM) guest
- V Managing virtual machines with QEMU
- VI Troubleshooting
- Glossary
- A Configuring GPU Pass-Through for NVIDIA cards
- B GNU licenses
3 Introduction to Xen virtualization #Edit source
This chapter introduces and explains the components and technologies you need to understand to set up and manage a Xen-based virtualization environment.
3.1 Basic components #Edit source
The basic components of a Xen-based virtualization environment are the following:
Xen hypervisor
Dom0
any number of other VM Guests
tools, commands and configuration files to manage virtualization
Collectively, the physical computer running all these components is called a VM Host Server because together these components form a platform for hosting virtual machines.
- The Xen hypervisor
The Xen hypervisor, sometimes simply called a virtual machine monitor, is an open source software program that coordinates the low-level interaction between virtual machines and physical hardware.
- The Dom0
The virtual machine host environment, also called Dom0 or controlling domain, is composed of several components, such as:
openSUSE Leap provides a graphical and a command line environment to manage the virtual machine host components and its virtual machines.
Note
The term “Dom0” refers to a special domain that provides the management environment. This may be run either in graphical or in command line mode.
The xl tool stack based on the xenlight library (libxl). Use it to manage Xen guest domains.
QEMU—an open source software that emulates a full computer system, including a processor and multiple peripherals. It provides the ability to host operating systems in both full virtualization or paravirtualization mode.
- Xen-based virtual machines
A Xen-based virtual machine, also called a VM Guest or DomU, consists of the following components:
At least one virtual disk that contains a bootable operating system. The virtual disk can be based on a file, partition, volume, or other type of block device.
A configuration file for each guest domain. It is a text file following the syntax described in the manual page
man 5 xl.conf.Several network devices, connected to the virtual network provided by the controlling domain.
- Management tools, commands, and configuration files
There is a combination of GUI tools, commands and configuration files to help you manage and customize your virtualization environment.
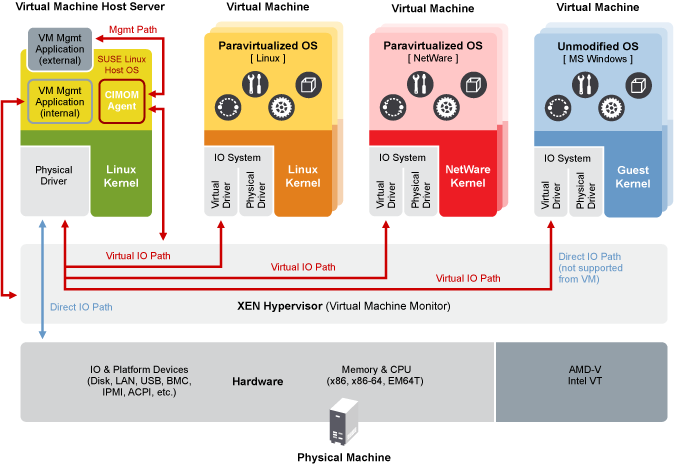
3.2 Xen virtualization architecture #Edit source
The following graphic depicts a virtual machine host with four virtual machines. The Xen hypervisor is shown as running directly on the physical hardware platform. Note that the controlling domain is also a virtual machine, although it has several additional management tasks compared to all the other virtual machines.
Figure 3.1: Xen virtualization architecture #
On the left, the virtual machine host’s Dom0 is shown running the openSUSE Leap operating system. The two virtual machines shown in the middle are running paravirtualized operating systems. The virtual machine on the right shows a fully virtual machine running an unmodified operating system, such as the latest version of Microsoft Windows/Server.